Frontiers The Gut Brain Axis How Microbiota And Host Inflammasome
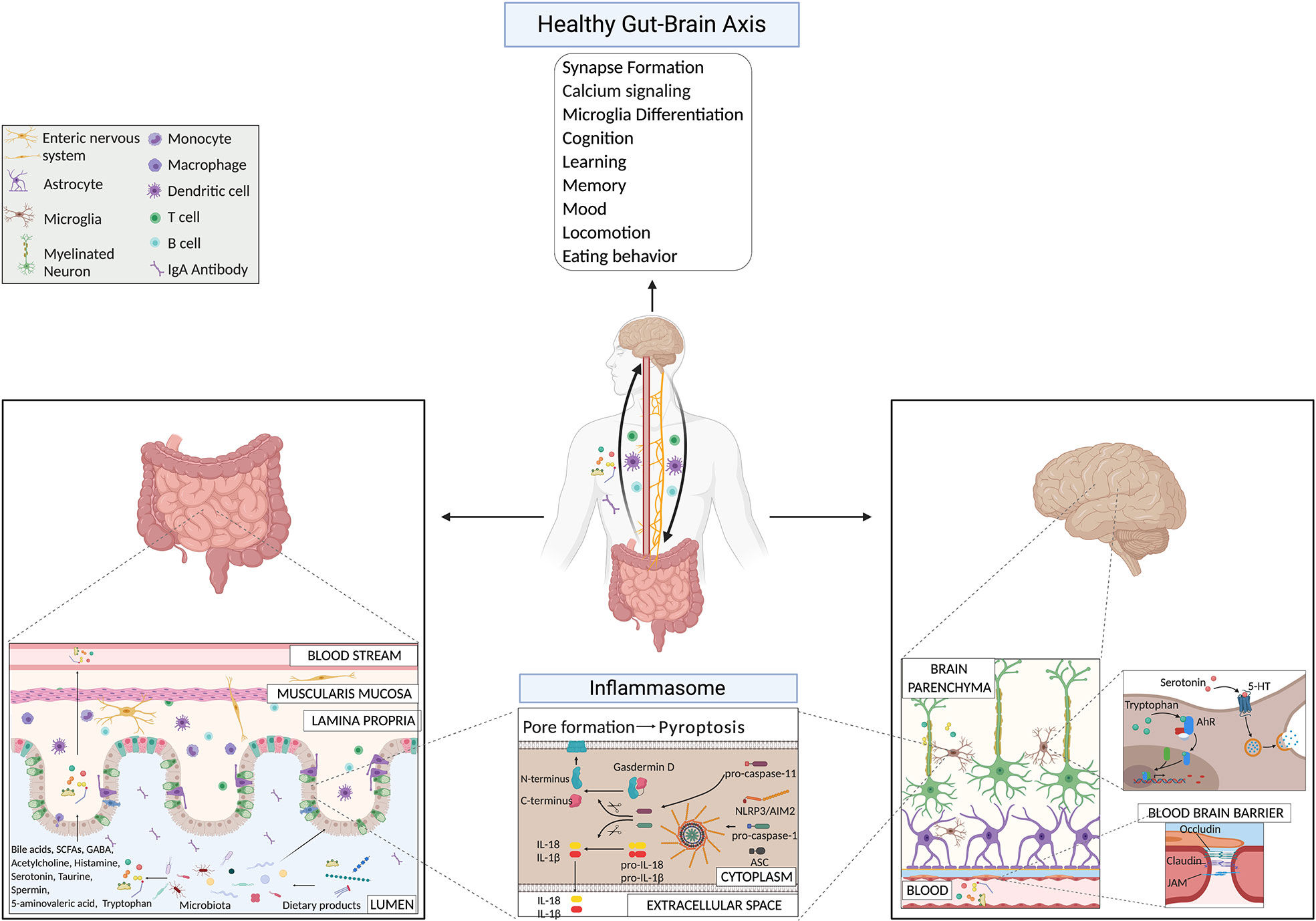
Frontiers The Gut Brain Axis How Microbiota And Host Inflammasome The gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology andrina rutsch johan b. kantsjö francesca ronchi * maurice müller laboratories, department of biomedical research, universitätsklinik für viszerale chirurgie und medizin inselspital, university of berne, berne, switzerland. The inflammasome complex assembles upon cell activation due to exposure to microbes, danger signals, or stress and lead to the production of pro inflammatory cytokines (interleukin 1β and interleukin 18) and to pyroptosis. evidences suggest that there is a reciprocal influence of microbiota and inflammasome activation in the brain.
