General Properties Of Quadratic Equation
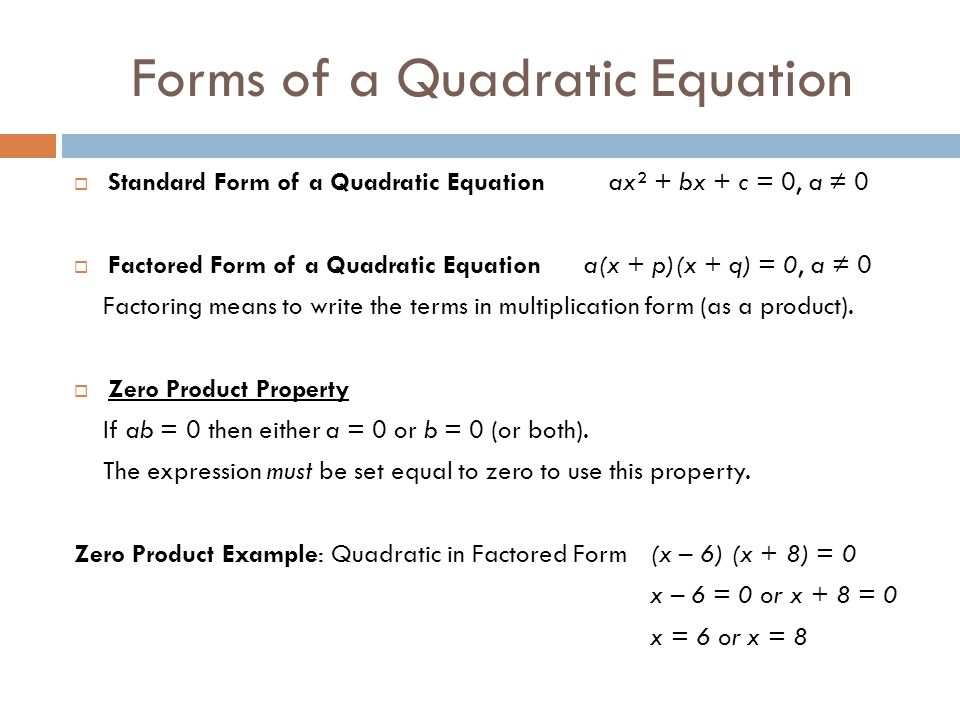
General Properties Of Quadratic Equation Quadratic equation. in mathematics, a quadratic equation (from latin quadratus ' square ') is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as [1] where x represents an unknown value, and a, b, and c represent known numbers, where a ≠ 0. (if a = 0 and b ≠ 0 then the equation is linear, not quadratic.). Example 4: the quad equation 2x 2 9x 7 = 0 has roots α, β. find the quadratic equation having the roots 1 α, and 1 β. solution: method 1: the quadratic equation having roots that are reciprocal to the roots of the equation ax 2 bx c = 0, is cx 2 bx a = 0. the given quadratic equation is 2x 2 9x 7 = 0.
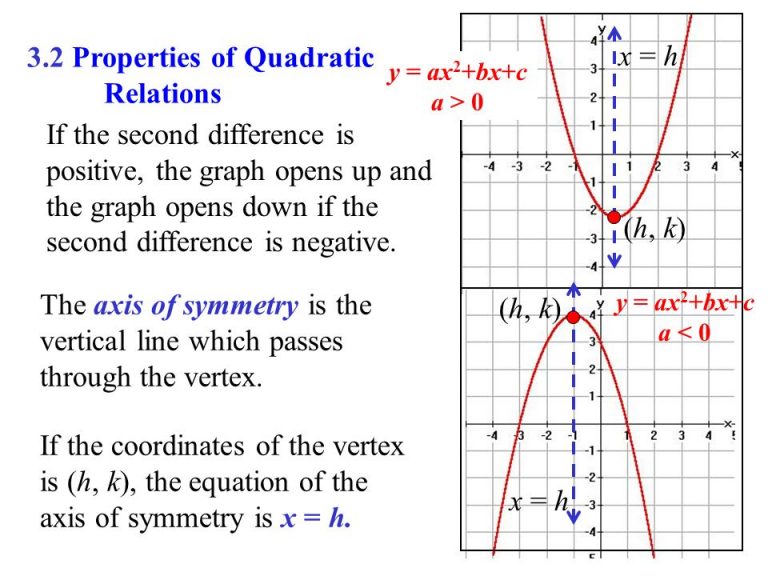
General Properties Of Quadratic Equation Quadratic equation in standard form: ax 2 bx c = 0. quadratic equations can be factored. quadratic formula: x = −b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) 2a. when the discriminant (b2−4ac) is: positive, there are 2 real solutions. zero, there is one real solution. negative, there are 2 complex solutions. We know that the general form of quadratic equation is ax^2 bx c = 0, where a is the co efficient of x^2, b is the coefficient of x, c is the constant term and a ≠ 0, since, if a = 0, then the equation will no longer remain a quadratic. when we are expressing any quadratic equation in the form of ax^2 bx c =0, we have in the left side. For a quadratic equation of the form \(y = k{(x a)^2} b\), the following diagram shows the main properties: if k > 0, the vertex is a minimum turning point if k < 0, the vertex is a maximum. Given a quadratic equation that cannot be factored, and with a = 1, first add or subtract the constant term to the right sign of the equal sign. x2 4x 1 = 0 x2 4x = − 1 multiply the b term by 1 2 and square it. 1 2(4) = 2 22 = 4 add (1 2)2 to both sides of the equal sign and simplify the right side.

General Properties Of Quadratic Equation For a quadratic equation of the form \(y = k{(x a)^2} b\), the following diagram shows the main properties: if k > 0, the vertex is a minimum turning point if k < 0, the vertex is a maximum. Given a quadratic equation that cannot be factored, and with a = 1, first add or subtract the constant term to the right sign of the equal sign. x2 4x 1 = 0 x2 4x = − 1 multiply the b term by 1 2 and square it. 1 2(4) = 2 22 = 4 add (1 2)2 to both sides of the equal sign and simplify the right side. A quadratic function is of the general form: f (x)=ax^2 bx c f (x) = ax2 bx c where a a, b b, and c c are constants and x x is the independent variable. the constants b b and c c can take any finite value, and a a can take any finite value other than 0 0. a quadratic equation is a specific case of a quadratic function, with the function set. Step 2. factorize ax^2 bx c ax2 bx c into two linear factors. step 3. put each linear factor equal to 0 0 (to apply the zero product rule). step 4. solve these linear equations and get two roots of the given quadratic equation. solve x^2 x 6 =0 x2 − x−6 = 0 by the method of factoring.

Comments are closed.