Heating Curve Practice Problems
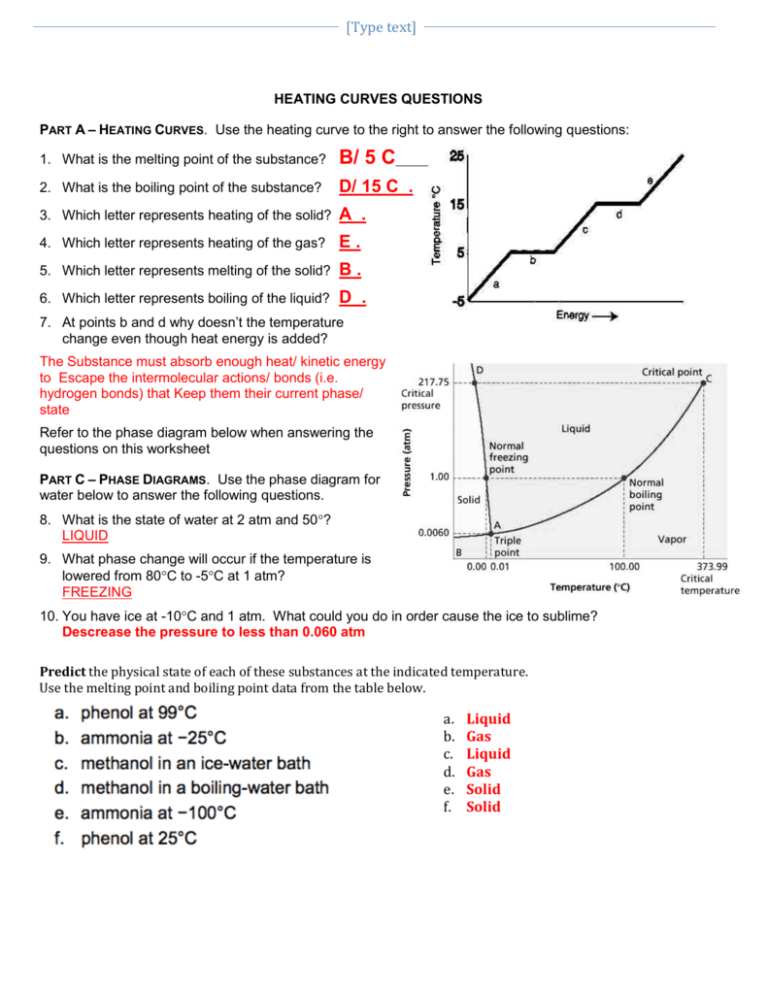
Heating Curves Worksheets Problem 8.1.2 8.1. 2. evaporation of sweat requires energy and thus take excess heat away from the body. some of the water that you drink may eventually be converted into sweat and evaporate. if you drink a 20 ounce bottle of water that had been in the refrigerator at 3.8 °c, how much heat is needed to convert all of that water into sweat and. Heating curve worksheet 1 the heating curve shown above is a plot of temperature vs time. it represents the heating of substance x at a constant rate of heat transfer. answer the following questions using this heating curve: 1. in what part of the curve would substance x have a definite shape and definite volume? 2.

States Of Matter Phase Change Heating Curve Practice Problems By Learn how to solve heating curve problems with this easy to follow video tutorial. you'll see examples, formulas, and tips for chemistry students. Multi step problems with changes of state. heating curves show the phase changes that a substance undergoes as heat is continuously absorbed. figure \(\pageindex{1}\): heating curve of water. (cc by nc; ck 12) the specific heat of a substance allows us to calculate the heat absorbed or released as the temperature of the substance changes. Total heat for converting 10 g of solid ice at 20°c to 10 g of gaseous steam at 140°c is the sum of all steps. qtot = 420j 3400j 4200j 22700 j 808 j = 31,528 j practice problems calculate the total heat energy needed to convert 100 g of ice at 10°c to steam at 110°c. chemistry heating curve worksheet. Boil water. heat steam from 100 °c to 120 °c. the heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: q = m × c × Δ t (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). the heat needed to induce a given change in phase is given by q = n × Δ h. using these equations with the appropriate values for specific.
