Gut Microbiome Disease
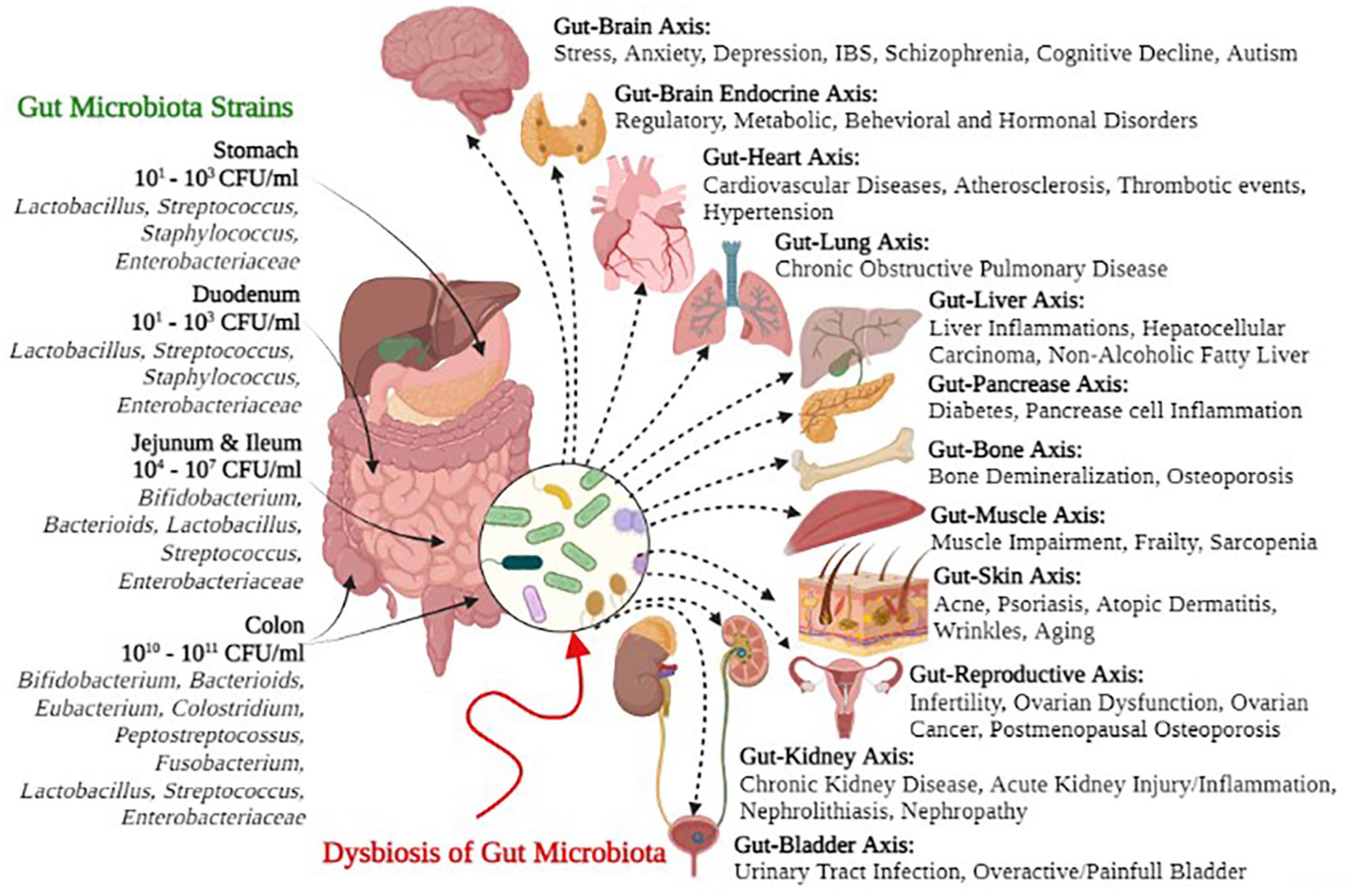
Frontiers Human Gut Microbiota In Health And Disease Unveiling The Such an integrated approach to microbiome based therapeutics (fig. 4), built on independent observations in the field of gut microbiome research, may offer more effective, predictable, and sustainable microbial restitution in cases of chronic disease in which microbiome perturbation and functional gene loss are prominent features. The human gut microbiome—the collection of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract—is thought to play a role in the etiology of various diseases, including inflammatory bowel.

Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health The Bmj Microbiome protects host and plays role in disease risk. the microbiome consists of the genes of tiny organisms (bacteria, viruses, and other microbes) found in the gastrointestinal tract, primarily in the small and large intestine. the normal gut flora — another term for the microbiome — protects its human host. The data of publications in the recent 5 years is used to assess the current research status of gut microbiome and disease. the timeline view of keywords co occurrence network reveals the development of gut microbiome and disease (supplementary figure 10). this network is divided into 21 clusters, which present the major subtopics in this field. The human gut microbiome has been associated with a diverse range of health deficits but there has been relatively little comparison of these effects between diseases 1.while a recent meta. Introduction to gut microbiota and disease. the intestinal microbiome has recently been implicated in a host of chronic diseases ranging from inflammatory bowel disease (ibd), type 2 diabetes (t2d), and cardiovascular disease (cvd) to colorectal cancer [1, 2, 3]. the community of ~200 prevalent bacteria, virus, and fungi inhabiting the human.