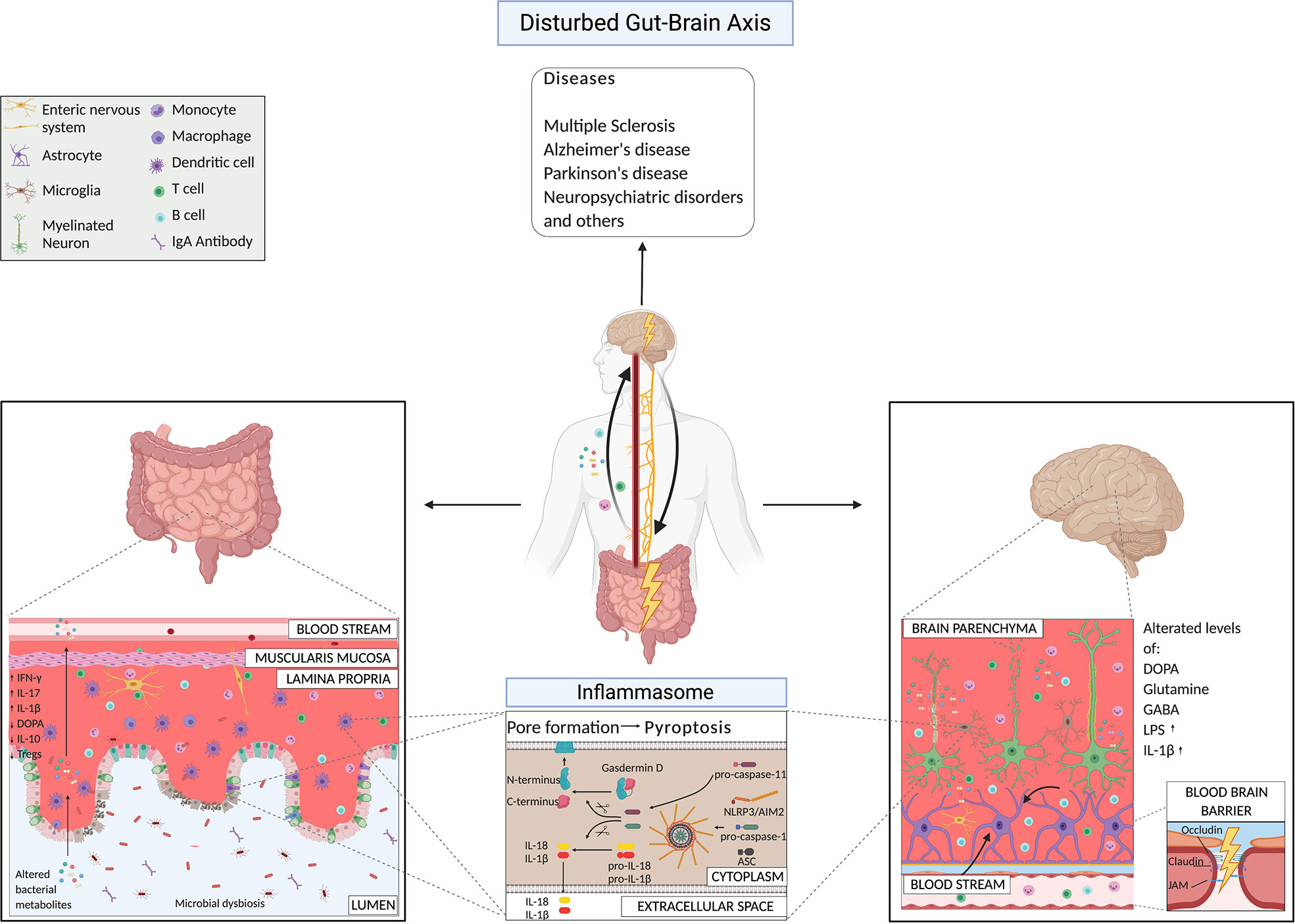
Frontiers The Gut Brain Axis How Microbiota And Host Inflammasome The communication between the cns, the intestine, and the microbiota happens through the so called gut brain axis (gba), a complex bidirectional communication network between the intestine and the cns (10, 48). this axis involves different pathways such as the autonomic and enteric nervous system, the endocrine system, the hypothalamic. The human microbiota has a fundamental role in host physiology and pathology. gut microbial alteration, also known as dysbiosis, is a condition associated not only with gastrointestinal disorders. Considering the crucial role of gut microbiota in maintaining organ and system homeostasis, the concept of “microbiota gut brain (mgb) axis” has also emerged. more and more evidence emphasizes the role of the mgb axis in regulating brain and intestinal function, and its correlation with inflammatory and infective diseases has also been received attention ( asadi et al., 2022 ). Doi: 10.3389 fimmu.2020.604179 corpus id: 228076636; the gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology @article{rutsch2020thega, title={the gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology}, author={andrina rutsch and johan b. kantsj{\"o} and francesca ronchi}, journal={frontiers in immunology}, year.
