Gut Microbiome Therapeutic Modulation To Alleviate Drug Induced Hepatic
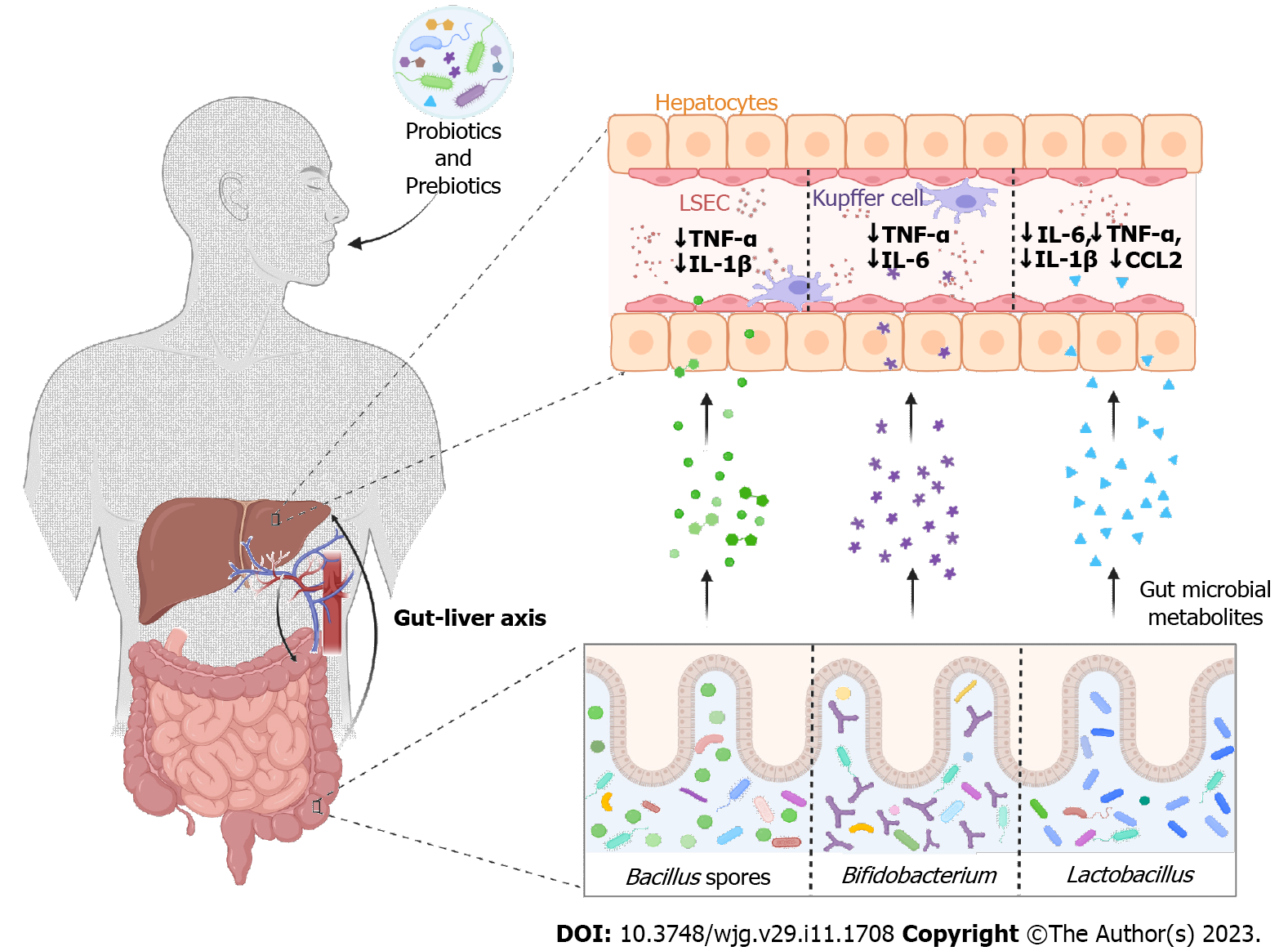
Gut Microbiome Therapeutic Modulation To Alleviate Drug Induced Hepatic Gut microbiota influences liver chemistry through its metabolites. gut dysbiosis during covid 19 treatment can promote liver inflammation. here, we highlighted the bidirectional association of liver physiology and gut microbiota (gut liver axis) and its potential to manipulate drug induced chemical abnormalities in the livers of covid 19 patients. Therefore, incorporation of the drug induced gut dysbiosis and its connection to hepatic injury could better elucidate the gut liver bidirectional axis association with covid 19 severity. a precise understanding of interaction between gut microbiota and liver physiology will facilitate the development of targeted therapeutics to improve the condition of covid 19 patients.
