Frontiers Fault Identification Classification And Localization In
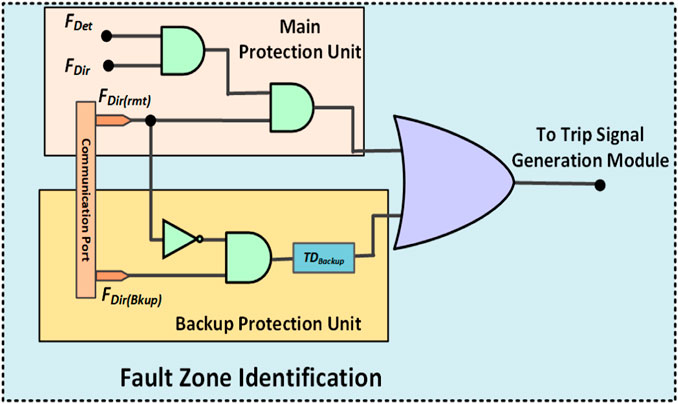
Frontiers Fault Identification Classification And Localization In A relevant trip signal is generated after receiving the fault occurrence, fault phase, and fault zone information from the fault detection and classification unit and fault zone identification unit. the generated trip signal is then used to operate the associated breaker in case of the occurrence of a forward fault within the zone of a relay. Observation based event detection, classification, and localization using real world data are usually challenging because labeled data is often lacking. such data inadequacy cannot support training of deep neural networks. one solution is use of data augmentation by generating an ensemble simulation based training data set.
Frontiers Image Recognitionвђ Based Identification Of Multifractal Keywords: deep learning, insulator, localization recognition, fault diagnosis, complex background, small objects. citation: zhang z, cai d and zhang z (2022) review on online operation insulator identification and fault diagnosis based on uav patrol images and deep learning algorithms. front. energy res. 10:912453. doi: 10.3389 fenrg.2022.912453. The reliable operation of power transmission networks depends on the timely detection and localization of faults. fault classification and localization in electricity transmission networks can be challenging because of the complicated and dynamic nature of the system. in recent years, a variety of machine learning (ml) and deep learning algorithms (dl) have found applications in the. Distributed energy generation increases the need for smart grid monitoring, protection, and control. localization, classification, and fault detection are essential for addressing any problems immediately and resuming the smart grid as soon as possible. simultaneously, the capacity to swiftly identify smart grid issues utilizing sensor data and easily accessible frequency and voltage data from. This manuscript addresses the critical challenge of fault classification and localization within smart distribution networks, exacerbated by the complex integration of distributed energy resources and the dynamic nature of modern power systems. traditional methods fall short in accurately and efficiently managing these tasks due to their reliance on linear models and manual inspection, which.

Comments are closed.