Gut Microbiota Influences The Efficiency Of Immune Checkpoint

Gut Microbiome In Modulating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ebiomedicine Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) are commonly utilized in tumor treatment. however, they still have limitations, including insufficient effectiveness and unavoidable adverse events. it has been demonstrated that gut microbiota can influence the effectiveness of icis, although the precise mechanis …. It has been demonstrated that gut microbiota can influence the effectiveness of icis, although the precise mechanism remains unclear. gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the formation and development of the immune system. gut microbiota and their associated metabolites play a regulatory role in immune balance.
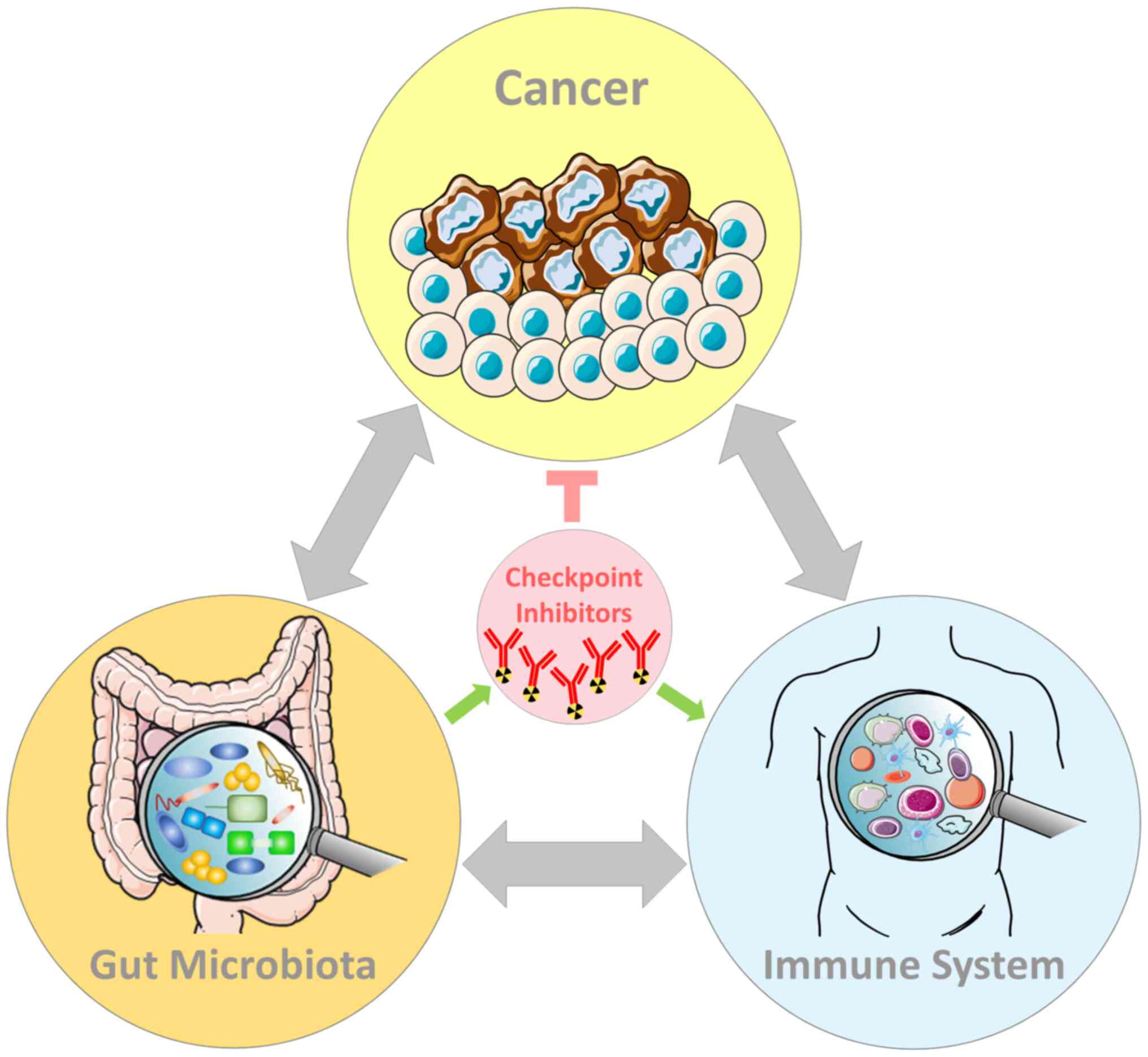
Gut Microbiota And Immune System The interaction between gut microbiota and immune system (1). bacteroides fragilis takes advantage of iga to settle down in the intestine of mice (2); sfb induces the appearance of cd4 t helper cells in lamina propria (3); clusters iv and xiva of the genus clostridium are associated with tregs accumulation in colon (4); scfas regulate foxp3 in tregs, inhibit immune response of t cells (5. The gut microbiota is a crucial regulator of anti tumour immunity during immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. several bacteria that promote an anti tumour response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeutic responses associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) in preclinical models and patient cohorts. this evidence hints. Furthermore, the addition of anti ctla 4 has a profound effect on gut barrier permeability 50,51, potentially changing the influence of the gut microbiome on icb response. nevertheless, the poor.

How Does The Gut Microbiome Influence Immune Checkpoint Blockade Gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeutic responses associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) in preclinical models and patient cohorts. this evidence hints. Furthermore, the addition of anti ctla 4 has a profound effect on gut barrier permeability 50,51, potentially changing the influence of the gut microbiome on icb response. nevertheless, the poor. The gut microbiota may have an effect on the therapeutic resistance and toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis). however, the associations between the highly variable genomes of gut. Diet and the gut microbiota are important factors that shape immune fitness. strong evidence of the role of the gut microbiota in shaping immune function is provided by studies involving germ free.

Gut Microbiome Directs The Efficacy Of Immune Checkpoint Therapy Both The gut microbiota may have an effect on the therapeutic resistance and toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis). however, the associations between the highly variable genomes of gut. Diet and the gut microbiota are important factors that shape immune fitness. strong evidence of the role of the gut microbiota in shaping immune function is provided by studies involving germ free.

Comments are closed.