Frontiers An Update Of The Effects Of Vitamins D And C In Critical
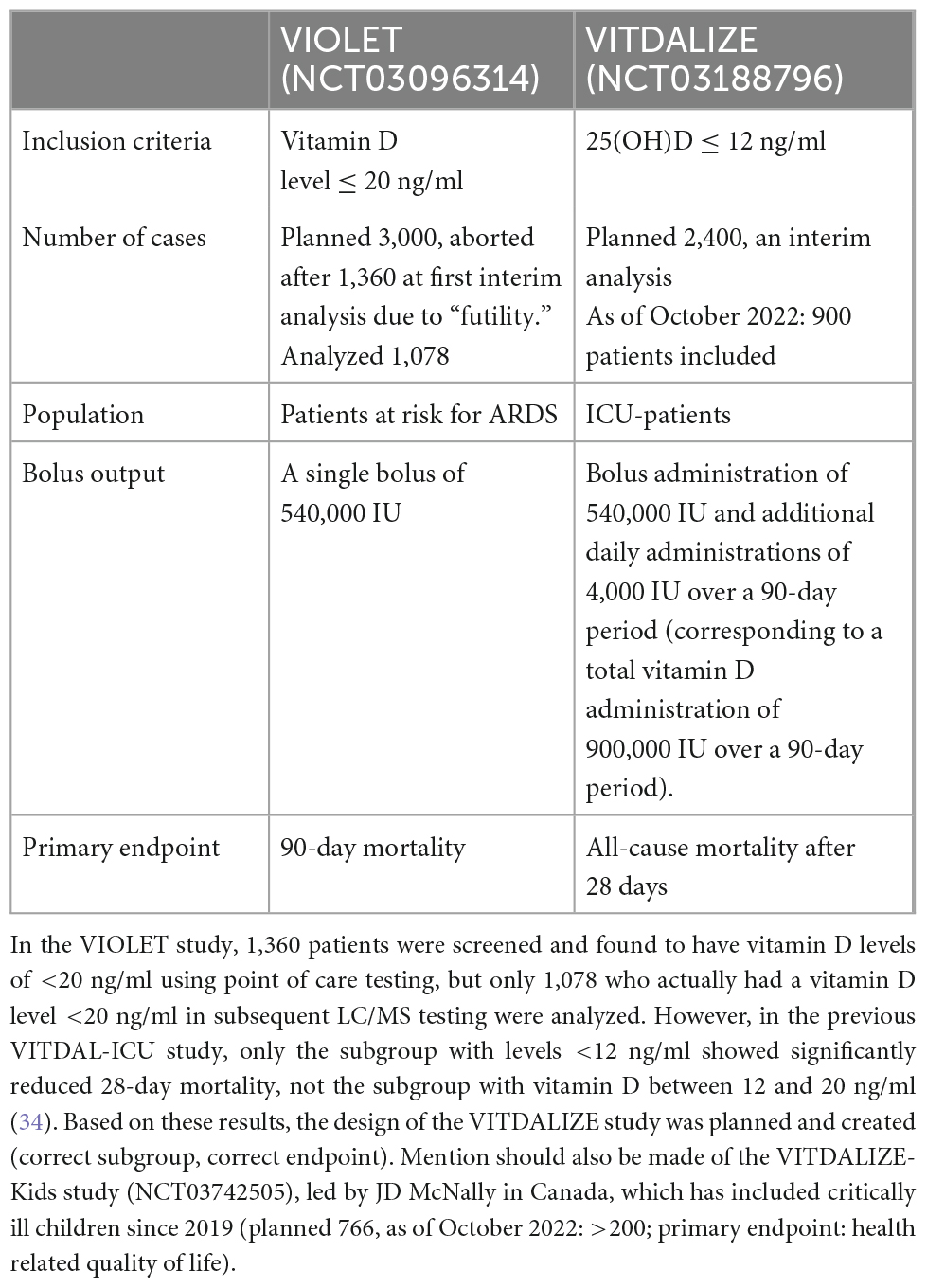
Frontiers An Update Of The Effects Of Vitamins D And C In Critical An update of the effects of vitamins d and c in critical illness. aileen hill 1,2* christina starchl 3 ellen dresen 4 christian stoppe 4,5 karin amrein 3*. 1 department of anesthesiology, university hospital rwth aachen, aachen, germany. 2 department of intensive and intermediate care, university hospital rwth aachen, aachen, germany. The supplementations of vitamin d and c represent cost effective and simple interventions with excellent safety profiles. regarding vitamin d, critically ill individuals require a loading dose to improve 25 (oh)d levels within a few days, followed by a daily or weekly maintenance dose, usually higher doses than healthy individuals are needed.