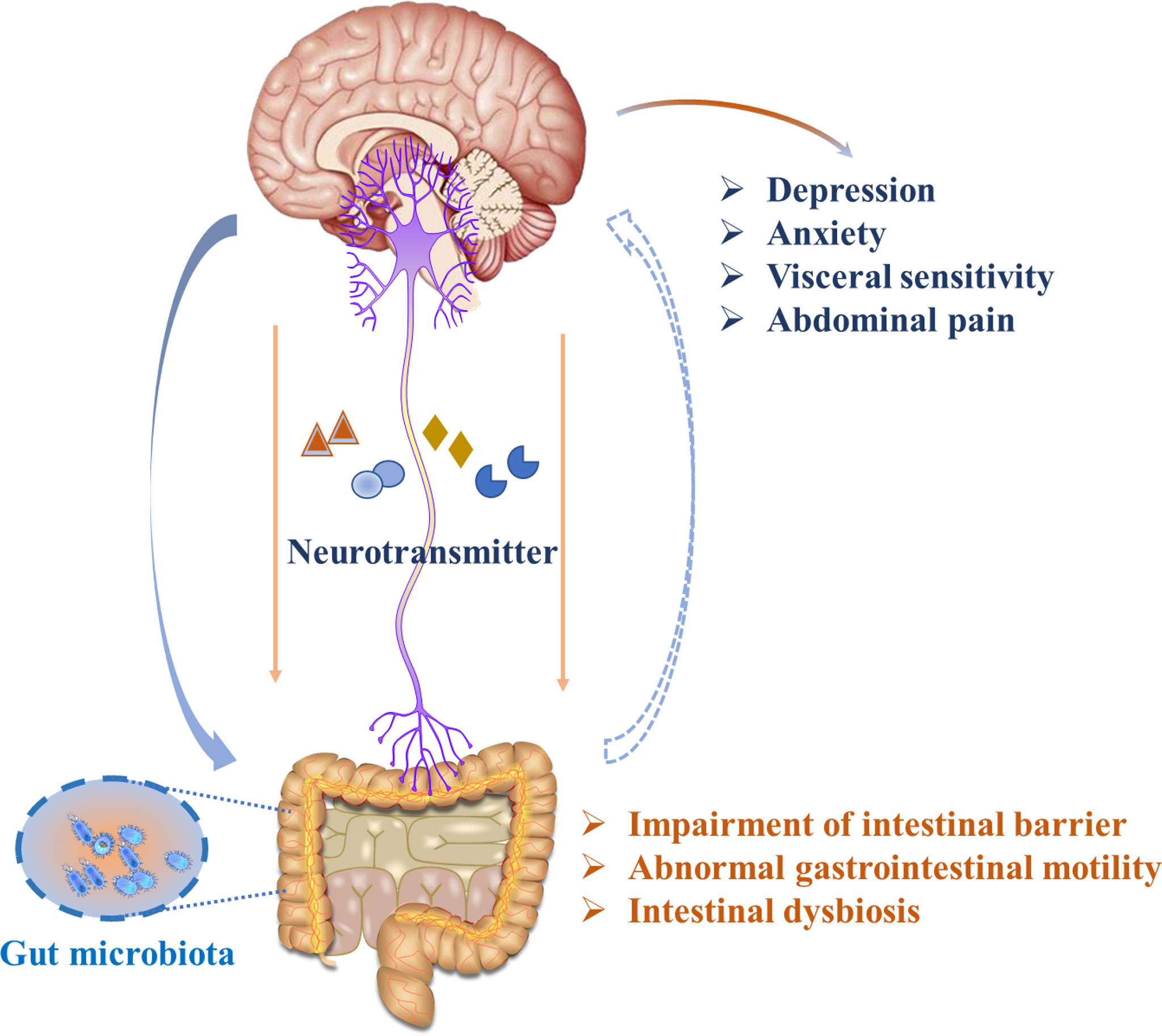
Frontiers Neurotransmitter And Intestinal Interactions Focus On The Considering the crucial role of gut microbiota in maintaining organ and system homeostasis, the concept of “microbiota gut brain (mgb) axis” has also emerged. more and more evidence emphasizes the role of the mgb axis in regulating brain and intestinal function, and its correlation with inflammatory and infective diseases has also been received attention ( asadi et al., 2022 ). Doi: 10.3389 fimmu.2020.604179 corpus id: 228076636; the gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology @article{rutsch2020thega, title={the gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology}, author={andrina rutsch and johan b. kantsj{\"o} and francesca ronchi}, journal={frontiers in immunology}, year. The gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. rutsch a, kantsjö jb, ronchi f. front immunol, 11:604179, 10 dec 2020 cited by: 38 articles | pmid: 33362788 | pmcid: pmc7758428. review free to read & use. The human microbiota has a fundamental role in host physiology and pathology. gut microbial alteration, also known as dysbiosis, is a condition associated the directory of open access journals.

Frontiers The Gut Brain Axis How Microbiota And Host 44 Off The gut brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. rutsch a, kantsjö jb, ronchi f. front immunol, 11:604179, 10 dec 2020 cited by: 38 articles | pmid: 33362788 | pmcid: pmc7758428. review free to read & use. The human microbiota has a fundamental role in host physiology and pathology. gut microbial alteration, also known as dysbiosis, is a condition associated the directory of open access journals.

Comments are closed.