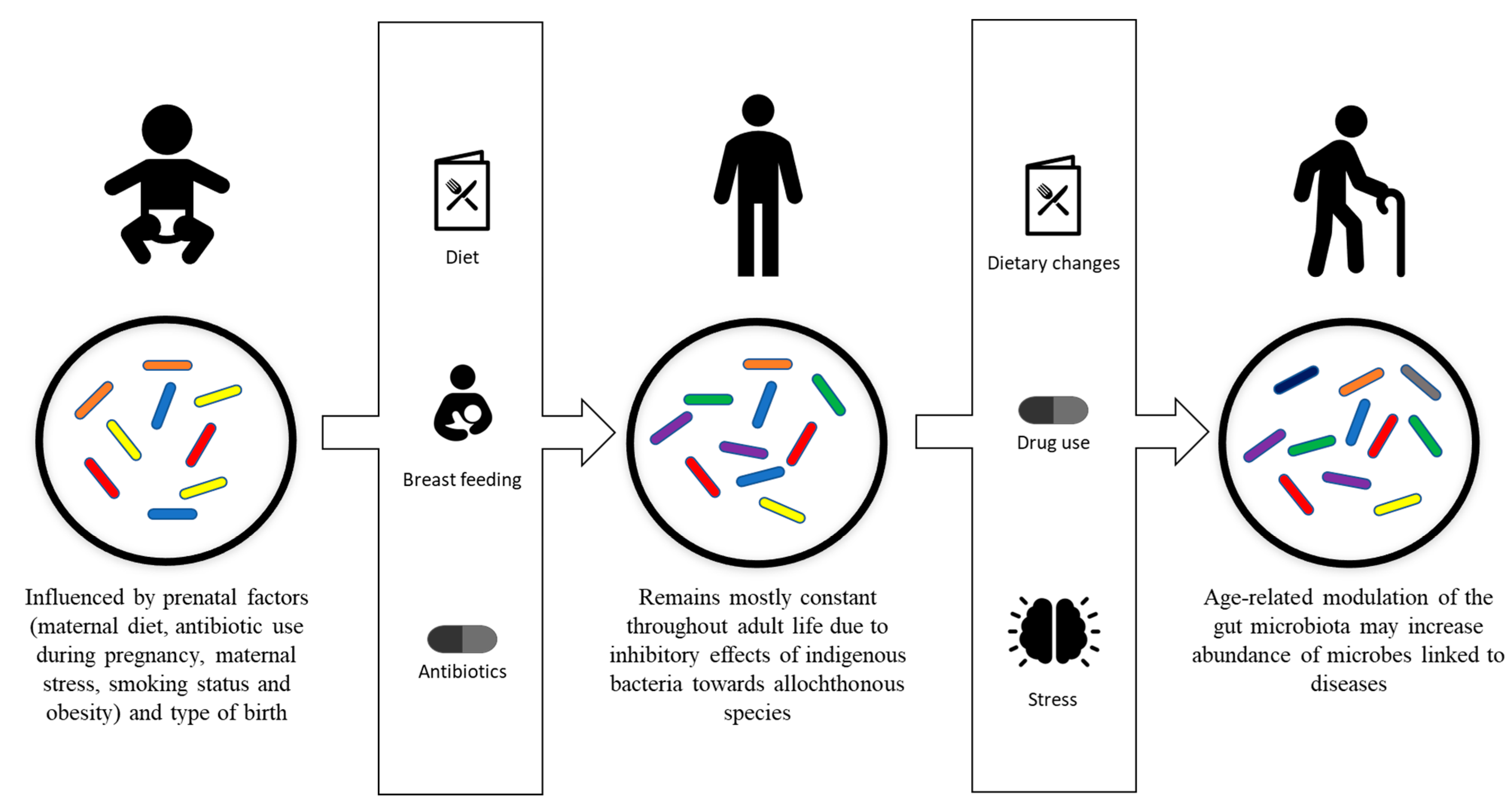
Gut Microbial Modulation Encyclopedia Mdpi Citation: ahsan k, anwar ma, munawar n. gut microbiome therapeutic modulation to alleviate drug induced hepatic damage in covid 19 patients.world j gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1708 1720. Regarding the role of gut liver axis in liver disease development, this study aimed to explore the potential role of gut microbiota in the treatment of oca in nafld mice induced by the high fat. Through the microbiome–gut–liver axis, the gut microbiota has an impact on the onset and progression of hcc as well as lt. this review summarizes the mechanisms by which the gut microbiota affects hcc and its bidirectional interactions with chronic liver disease that can develop into hcc as well as the diagnostic and prognostic value of the gut microbiota in hcc. The large drug inventory of drug induced liver injury severity and toxicity, which includes 1279 drugs, shows that antidepressants and antiepileptics have a high rate of potential drug induced liver injury and that clinical use of this pharmacologic class requires attention to hepatic safety monitoring. 103 a multicenter case control study conducted in italian hospitalized patients revealed.
