How Does X Ray Diffraction Work A Beginners Guide

How Does X Ray Diffraction Work A Beginner S Guide Youtube Unveiling the secrets: how x ray diffraction works • x ray diffraction revealed • discover the fascinating world of x ray diffraction and how it uncovers the. X ray diffraction (xrd) is a non destructive technique for analyzing the structure of materials, primarily at the atomic or molecular level. it works best for materials that are crystalline or partially crystalline (i.e., that have periodic structural order) but is also used to study non crystalline materials.
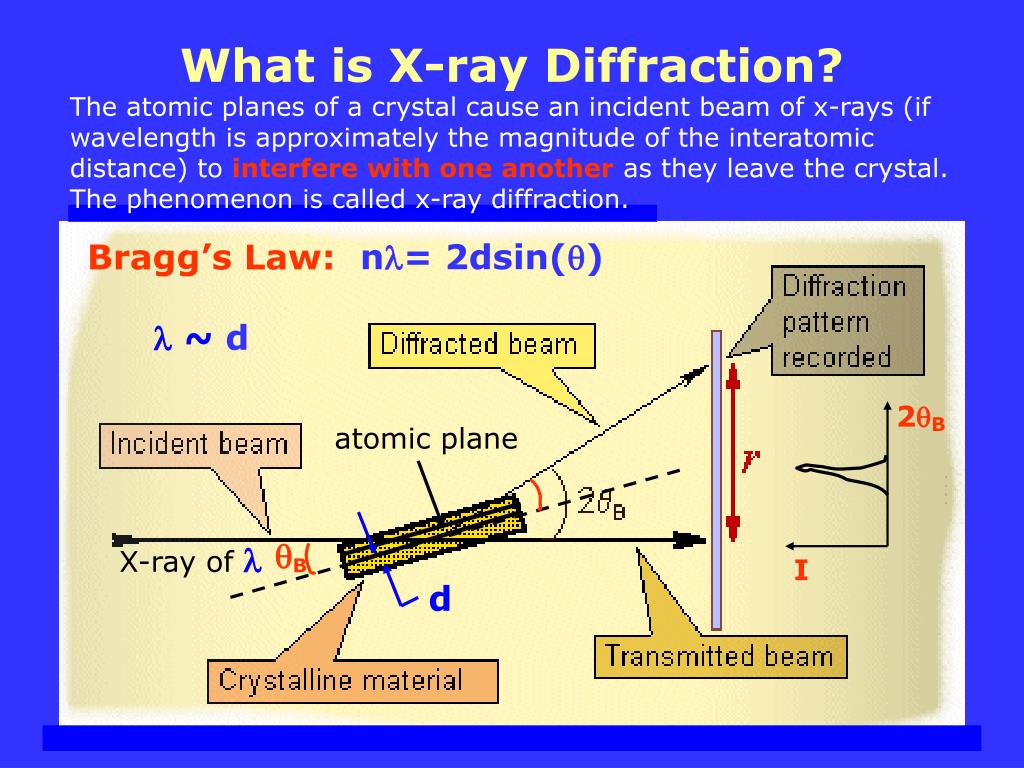
X Ray Diffraction Schematic Diagram X ray diffraction is a common technique that determine a sample's composition or crystalline structure. for larger crystals such as macromolecules and inorganic compounds, it can be used to determine the structure of atoms within the sample. if the crystal size is too small, it can determine sample composition, crystallinity, and phase purity. X ray scattering by an atom. x rays are scattered by electrons in an atom into (approximately) all directions, though peaked in the forward direction. wave picture of light is useful here: strength of the scattering depends on the number of electrons ~ z2 (z is the atomic number) x ray. scattering. by two (or several) atoms. The sherrer formula describes the relationship between the grain size and the half width of the diffraction peak. the scherreer formula: d=kλ (βcosθ) the use of this equation to calculate the average grain size requires attention: 1. β is the half peak width, that is, the width where the diffraction intensity is half of the maximum value. An x ray diffractometer is the instrument we use to produce monochromatic x rays, focus the beam on a sample, scan through a range of 2θ, and then detect the reflected x rays and their intensity. monochromatic x rays are generated in a cathode ray tube. a filament of tungsten is heated to produce electrons which are then accelerated towards an.
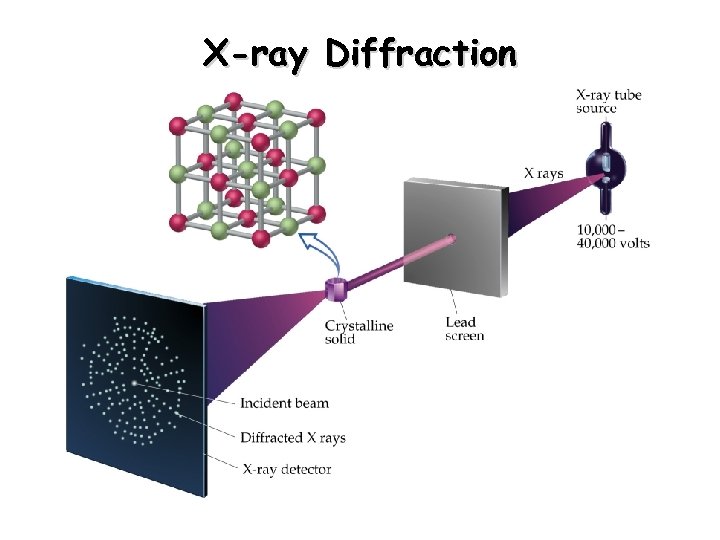
X Ray Diffraction Schematic Diagram The sherrer formula describes the relationship between the grain size and the half width of the diffraction peak. the scherreer formula: d=kλ (βcosθ) the use of this equation to calculate the average grain size requires attention: 1. β is the half peak width, that is, the width where the diffraction intensity is half of the maximum value. An x ray diffractometer is the instrument we use to produce monochromatic x rays, focus the beam on a sample, scan through a range of 2θ, and then detect the reflected x rays and their intensity. monochromatic x rays are generated in a cathode ray tube. a filament of tungsten is heated to produce electrons which are then accelerated towards an. The science behind x ray diffraction (xrd) during xrd analysis, a beam of x rays is directed toward a sample, and the scattered intensity is measured as a function of the outgoing direction. by convention, the angle between the incoming and outgoing beam directions is called 2θ, or 2 theta. the angle between the incoming and outgoing beam. The 2 theta values for the peak depend on the wavelength of the anode material of the x ray tube. it is therefore customary to reduce a peak position to the interplanar spacing d that corresponds to the h, k, l planes that caused the reflection. the value of the d spacing depend only on the shape of the unit cell.

Comments are closed.