Food Web Arctic Tundra
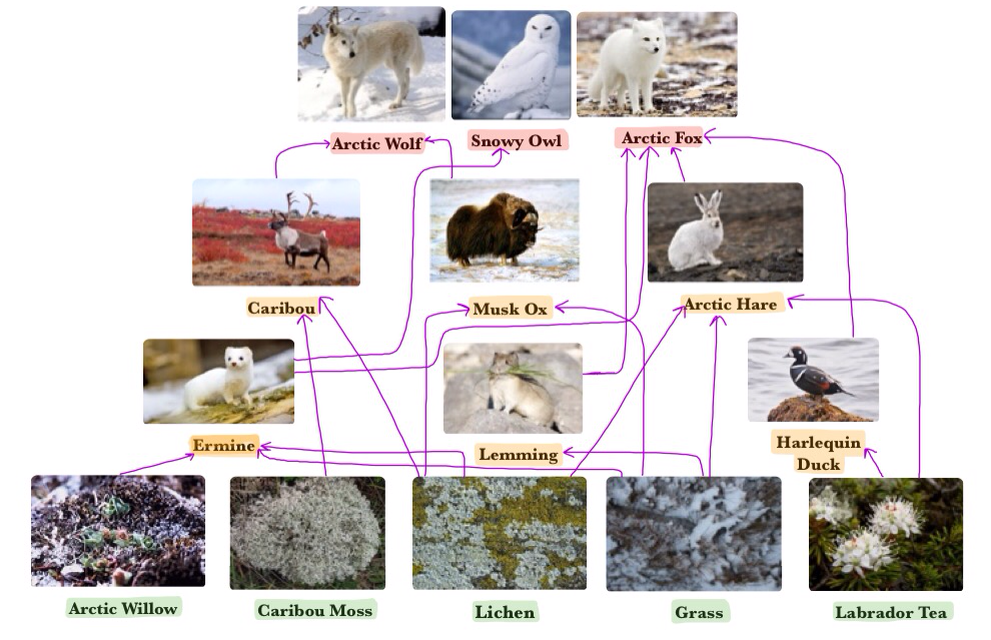
Arctic Food Web Arctic Tundra Learn about the tundra food web, also known as the tundra food chain. arctic tundra food chain. a food chain is a representation of the energy flow through the organisms that live in an. Learn how energy flows in the tundra ecosystem, from producers to decomposers, with examples of organisms and a simple diagram. find out the differences between arctic, antarctic, and alpine tundra and their food chains.
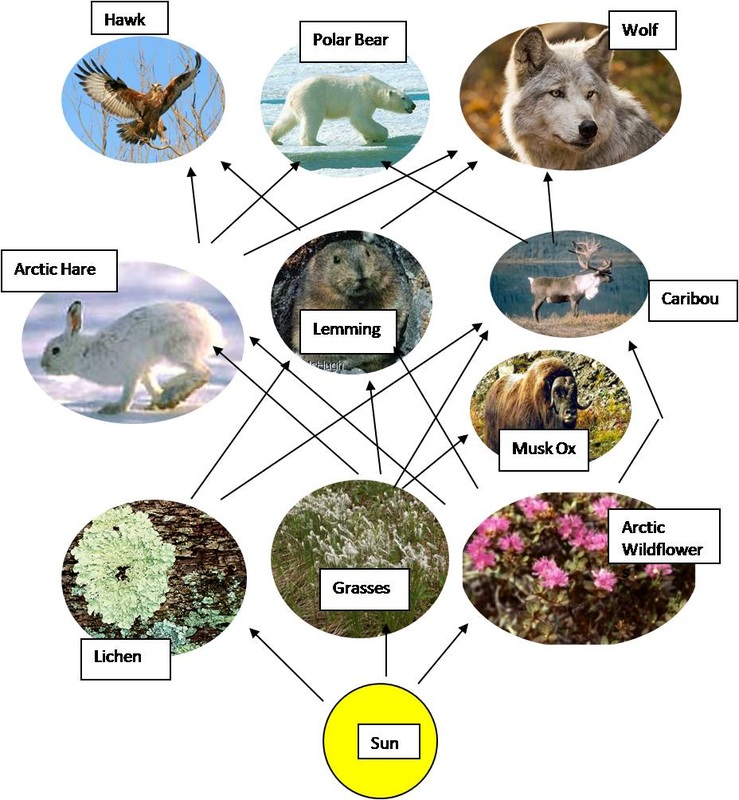
Food Web Interaction The Arctic Tundra Learn how energy flows through the arctic ecosystem, from primary producers to top predators, and how different animals fit into the trophic levels. see examples of food chains and food webs, and play a game to test your knowledge. Top of the arctic tundra food chain. at the top of the arctic food chain are polar bears, grey wolves, and grizzly bears. if these animals no longer existed, the middle tiers of the food chain would become overpopulated, and the lower middle tier would not be able to reproduce fast enough to feed the overpopulated upper middle food chain. This article reviews the evidence and mechanisms of population cycles in arctic tundra species, especially lemmings, and their role in the plant based food web. it also discusses how climate change may affect the dynamics and consequences of these cycles. A team of researchers found that warming temperatures have shifted the diet of animals from green to brown food sources, derived from plants and microbes. this affects the carbon flow and nutrient cycling in the arctic tundra and boreal forests.

Arctic Tundra This article reviews the evidence and mechanisms of population cycles in arctic tundra species, especially lemmings, and their role in the plant based food web. it also discusses how climate change may affect the dynamics and consequences of these cycles. A team of researchers found that warming temperatures have shifted the diet of animals from green to brown food sources, derived from plants and microbes. this affects the carbon flow and nutrient cycling in the arctic tundra and boreal forests. Legagneux, p. et al. disentangling trophic relationships in a high arctic tundra ecosystem through food web modeling. ecology 93, 1707–1716 (2012). This reliance on fungal energy is consistent with studies showing that fungi regulate the coupling of green and brown food webs in boreal forest and arctic tundra ecosystems 17,18,40,41.

Comments are closed.