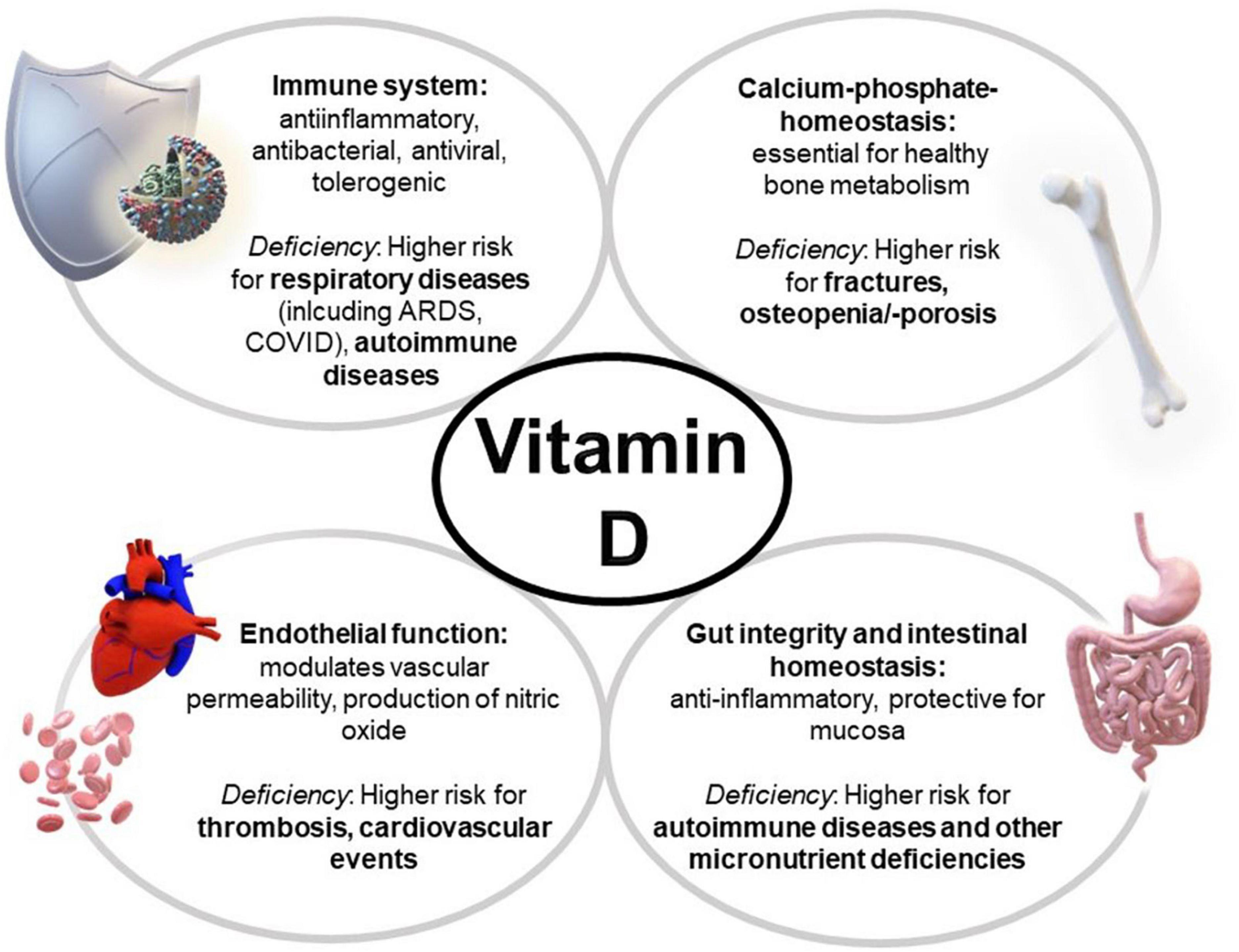
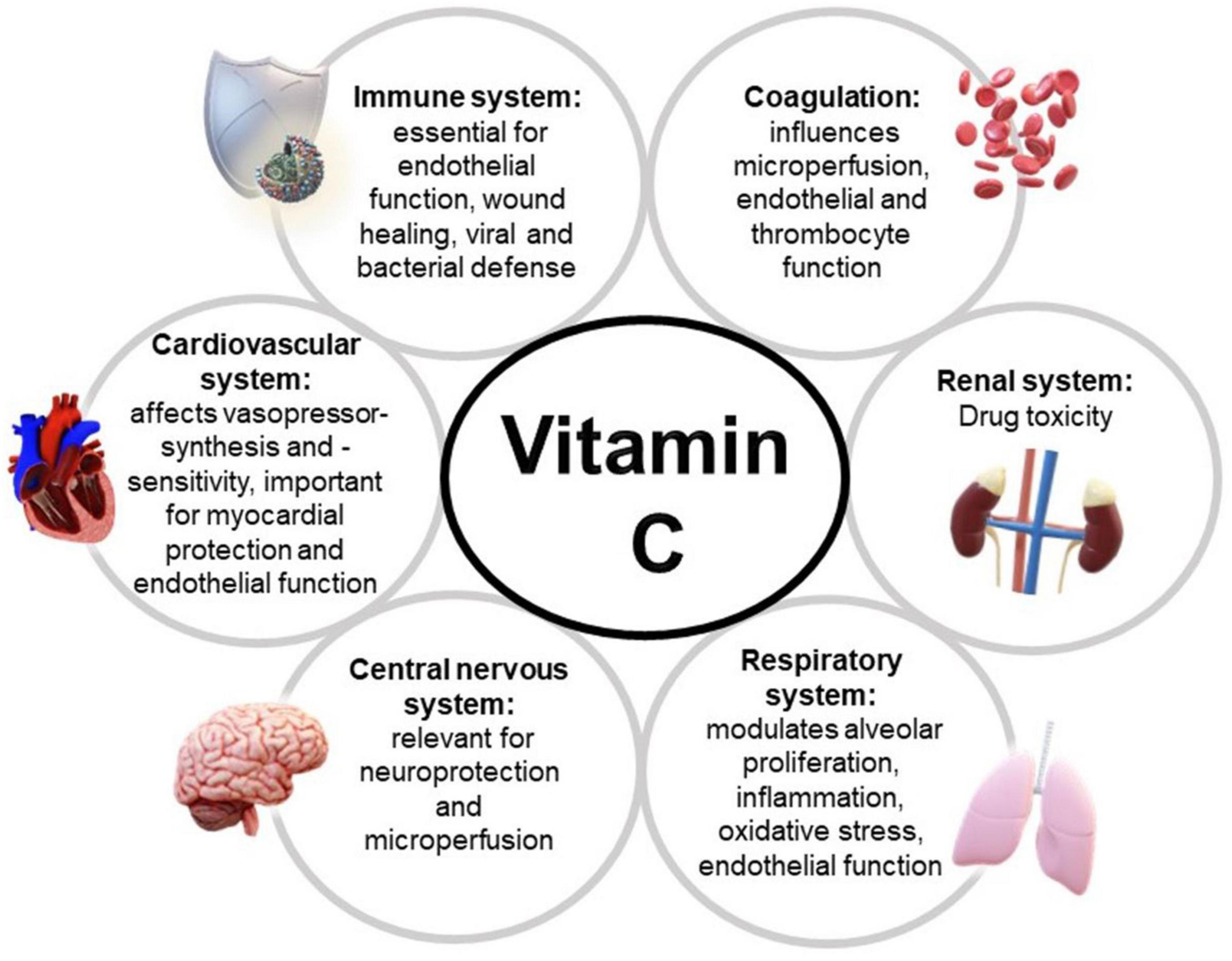
Frontiers An Update Of The Effects Of Vitamins D And C In Critical Vitamin d deficiency is a rapidly modifiable risk factor in critically ill patients. •. the 25 (oh)d level is a relatively stable and now readily available laboratory value after the hyperacute phase of acute illness outside the initial phase of major surgery that reliably detects vitamin d deficiency (<20 ng ml). •. For vitamin c, dosages of 100–200 mg d are recommended for patients receiving parenteral nutrition, but needs may be as high as 2–3 g d in acutely ill patients. Vitamin d, a group of fat soluble vitamins, plays a critical part in the regulation of bone metabolism and extraskeletal pleiotropic processes, such as immunomodulatory, antimicrobial, and cardiovascular (1, 2). vitamin d deficiency is relevant to various disorders, including infections, diabetes, myocardial infarction, and autoimmune disease. Vitamin d with the effects of immunomodulation and anti microbes may be an optimal agent to prevent sepsis. vitamin d deficiency is common in critically ill patients with severe infection and is strongly associated with increased mortality (14, 16). vitamin d deficiency is an independent risk factor for sepsis, and higher 25 hydroxyvitamin d.
Frontiers An Update Of The Effects Of Vitamins D And C In Critical Vitamin d, a group of fat soluble vitamins, plays a critical part in the regulation of bone metabolism and extraskeletal pleiotropic processes, such as immunomodulatory, antimicrobial, and cardiovascular (1, 2). vitamin d deficiency is relevant to various disorders, including infections, diabetes, myocardial infarction, and autoimmune disease. Vitamin d with the effects of immunomodulation and anti microbes may be an optimal agent to prevent sepsis. vitamin d deficiency is common in critically ill patients with severe infection and is strongly associated with increased mortality (14, 16). vitamin d deficiency is an independent risk factor for sepsis, and higher 25 hydroxyvitamin d. Vitamin d deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide on falls and fractures–a critical appraisal of the quality of the evidence and an overview of the available guidelines. In vitro studies have shown that 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin d, the active form of vitamin d, has an anti inflammatory effect. recent epidemiological evidence has indicated a significant association between vitamin d deficiency and an increased incidence, or aggravation, of infectious diseases and inflammatory autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid.

Comments are closed.