Figure 1 From The Role Of Gut Microbiome In Modulating Response To

Figure 1 From The Role Of Gut Microbiome In Modulating Response To Figure 1 the role of gut microbiome in regulating response to icpi. right: gut microbiome and icpi response. enrichment of certain gut bacteria are associated with improvement in response (faecalibacterium, bifidobacterium and lactobacillus sp) or worse response (bacteroides sp) to icpis. possible mechanisms of icpi response modulation include. Although the immune modulating properties of the human gut bacterial ecosystem are yet to be fully elucidated, there has been growing interest in evaluating the role of the gut microbiome in shaping the therapeutic response to cancer immunotherapy. considerable research efforts are currently directed to utilizing metagenomic and metabolic.
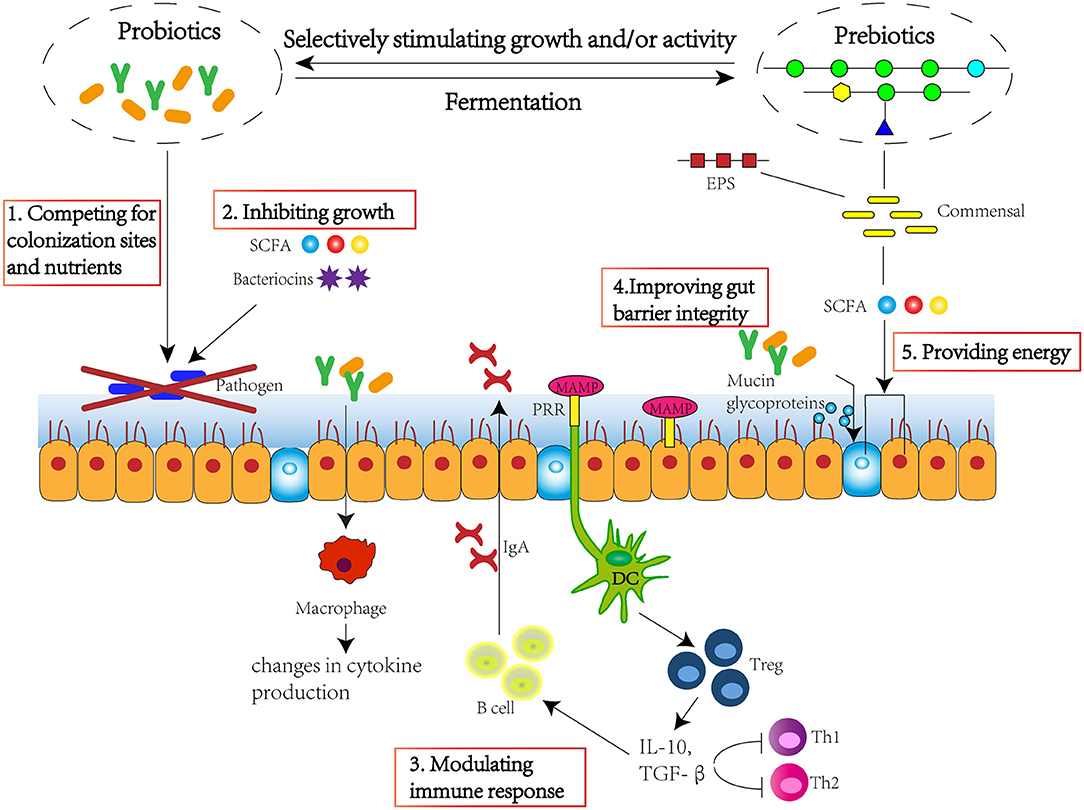
Frontiers Modulation Of Gut Microbiota And Immune System By Key emerging data supporting the role of gut microbiome in regulating response to icpis in cancer are summarized and highlighted. immunotherapy has led to a paradigm shift in the treatment of several cancers. there have been significant efforts to identify biomarkers that can predict response and toxicities related to immune checkpoint inhibitor (icpi) therapy. despite these advances, it has. The role of gut microbiome in regulating response to icpi. right: gut microbiome and icpi response. enrichment of certain gut bacteria are associated with improvement in response (faecalibacterium. Gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeutic responses associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) in preclinical models and patient cohorts. this evidence hints. Figure 2. gut microbiota modulation improves the efficiency of cancer immunotherapy. different strategies can be used to regulate the gut microbiome and can be used as interventional measures to improve the ef ciency of cancer immunotherapy. i.e., fi. fmt in combination with checkpoint inhibitors are able to reprogramme the tumor.

The Gut Microbiota Modulates The Intestinal Immune Response The Gut Gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized for its influence on a diverse array of human diseases including cancer, and may also influence the outcome of cancer therapies. a prime example is seen in immunotherapy, for which gut microbes determine the therapeutic responses associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) in preclinical models and patient cohorts. this evidence hints. Figure 2. gut microbiota modulation improves the efficiency of cancer immunotherapy. different strategies can be used to regulate the gut microbiome and can be used as interventional measures to improve the ef ciency of cancer immunotherapy. i.e., fi. fmt in combination with checkpoint inhibitors are able to reprogramme the tumor. This systematic literature review and meta analysis provide an overview of the critical role of gut microbiota in modulating the efficacy of immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. gut microbes influence host immune responses through multiple mechanisms including modulation of immune cell activity, metabolite action, and immune tolerance. Recent research has highlighted the benefits of certain prebiotics in enhancing the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy by modulating the metabolism of gut microbes. 111 one major example is inulin, which can improve response of t cells and enhance anti pd 1 efficacy by regulating the gut microbiome. 112, 113 similarly, ginseng polysaccharides.

Gut Microbiome In Modulating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ebiomedicine This systematic literature review and meta analysis provide an overview of the critical role of gut microbiota in modulating the efficacy of immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. gut microbes influence host immune responses through multiple mechanisms including modulation of immune cell activity, metabolite action, and immune tolerance. Recent research has highlighted the benefits of certain prebiotics in enhancing the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy by modulating the metabolism of gut microbes. 111 one major example is inulin, which can improve response of t cells and enhance anti pd 1 efficacy by regulating the gut microbiome. 112, 113 similarly, ginseng polysaccharides.

Comments are closed.