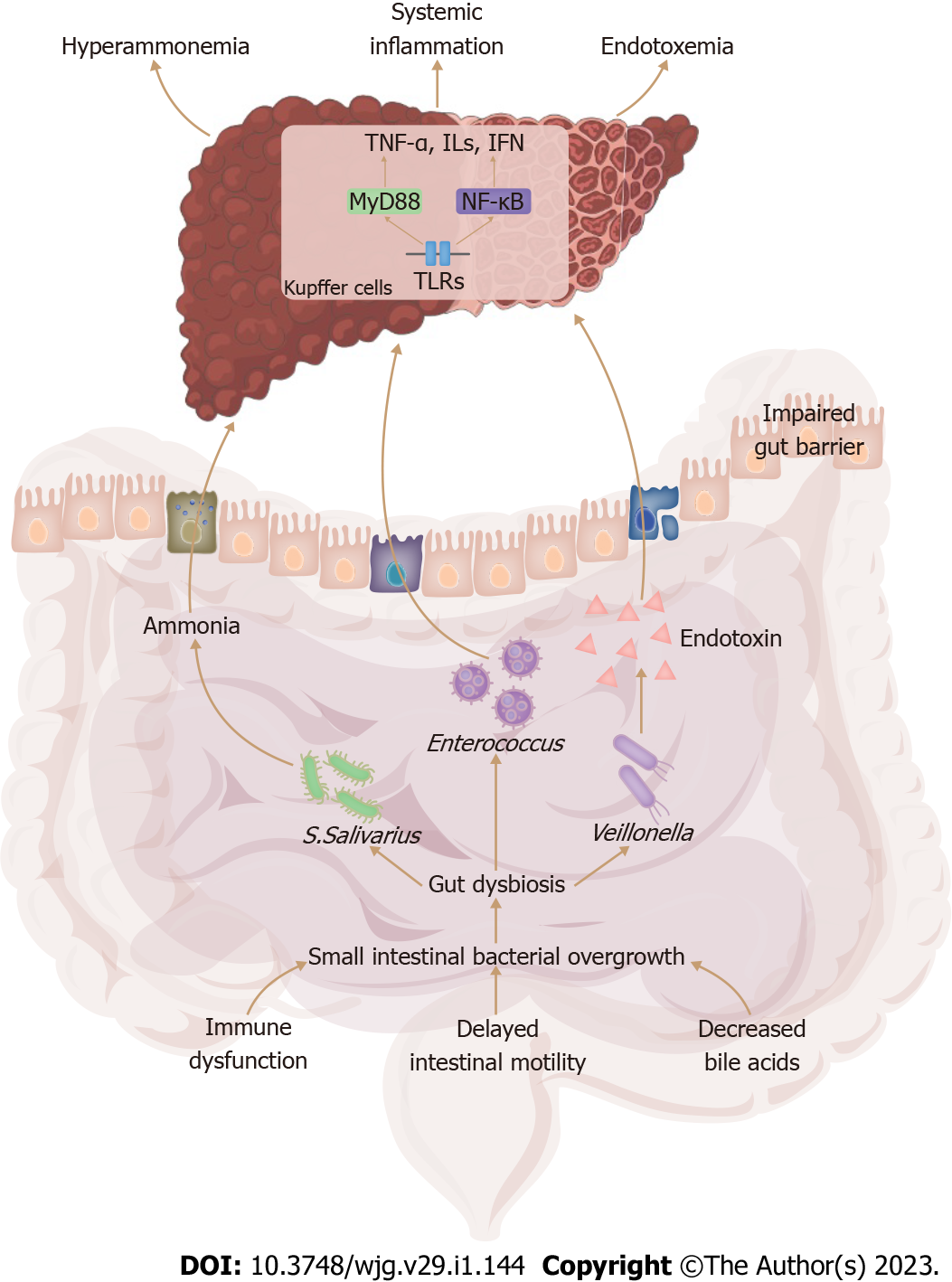
Role Of Gut Microbiota In The Pathogenesis And Therapeutics Of Minimal Through the microbiome–gut–liver axis, the gut microbiota has an impact on the onset and progression of hcc as well as lt. this review summarizes the mechanisms by which the gut microbiota affects hcc and its bidirectional interactions with chronic liver disease that can develop into hcc as well as the diagnostic and prognostic value of the gut microbiota in hcc. The large drug inventory of drug induced liver injury severity and toxicity, which includes 1279 drugs, shows that antidepressants and antiepileptics have a high rate of potential drug induced liver injury and that clinical use of this pharmacologic class requires attention to hepatic safety monitoring. 103 a multicenter case control study conducted in italian hospitalized patients revealed. Drug induced liver injury (dili) is defined as the liver damage induced by a variety of drugs and its associated metabolites, including natural medicine, traditional chinese medicine, and prescription or over the counter chemical drugs [1]. the incidence of dili is about 14 19 cases per 100 000 people [ 2, 3 ], while in china it is estimated to. Diet and gut microbiota impact the progression of non alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash). an unhealthy diet, rich in fat and sugar, promotes gut microbiota dysbiosis, leading to the translocation of lipopolysaccharides (lps) and other harmful pathogen associated molecular patterns to the liver, triggering hepatic inflammation and aggravating nash.

Comments are closed.