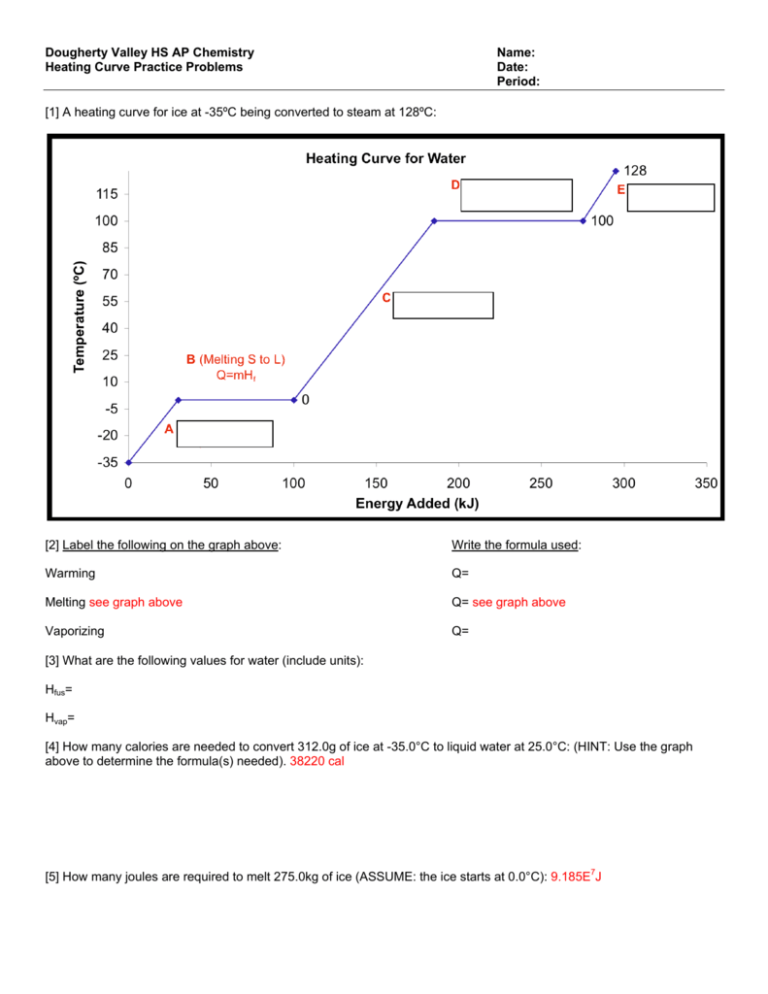
Dougherty Valley Hs Ap Chemistry Name Heating Curve Practice Total heat for converting 10 g of solid ice at 20°c to 10 g of gaseous steam at 140°c is the sum of all steps. qtot = 420j 3400j 4200j 22700 j 808 j = 31,528 j practice problems calculate the total heat energy needed to convert 100 g of ice at 10°c to steam at 110°c. chemistry heating curve worksheet. Boil water. heat steam from 100 °c to 120 °c. the heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: q = m × c × Δ t (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). the heat needed to induce a given change in phase is given by q = n × Δ h. using these equations with the appropriate values for specific. Five step problem for water melting point boiling point heat of fusion heat of vapor. cp (solid) cp liquid) cp (vapor) 0.0°c 100.0°c 334 j g 2260 j g 2.05 j gºc 4.18 j gºc 1.90 j gºc the data below are for water (h 2 o) 1. heat needed to raise the temperature of ice at 20°c to 0°c. determine the heat needed to 15 g of ice. Heating curve of substance x 20 22 24 26 28 30 80 75 70 60 55 temp. (oc) 5 0 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 12 14 16 time (minutes) 18 the heating curve shown above is a plot of temperature vs time.

Comments are closed.