How Does Carbon Dioxide Cycle Through The Oceans Communicating
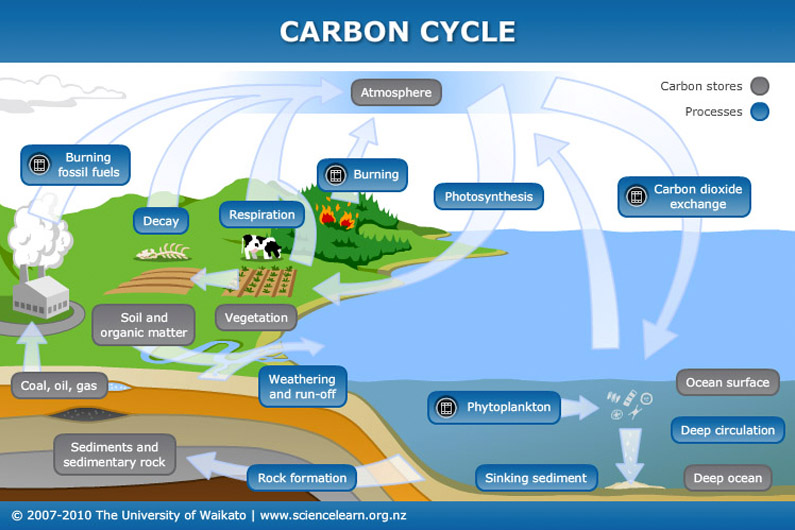
How Does Carbon Dioxide Cycle Through The Oceans Communicating The oceans play an important role to the earth’s climate change because it can take in a huge amount of carbon above and store carbon in the atmosphere. in fact, more than 9 3% of the carbon dioxide (co2) in the world is stored in the oceans. fortunately, most of the co2 is stored in the oceans, which leaves less co2 in the atmosphere. The ocean plays an important part in the carbon cycle. overall, the ocean is called a carbon ‘sink’ because it takes up more carbon from the atmosphere than it gives up. carbon dioxide from the atmosphere dissolves in the surface waters of the ocean. some of the carbon dioxide stays as dissolved gas, but much of it gets turned into other.
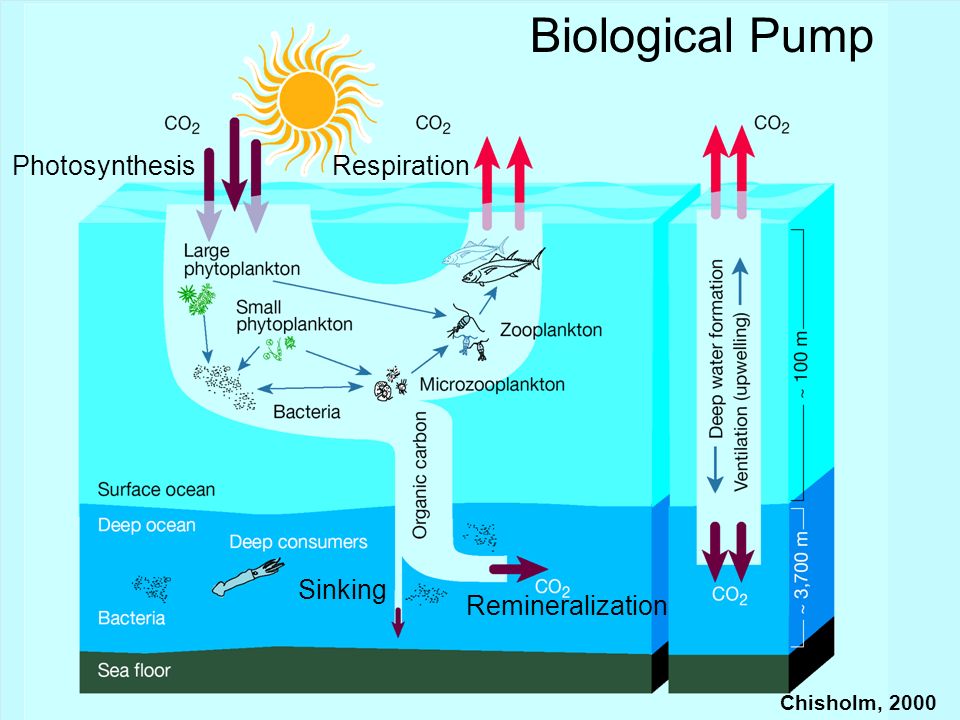
How Does Carbon Dioxide Cycle Through The Oceans Communicating As a result, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is rapidly rising; it is already greater than at any time in the last 3.6 million years. the ocean absorbs much of the carbon dioxide that is released from burning fossil fuels. this extra carbon dioxide is lowering the ocean’s ph, through a process called ocean acidification. Part of the marine carbon cycle transforms carbon between non living and living matter. three main processes (or pumps) that make up the marine carbon cycle bring atmospheric carbon dioxide (co 2) into the ocean interior and distribute it through the oceans. these three pumps are: (1) the solubility pump, (2) the carbonate pump, and (3) the. This movement of carbon from one place to another, which is caused by natural and human processes, is known as the carbon cycle. the oceans play a particularly important role in the carbon cycle. surface waters exchange gases with the atmosphere, absorbing and releasing carbon dioxide, oxygen, and other gases. plant like phytoplankton living in. The ocean carbon cycle. carbon, a building block of life, is constantly moving through different environmental compartments such as biota, the atmosphere, the ocean, soil and sediment, as part of what is called ‘the global carbon cycle.’. a change in any of these fluxes could have wide ranging impacts on ecosystems and our climate.

Comments are closed.