Food Chains Food Webs Energy Pyramids

Ecosystem Trophic Levels Food Chains Interactions Britannica Arrows on a food chain, or food web, represent the flow of energy. the placement of the arrows in a food chain or food web is very important. the arrows always show the direction of the energy as it is transferred from one organism to another. the flow of energy can also be represented within an energy pyramid. Explore food chains, food webs, energy pyramids, and the power of biodiversity in this ecology video by the amoeba sisters! this video also introduces genera.
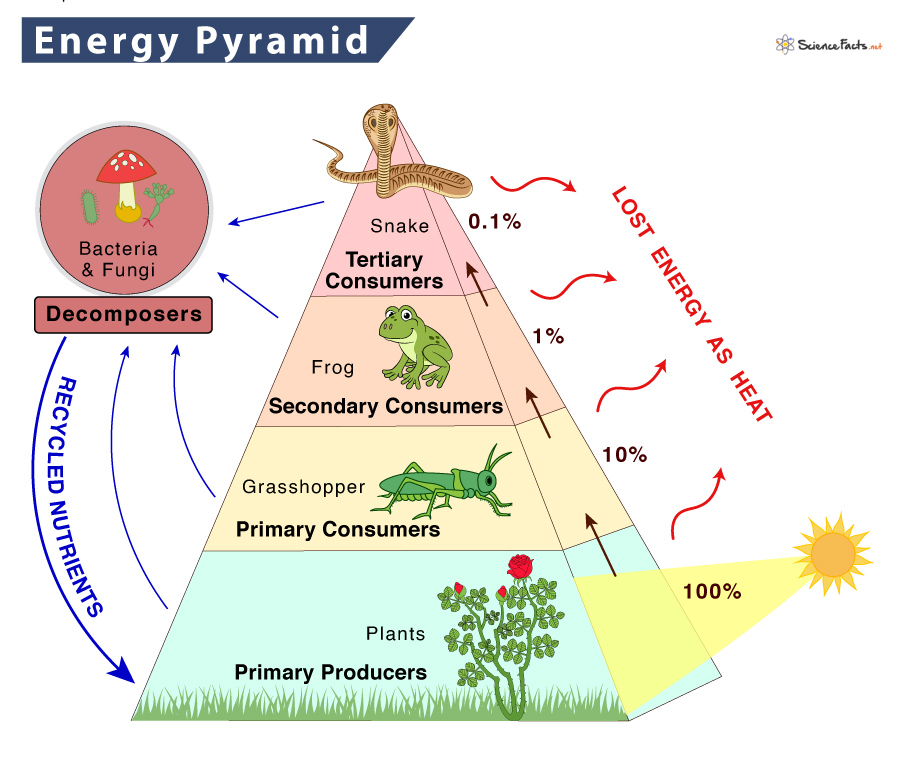
Energy Pyramid вђ Definition Trophic Levels And Example The energy flow takes place via the food chain and food web. during the process of energy flow in the ecosystem, plants being the producers absorb sunlight with the help of the chloroplasts and a part of it is transformed into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis. this energy is stored in various organic products in the plants and. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. To show the flow of energy through ecosystems, food chains are sometimes drawn as energy pyramids. each step of the pyramid represents a different trophic level, starting with primary producers at the bottom. the width of each step represents the rate of energy flow through each trophic level. The pyramid of energy figure 17.1.2.2 silver springs. conversions efficiencies are always much less than 100%. at each link in a food chain, a substantial portion of the sun's energy — originally trapped by a photosynthesizing autotroph is dissipated back to the environment (ultimately as heat).
