Genes Free Full Text Network Based Approaches To Explore Complex

Genes Free Full Text Network Based Approaches To Explore Complex Network medicine relies on different types of networks: from the molecular level of protein–protein interactions to gene regulatory network and correlation studies of gene expression. among network approaches based on the analysis of the topological properties of protein–protein interaction (ppi) networks, we discuss the widespread diamond (disease module detection) algorithm. starting. Network and systemic approaches to studying human pathologies are helping us to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms of and potential therapeutic interventions for human diseases, especially for complex diseases where large numbers of genes are involved. the complex human pathological landscape is traditionally partitioned into discrete “diseases”; however, that partition is.

Genes Free Full Text Network Based Approaches To Explore Complex Although indirect, these results suggest that our regression based method for constructing a transcription regulatory network is able to capture, at least on a high level, the structure of the regulatory relationships among a large number of tfs and their target genes, which led us to explore the possibility of network based annotation of transcription factors. Deep learning based approaches use neural networks to infer complex relationships between tfs, cres, genes and cells. full size image correlation based approaches. Network based approach exploits observations that genes with similar phenotypic roles tend to co localize in a specific region of a protein protein interaction (ppi) network 18,19. A data driven model recently developed to explore the lncrna associated cerna activity in breast invasive carcinoma is described and swim tool, a very promising example of the co expression network, is described along with its applications to cancer research and its predictions with diamond disease genes. network medicine relies on different types of networks: from the molecular level of.
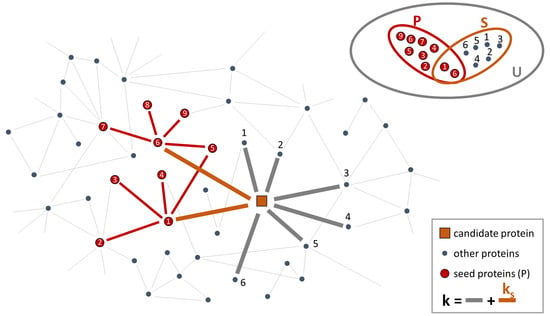
Genes Free Full Text Network Based Approaches To Explore Complex Network based approach exploits observations that genes with similar phenotypic roles tend to co localize in a specific region of a protein protein interaction (ppi) network 18,19. A data driven model recently developed to explore the lncrna associated cerna activity in breast invasive carcinoma is described and swim tool, a very promising example of the co expression network, is described along with its applications to cancer research and its predictions with diamond disease genes. network medicine relies on different types of networks: from the molecular level of. A subsequent approach, mogrify [97], prioritizes genes based on proximity on an input skeleton network and a measure of differential expression, which is informed by the lineage structure of cell types. both approaches successfully recapitulated known cell fate specification genes, and also predicted new genes that were validated to be important regulators for establishing a specific fate. In this review, we discussed recent promising approaches for two major problems: network reconstruction and network based interpretation. going forward we envision addressing one major challenge: to build network based causal, predictive models of complex phenotypes. this will require us to construct networks and prioritize experiments in.
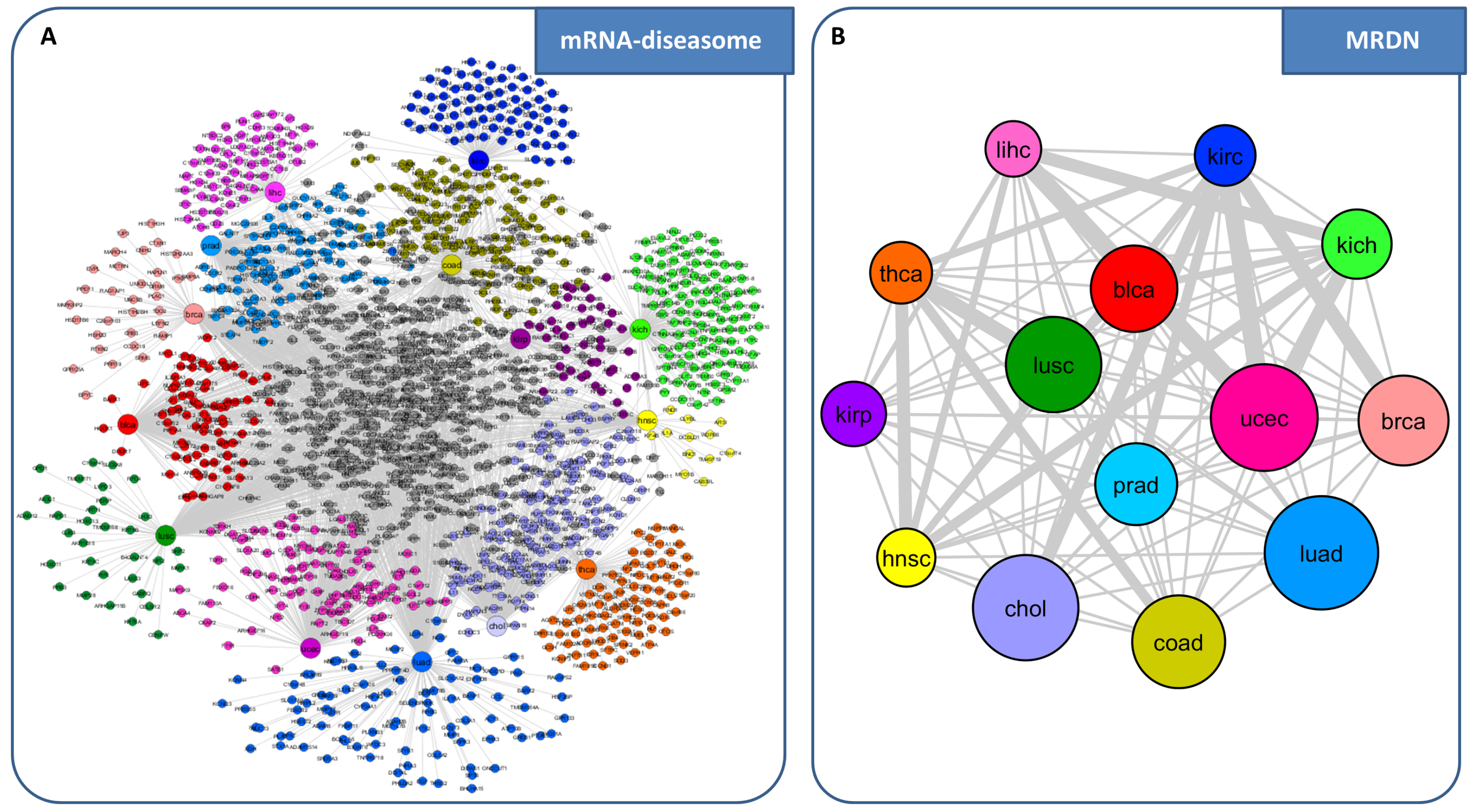
Genes Free Full Text Network Based Approaches To Explore Complex A subsequent approach, mogrify [97], prioritizes genes based on proximity on an input skeleton network and a measure of differential expression, which is informed by the lineage structure of cell types. both approaches successfully recapitulated known cell fate specification genes, and also predicted new genes that were validated to be important regulators for establishing a specific fate. In this review, we discussed recent promising approaches for two major problems: network reconstruction and network based interpretation. going forward we envision addressing one major challenge: to build network based causal, predictive models of complex phenotypes. this will require us to construct networks and prioritize experiments in.

Comments are closed.