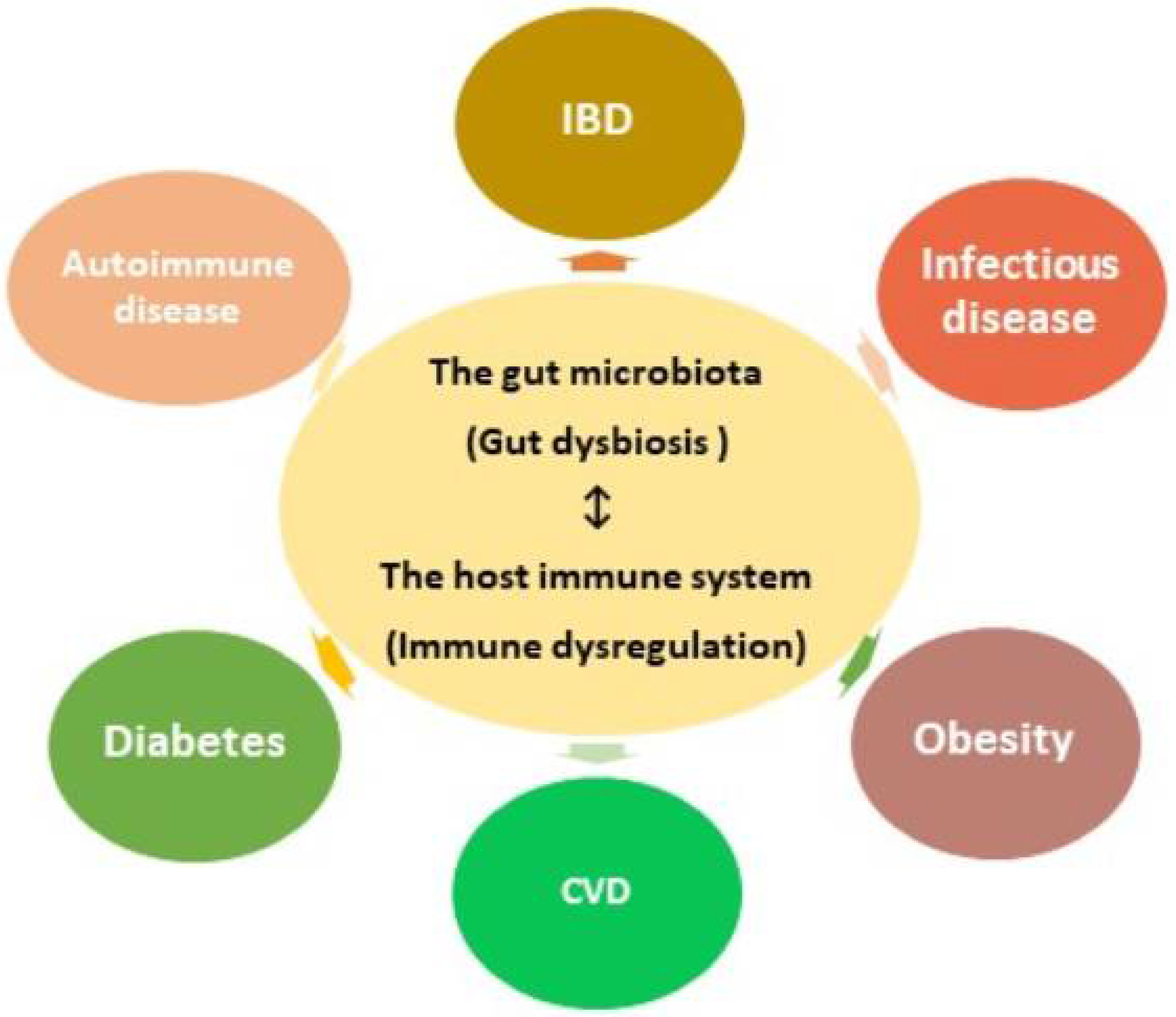
Gut Microbiota And Related Diseases Encyclopedia Mdpi The human gut microbiome has been associated with a diverse range of health deficits but there has been relatively little comparison of these effects between diseases 1.while a recent meta. Introduction to gut microbiota and disease. the intestinal microbiome has recently been implicated in a host of chronic diseases ranging from inflammatory bowel disease (ibd), type 2 diabetes (t2d), and cardiovascular disease (cvd) to colorectal cancer [1, 2, 3]. the community of ~200 prevalent bacteria, virus, and fungi inhabiting the human. The human gut microbiome, composed of bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoa, constitutes an intricate and dynamic ecosystem that has a substantial role in human health and disease 1. the gut. The results of a machine learning approach applied to the integration of blood glucose levels, dietary habits, and gut microbiome data, among other factors, predicted personalized postprandial.

Comments are closed.