Heating Curves Temperature Energy Graphs Gcse Physics

Heating Curves Temperature Energy Graphs Gcse Physics Youtube What happens to a substance when we heat it and it changes state? find out what happens to temperature in the heating curve of water using a temperature ener. Edexcel. spanish. past papers. cie. spanish language & literature. past papers. other subjects. accounting. revision notes on 3.2.5 heating & cooling graphs for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams.
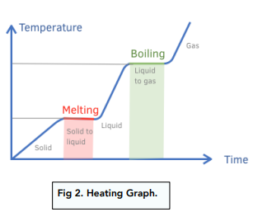
Heating And Cooling Graphs Gcse Physics Study Mind Heating graph. heating and cooling graphs. we are going to discuss the heating graph step by step: solid heating – as temperature and time increases, the solid is starting to heat up. melting – once the solid reaches its melting point (in this case it is 0 degrees), it starts to melt and turn into a liquid. liquid heating – as temperature. A heating curve is a graph showing the temperature of a substance plotted against the amount of energy it has absorbed. you may also see a cooling curve, which is obtained when a substance cools. Latent heat can be measured from a heating or cooling curve line graph. if a heater of known power is used, such as a 60 w immersion heater that provides 60 j s, the temperature of a known mass of. Molecular polarity 10m. intermolecular forces 20m. intermolecular forces and physical properties 9m. clausius clapeyron equation 18m. phase diagrams 13m. heating and cooling curves 25m. atomic, ionic, and molecular solids 11m. crystalline solids 4m. simple cubic unit cell 7m.

Comments are closed.