Hierachy Of Courts In India Overview And Analysis
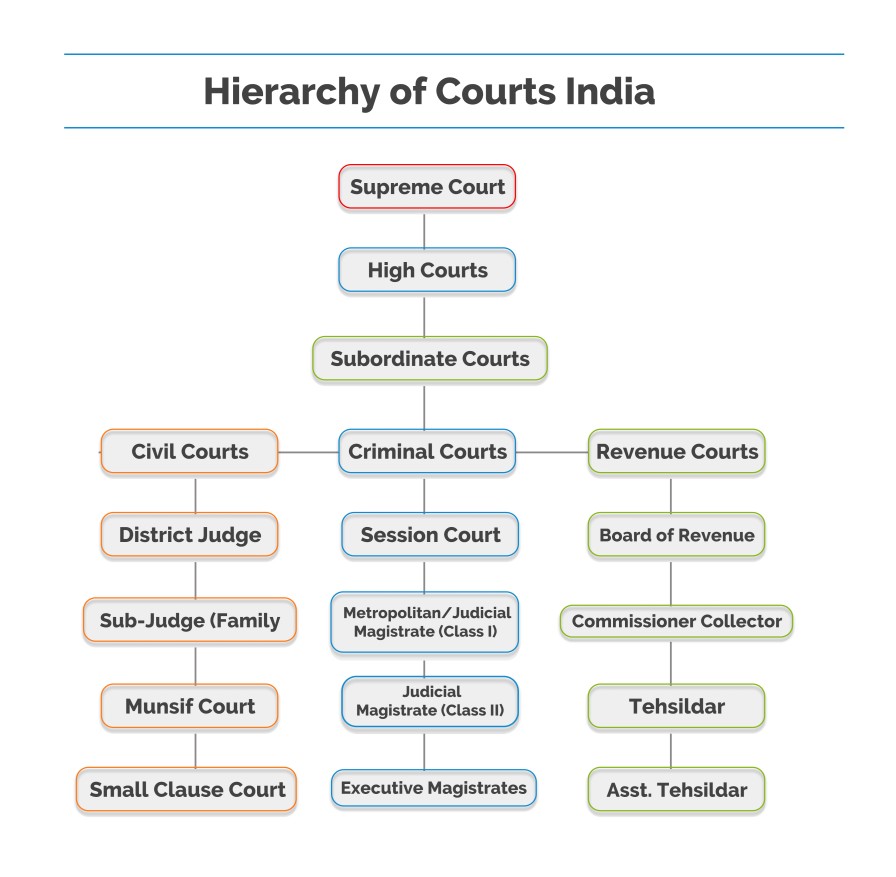
Hierarchy Of Courts And Justice System In India Law Corner The appeal against the order of the district court can be filed in the high court of the state. the hierarchy of the criminal courts in india is given in section 6 of the criminal procedure code, 1973 which is given as follows: session court. judicial magistrate of the first class. I n indian judiciary system, the judges have a hierarchy according to which they are seated in the respective courts. the judges at different levels have different powers and functions. the higher the judges are seated, the more is their power. indian courts are in a hierarchy for smooth functioning and to remove the pendency of cases.
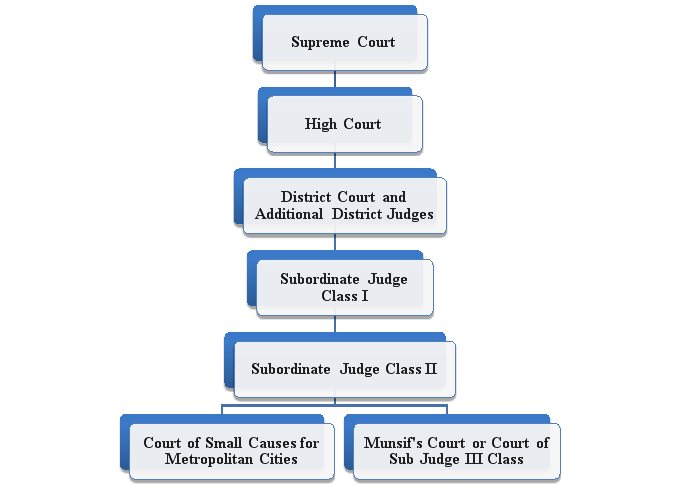
Hierachy Of Courts In India Overview And Analysis High courts have jurisdiction over the states in which they are located. there are at present, 25 high courts in india. however, few of the high courts have jurisdiction over more than one state. At the top of the hierarchy in india is the supreme court. it is the highest court of appeal and is vested with various powers, to exercise original, appellate and advisory jurisdiction. in respect to civil matters, the supreme court has been conferred with many power: article 129 gives power to the supreme court to punish for contempt of court. The hierarchy in civil courts and further categorization are as follows: chart no.1: the civil courts structure in the indian district judiciary. any civil suit has to be filed before the lowest court possible, i.e., munsif court. however, based on certain aspects of jurisdiction, the competent court to try the matter will be decided. Before delving into the details, have a quick overview of the hierarchy of courts in india. below is the answer to “what is the structure of judiciary in india?”: supreme court of india: the apex judicial body at the national level. high courts: the highest judicial authorities at the state level. subordinate courts: courts operating below.

Comments are closed.