Gut Microbiome In Modulating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ebiomedicine

Gut Microbiome In Modulating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ebiomedicine Gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeutic responses associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) in preclinical models and patient cohorts. this evidence hints. Figure 2. gut microbiota modulation improves the efficiency of cancer immunotherapy. different strategies can be used to regulate the gut microbiome and can be used as interventional measures to improve the ef ciency of cancer immunotherapy. i.e., fi. fmt in combination with checkpoint inhibitors are able to reprogramme the tumor.

Gut Microbiome In Modulating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ebiomedicine The gut microbiome can modulate the efficacy of anticancer drugs. 254 alterations in the gut microbiome are associated with tumor resistance to chemotherapeutic agents or immune checkpoint. Indeed several recent publications have reported that the gut microbiome may influence response to immune checkpoint therapy,2,3 potentially improving treatment efficacy, and may predict which. Accumulating evidence demonstrated the crucial role of gut microbiota in many human diseases, including cancer. checkpoint inhibitor therapy has emerged as a novel treatment and has been clinically accepted as a major therapeutic strategy for cancer. gut microbiota is related to cancer and the effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis), and. (2022) li et al. ebiomedicine. gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeuti.

The Gut Microbiome And Response To Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Accumulating evidence demonstrated the crucial role of gut microbiota in many human diseases, including cancer. checkpoint inhibitor therapy has emerged as a novel treatment and has been clinically accepted as a major therapeutic strategy for cancer. gut microbiota is related to cancer and the effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis), and. (2022) li et al. ebiomedicine. gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeuti. Although the immune modulating properties of the human gut bacterial ecosystem are yet to be fully elucidated, there has been growing interest in evaluating the role of the gut microbiome in shaping the therapeutic response to cancer immunotherapy. considerable research efforts are currently directed to utilizing metagenomic and metabolic. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) therapy is a novel strategy for cancer treatments in recent years. however, it was observed that most patients treated with icis could not get benefit from the therapy, which led to the limitation of clinical application. motivated by potent and durable efficacy of icis, oncologists endeavor to explore the.
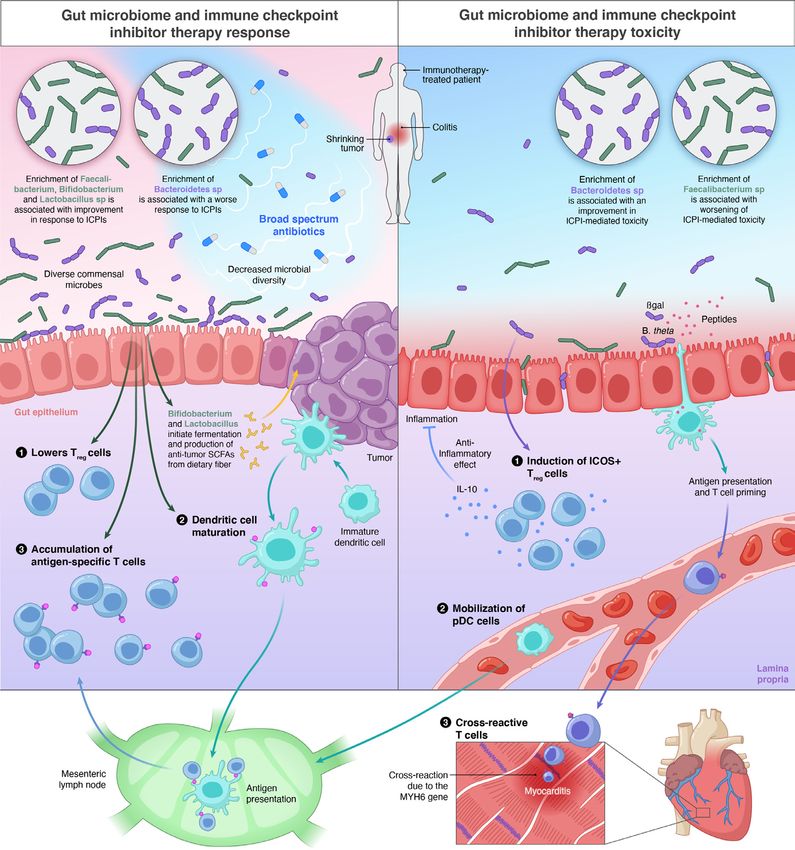
The Role Of Gut Microbiome In Modulating Response To Immune Checkpoint Although the immune modulating properties of the human gut bacterial ecosystem are yet to be fully elucidated, there has been growing interest in evaluating the role of the gut microbiome in shaping the therapeutic response to cancer immunotherapy. considerable research efforts are currently directed to utilizing metagenomic and metabolic. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) therapy is a novel strategy for cancer treatments in recent years. however, it was observed that most patients treated with icis could not get benefit from the therapy, which led to the limitation of clinical application. motivated by potent and durable efficacy of icis, oncologists endeavor to explore the.

Gut Microbiome Directs The Efficacy Of Immune Checkpoint Therapy Both

Comments are closed.