Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
Cardiovascular System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses In order to understand how that happens, it is necessary to understand the anatomy and physiology of the heart. location of the heart. the human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. The aortic semilunar valve is between the left ventricle and the opening of the aorta. it has three semilunar cusps leaflets: left left coronary, right right coronary, and posterior non coronary. in clinical practice, the heart valves can be auscultated, usually by using a stethoscope.

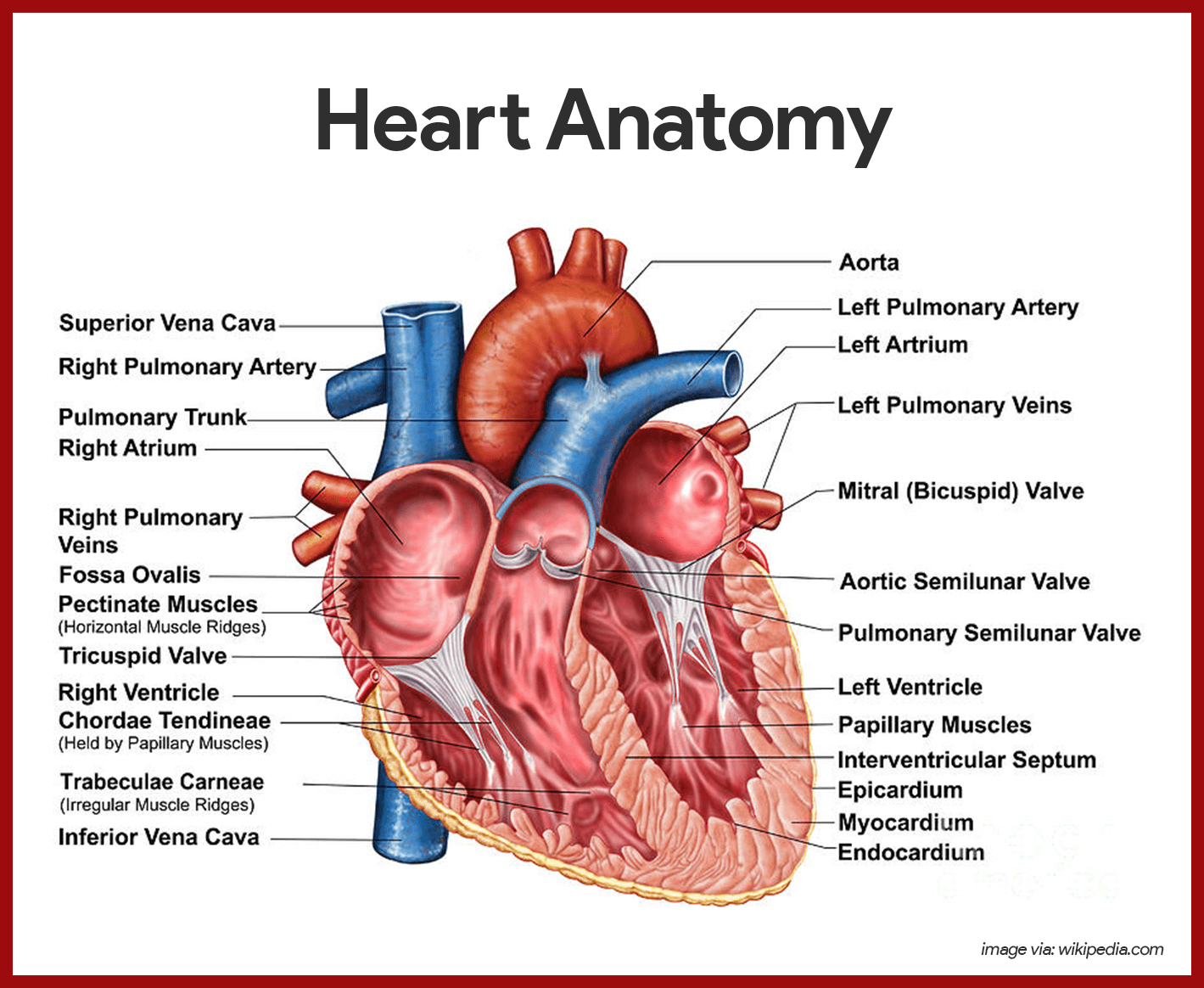
Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology Learn about the structure, function and blood supply of the heart, the muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, with this comprehensive guide. Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. your heart contains four muscular sections (chambers) that briefly hold blood before moving it. electrical impulses make your heart beat, moving blood through these chambers. your brain and nervous system direct your heart’s function. advertisement. The heart is subdivided by septa into right and left halves, and a constriction subdivides each half of the organ into two cavities, the upper cavity being called the atrium, the lower the ventricle. the heart, therefore, consists of four chambers: right atrium. left atrium. right ventricle. left ventricle [6]. Heart anatomy in basic terms. the heart is a crucial organ that functions as the body's pump, ensuring blood circulation throughout the body. it consists of four main chambers: left and right atria (upper chambers) left and right ventricles (lower chambers) these chambers work in a coordinated manner to receive oxygen poor blood, pump it to the.

Cardiovascular System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses The heart is subdivided by septa into right and left halves, and a constriction subdivides each half of the organ into two cavities, the upper cavity being called the atrium, the lower the ventricle. the heart, therefore, consists of four chambers: right atrium. left atrium. right ventricle. left ventricle [6]. Heart anatomy in basic terms. the heart is a crucial organ that functions as the body's pump, ensuring blood circulation throughout the body. it consists of four main chambers: left and right atria (upper chambers) left and right ventricles (lower chambers) these chambers work in a coordinated manner to receive oxygen poor blood, pump it to the. 6.1 heart anatomy. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the location and position of the heart within the body cavity. describe the internal and external anatomy of the heart. identify the tissue layers of the heart. relate the structure of the heart to its function as a pump. Contributors. the heart is a muscular organ just slightly bigger than a person’s loosely clenched fist. it is located in the thorax more specifically, between the two lungs, in a space called the mediastinum. the heart is covered by a tough membrane called the pericardium, that separates the heart from the other structures in the mediastinum.

Anatomy And Physiology Of Heart Download Scientific Diagram 6.1 heart anatomy. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the location and position of the heart within the body cavity. describe the internal and external anatomy of the heart. identify the tissue layers of the heart. relate the structure of the heart to its function as a pump. Contributors. the heart is a muscular organ just slightly bigger than a person’s loosely clenched fist. it is located in the thorax more specifically, between the two lungs, in a space called the mediastinum. the heart is covered by a tough membrane called the pericardium, that separates the heart from the other structures in the mediastinum.

Comments are closed.