Heat Equation
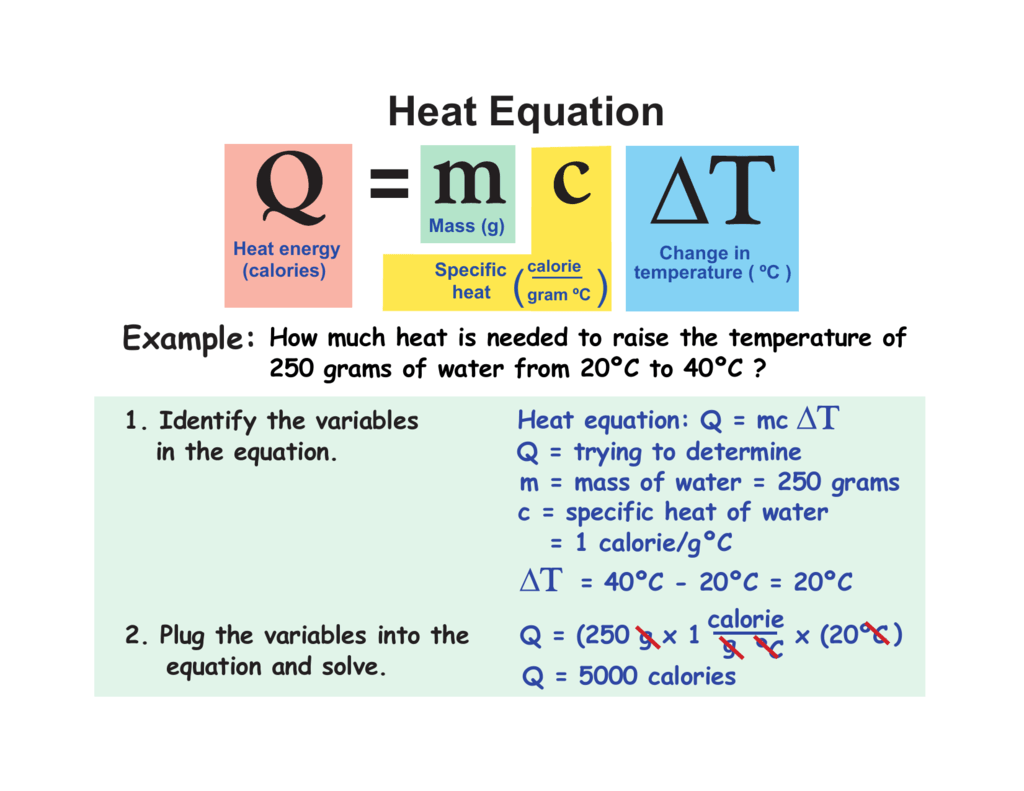
Heat Equation The heat equation is a partial differential equation that describes how heat diffuses through a medium. learn about its mathematical and physical interpretation, applications, variants, and solutions. Learn how to solve the heat equation in a uniform bar using separation of variables and fourier series. find the formal solution, the initial condition, and the boundary conditions for the problem.
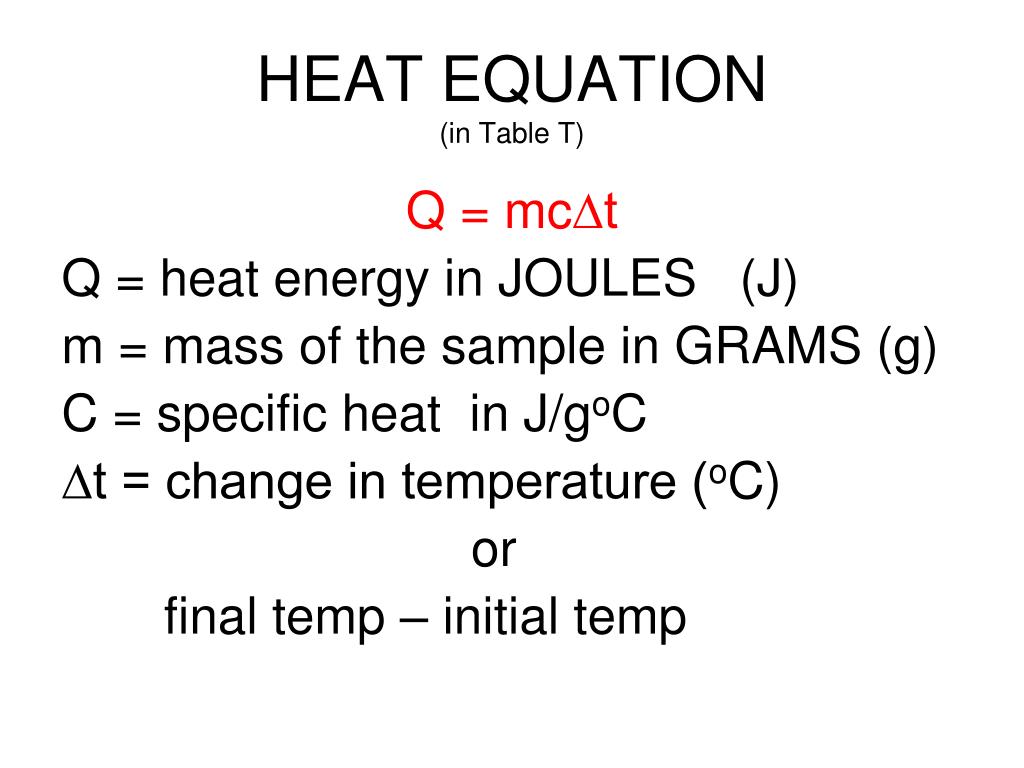
Ppt Heat Equation In Table T Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Below we provide two derivations of the heat equation, ut ¡ kuxx = 0 k > 0: (2.1) this equation is also known as the diffusion equation. 2.1.1 diffusion. consider a liquid in which a dye is being diffused through the liquid. the dye will move from higher concentration to lower concentration. Learn the definition, form and properties of the heat equation, which governs the temperature distribution in an object. see how to derive the equation from fourier's law and simplify it for constant thermal properties. Learn about heat, the thermal energy transfer between systems or bodies due to a temperature difference. find out how heat relates to entropy, enthalpy, and thermodynamics. Learn the physical derivation, initial and boundary conditions, and separation of variables method for the 1 d heat equation. see examples, dimensionless problem, and solutions for different types of boundary conditions.

What Does It Mean To Solve The Heat Equation Pde An Introduction With Learn about heat, the thermal energy transfer between systems or bodies due to a temperature difference. find out how heat relates to entropy, enthalpy, and thermodynamics. Learn the physical derivation, initial and boundary conditions, and separation of variables method for the 1 d heat equation. see examples, dimensionless problem, and solutions for different types of boundary conditions. Specific heat is closely related to the concept of heat capacity. heat capacity is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of a substance by 1.00 °c °c. in equation form, heat capacity c is c = m c c = m c, where m is mass and c is specific heat. note that heat capacity is the same as specific heat, but without any dependence. Learn how to solve the heat equation using different methods, such as separation of variables, relaxation, and finite difference. the heat equation describes the diffusion of heat in a one dimensional slab with constant thermal conductivity.

Comments are closed.