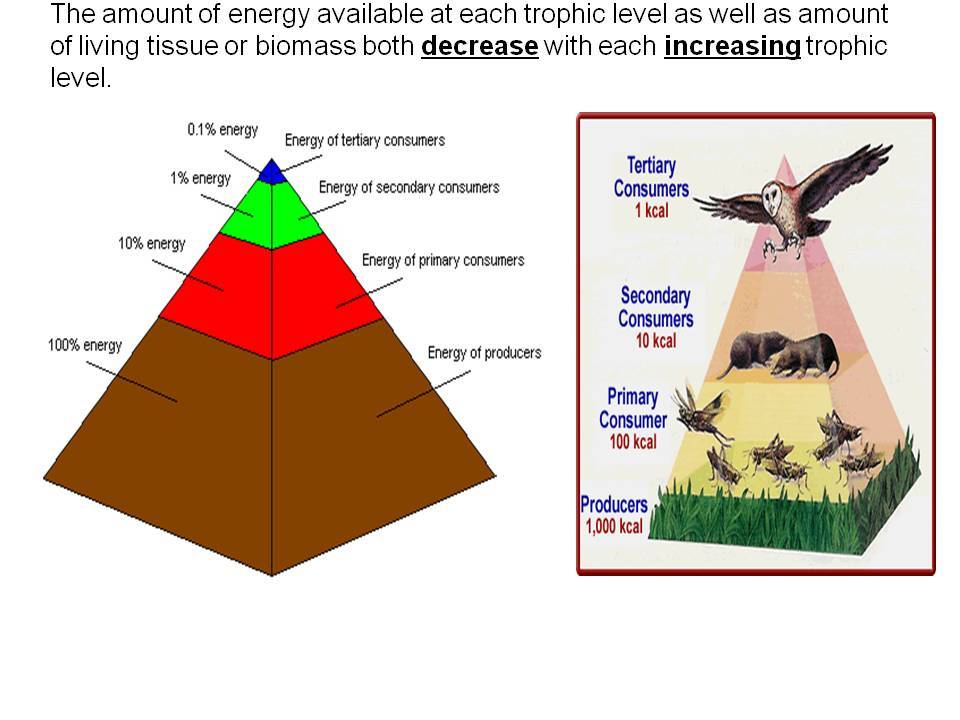
Food Chains Webs Pyramids Ms Blount S Biology Class 5 To show the flow of energy through ecosystems, food chains are sometimes drawn as energy pyramids. each step of the pyramid represents a different trophic level, starting with primary producers at the bottom. the width of each step represents the rate of energy flow through each trophic level. The pyramid of energy figure 17.1.2.2 silver springs. conversions efficiencies are always much less than 100%. at each link in a food chain, a substantial portion of the sun's energy — originally trapped by a photosynthesizing autotroph is dissipated back to the environment (ultimately as heat). A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.
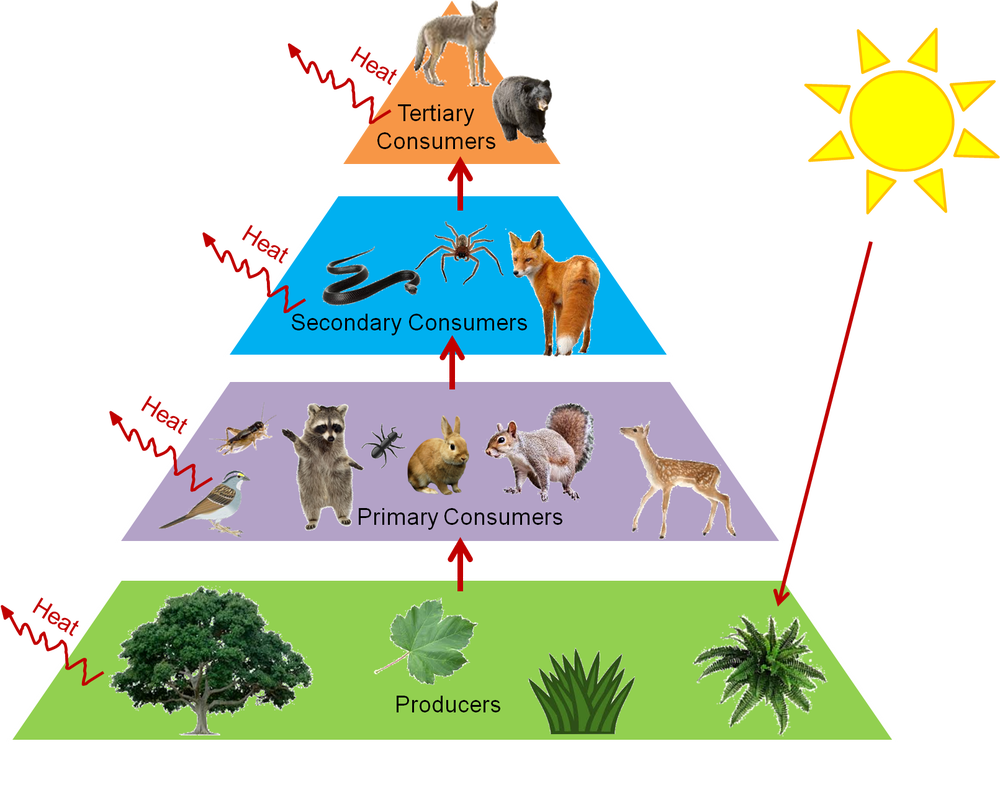
Food Webs And Trophic Levels Katie S Ecology Project A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Food Chain Energy Pyramid 5th Grade Elementary Science 7th Grade

Comments are closed.