Functions Of Lipids Definition Classification Examples
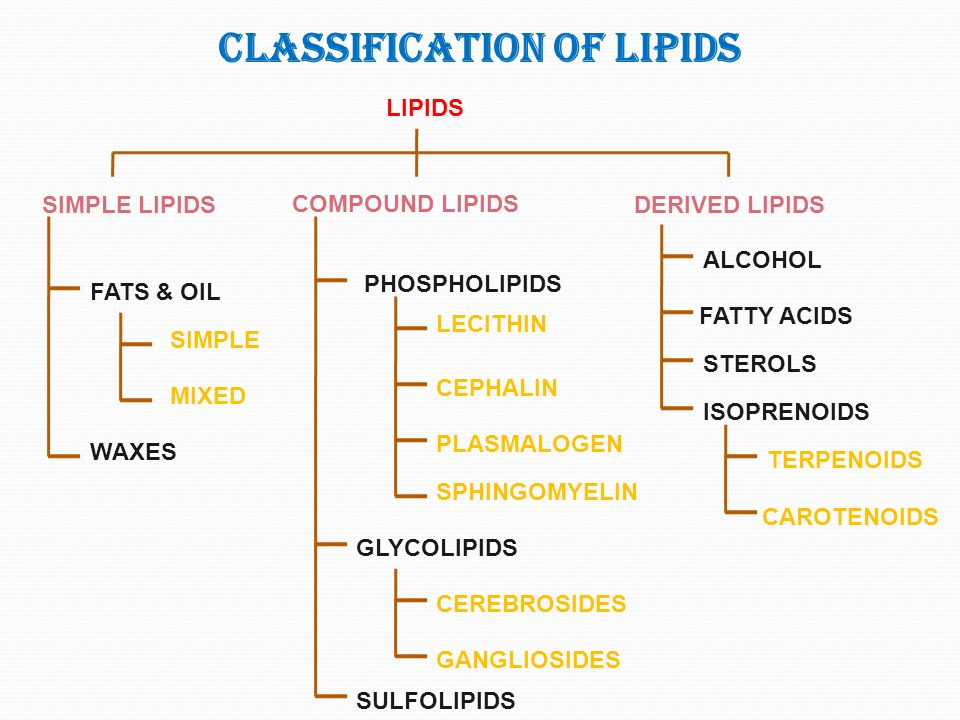
Functions Of Lipids Definition Classification Examples Recent news. lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. one type of lipid, the triglycerides, is sequestered as fat in adipose cells, which serve as the energy storage depot for organisms and. Classification of lipids. lipids can be classified according to their hydrolysis products and according to similarities in their molecular structures. three major subclasses are recognized: 1. simple lipids (a) fats and oils which yield fatty acids and glycerol upon hydrolysis. (b) waxes, which yield fatty acids and long chain alcohols upon.

1 Lipids Definition Classification Functions Lipid Chemistry 1 Lipid: definition, classification, examples, and 7 reliable function. lipid is the fatty acids and their derivatives, and substances related biosynthetically or functionality to these compounds. lipids are organic molecules with oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen atoms that serve as the building blocks for the structure and function of living cells. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body. lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains. lipids are energy rich organic molecules, which provide energy for different life processes. lipids are a class of compounds characterised by their solubility in nonpolar. Lipids comprise a group of compounds such as fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms. both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess lipids, which play many important roles biologically, such as membrane formation, protection, insulation, energy storage, cell division and more. in medicine, lipids refer to blood fats. Lipids, by definition, are a heterogeneous group of organic compounds. these compounds are characterized by their insolubility in water and solubility in non polar organic solvents. therefore, they can be distinctly recognized from many other organic compounds due to this particular trait. in the realm of biology, lipids have a broad presence.

Comments are closed.