Genotype Definition Characteristics Explanation And Examples
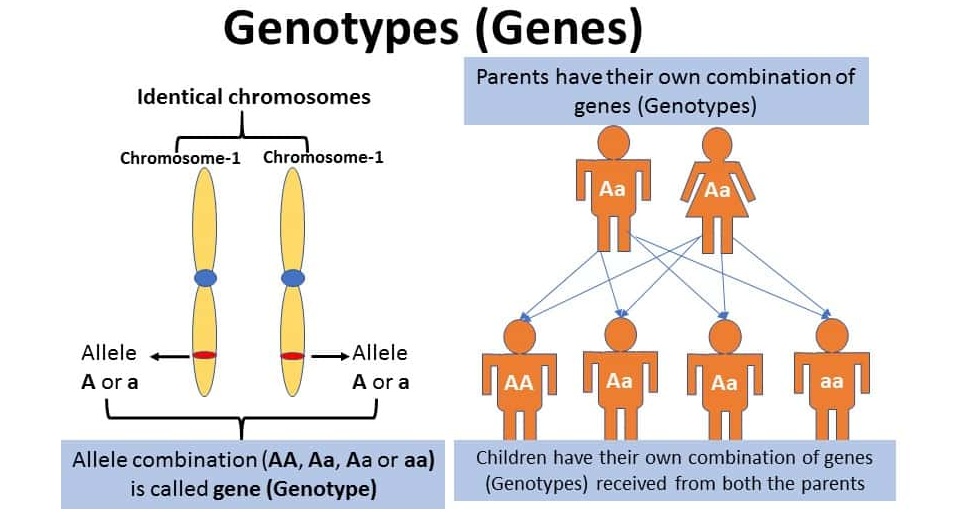
Genotype Definition Characteristics Explanation And Examples Genotype definition. the genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. a genotype consists of all the nucleic acids present in a dna molecule that code for a particular trait. the outward appearance, or phenotype, is the result of interactions of proteins. For example, consider a cross between two plants and a gene that controls the plant height allele. in this example, t is the dominant allele, for tall and t is the recessive allele, for short. so, plants with the genotype tt or tt are tall. plants with the genotype tt are short. the phenotypes are tall and short.
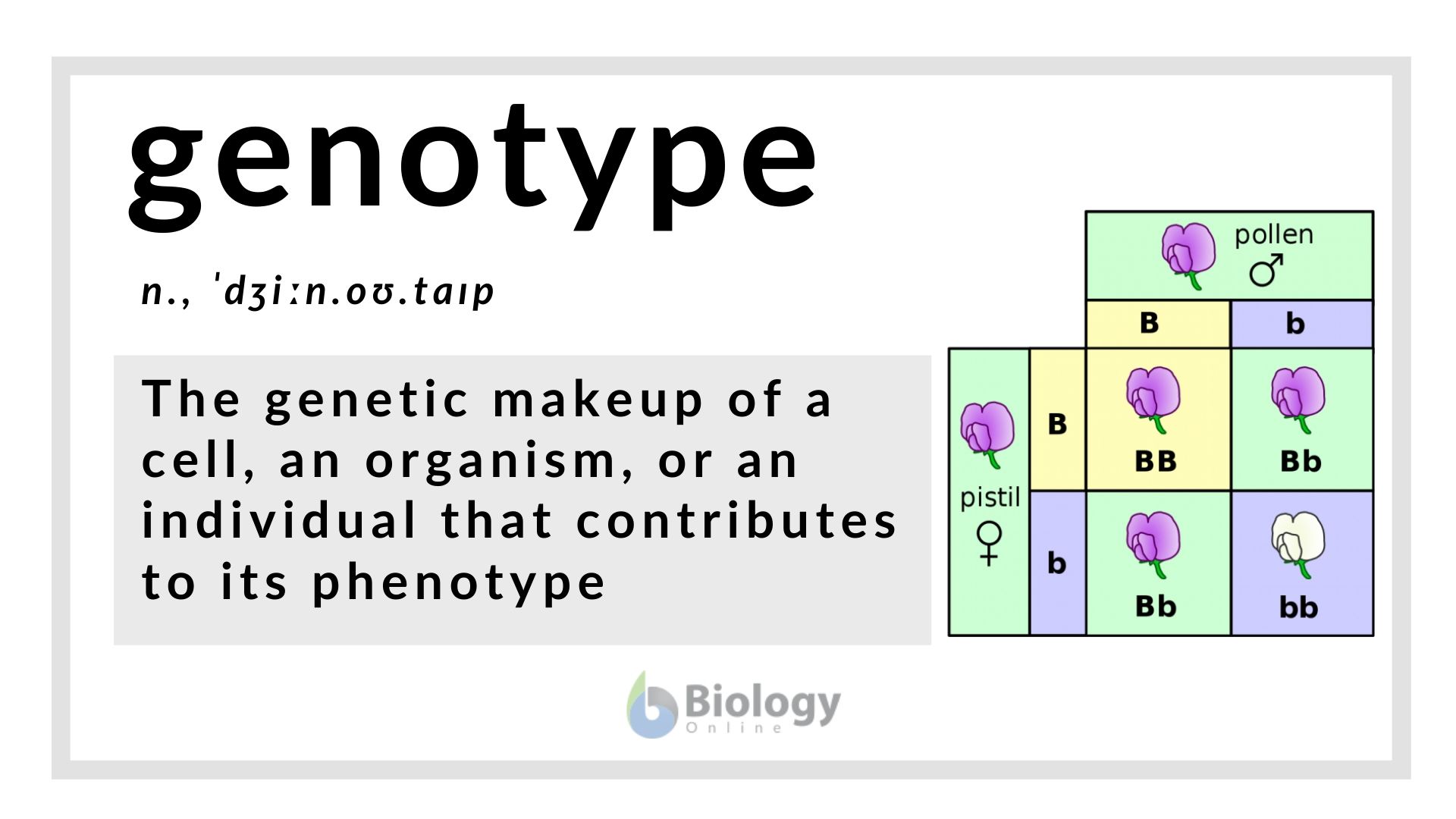
Genotype Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Genotype vs phenotype: observing observing the phenotype is simple – we take a look at an organism’s outward features and characteristics, and form conclusions about them. observing the genotype, however, is a little more complex. genotyping is the process by which differences in the genotype of an individual are analyzed using biological. Genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual cell or organism that determines or contributes to its phenotype. the contrasting terms genotype and phenotype are used to define the characteristics or traits of an organism. the genotype identifies the alleles related to a single trait (e.g. aa), or to a number of traits (e.g. aa bb cc). Functions of genotype. 1. determines traits. the genotype holds the genetic information that decides an organism’s traits, such as eye color, height, and even aspects of behavior. this genetic blueprint is unique to each individual and guides how physical and biochemical traits develop. 2. The genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. it is the combination of the inherited alleles of an individual, and it influences the individual's phenotype; the phenotype can't exist without the genotype. reasons to study genotype include learning about carriers of inherited diseases.

Comments are closed.