Free Energy Generation By A Power Plant And Its Subsequent Dissipation

Free Energy Generation By A Power Plant And Its Subsequent Dissipation Download scientific diagram | free energy generation by a power plant and its subsequent dissipation by a dissipative system 1 from publication: sustaining the terrestrial biosphere in the. We have numerically investigated the natural convective heat transfer and entropy generation characteristic inside a wavy solar power plant filled with mwcnt fe3o4 water nanofluid using the finite element method. the simulated flow and temperature fields are investigated in terms of streamline contour, isotherm contour, local nusselt number, average nusselt number, dimensionless total entropy.
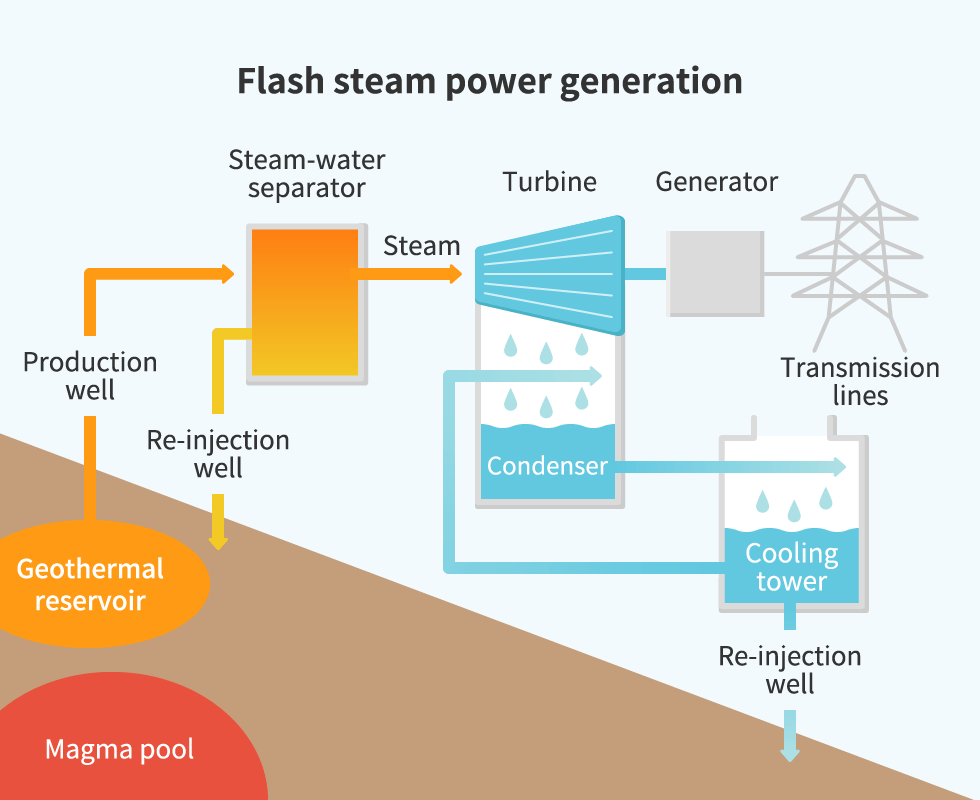
Basic Mechanism Of A Geothermal Power Plant The heat generated, denoted q, is directly proportional to the mass m of the object, specific heat capacity c and change in temperature Δ t. this relationship is given by the formula: q = m ∗ c ∗ Δ t. q is the heat energy generated in joules. m is the mass of the object in kilograms. Specifically, as the number of retention times increases, energy efficiency in recycle can be described in two stages: (i) a proportonal increase in work (j kg −1) with time whilst high power densities are sustained, followed by (ii) a subsequent rapid decline in work produced (fig. 4 a). Free energy generation by a power plant and its subsequent dissipation by a dissipative system 1 generation and dissipation of free energy by the biosphere and its relation to chemical. Review: dynamic power. each charge discharge cycle dissipates total energy e = c v 2 vdd l dd. to compute power, account for switching the circuit at frequency f. typically, output does not switch every cycle, so we scale the power by the probability of a transition α.

Comments are closed.