First Law Of Thermodynamics
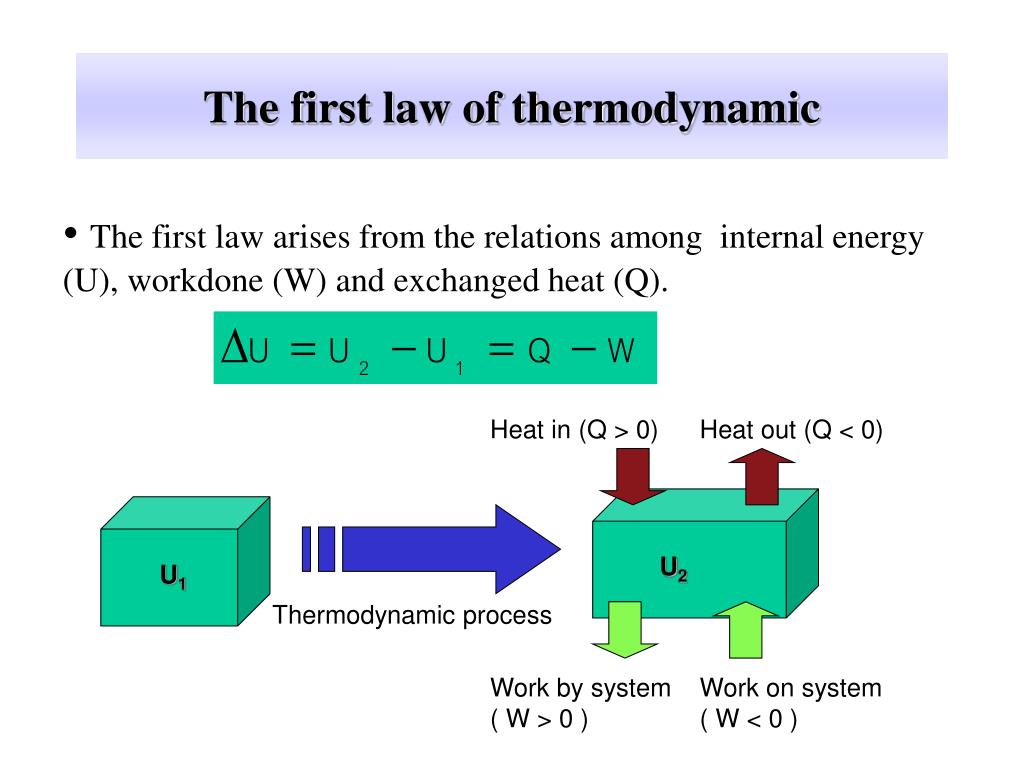
Ppt Chapter 17 The First Law Of Thermodynamics Powerpoint Learn the definition, history and applications of the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be transformed from one form to another. the law also defines the internal energy, heat and work of a system and distinguishes between isolated, closed and open systems. Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat, work, temperature, and energy. the first law of thermodynamics is put into action by considering the flow of energy across the boundary separating a system from its surroundings. consider the classic example of a gas enclosed in a cylinder with a movable piston.

Forms Of Energy In Thermodynamics At Glennis Fluharty Blog Learn the definition, formula and sign conventions of the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy is conserved in any process. see solved examples and faqs on this topic. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q − w. (15.1.1) (15.1.1) Δ u = q − w. here Δu Δ u is the change in internal energy u u of the system. Learn about the four laws of thermodynamics, which define and describe the properties and processes of thermodynamic systems. the first law states the conservation of energy, and the second law states the increase of entropy in natural processes. Learn how the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is conserved and how it applies to heat engines and internal energy. explore the concepts of heat, work, and state functions with examples and equations.
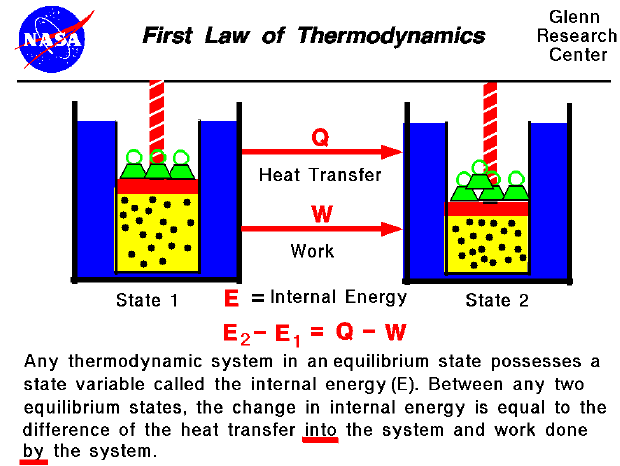
First Law Of Thermodynamics Learn about the four laws of thermodynamics, which define and describe the properties and processes of thermodynamic systems. the first law states the conservation of energy, and the second law states the increase of entropy in natural processes. Learn how the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is conserved and how it applies to heat engines and internal energy. explore the concepts of heat, work, and state functions with examples and equations. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a closed system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q − w. Δ u = q − w. 12.6. Learn the definition, formula and examples of the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy is conserved in any process involving heat and work. explore the concepts of thermodynamic system, heat capacity, and natural variables with interactive problems and solutions.
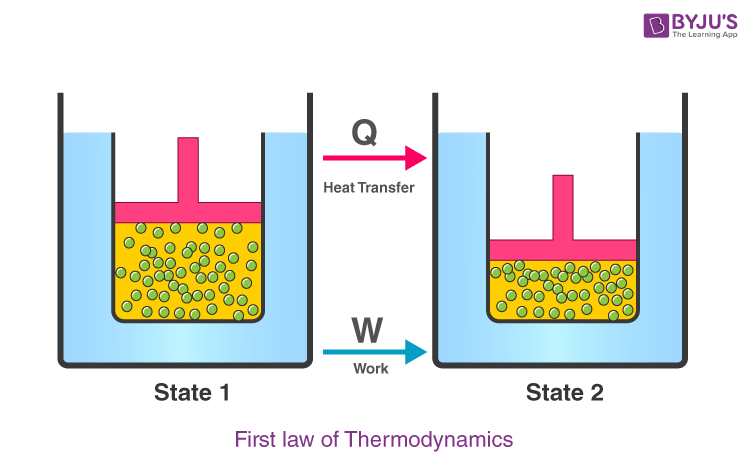
First Law Of Thermodynamics Equation Statement Examples The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a closed system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q − w. Δ u = q − w. 12.6. Learn the definition, formula and examples of the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy is conserved in any process involving heat and work. explore the concepts of thermodynamic system, heat capacity, and natural variables with interactive problems and solutions.

Comments are closed.