Fault Locating With Traveling Waves

Fault Locating With Traveling Waves Youtube The double ended traveling wave method precisely measures the first traveling wave arrival times at both line terminals and uses time synchronization between the two relays to calculate the fault location. double ended traveling wave fault locating can be applied to two terminal lines, including overhead lines, cable lines, and hybrid lines. In type d tw fault locating, the required wave arrival times are measured with a common time reference and are exchanged in order to calculate the fault location as follows: 1. t t2 l r . where: s the line length.tl is the tw arrival time at l.tr is the tw a.

Introduction To Qualitrolтащs юааtravellingюаб юааwaveюаб юааfaultюаб юааlocatorюаб Qualitrol Corp Traveling wave fault locating technology calculates the locations of temporary and permanent faults by measuring the arrival times of the naturally occurring traveling waves caused by a transmission line fault. accurately detecting these waves requires ultra high resolution monitoring, and locating is accurate to within one tower span (±300 m). Faults on overhead transmission lines cause transients that travel at the speed of light and propagate along the power line as traveling waves (tws). this paper provides an overview of tws and tw fault locators. it explains the physics, reviews the theory of tws, explains the foundations of various types of tw fault locators, and provides an in depth discussion on a number of tw fault locating. This paper reviews traveling wave based fault localization methods, including the traditional single ended and the double ended methods, and a most recent one. the first method relies on local measurements only while the second one relies on measurements from both ends. both methods require the information of line length and traveling wave propagation speed. to determine the speed, an. Fault location in the power grid is done in three ways; impedance based methods [1, 2], traveling wave based fault location (twfl) [3 5], and artificial intelligence based methods [6, 7]. the impedance based method use power frequency components of voltages and currents while the traveling wave based methods adopt high frequency transient.

Figure 1 From Fault Location On Transmission Lines Based On Travelling This paper reviews traveling wave based fault localization methods, including the traditional single ended and the double ended methods, and a most recent one. the first method relies on local measurements only while the second one relies on measurements from both ends. both methods require the information of line length and traveling wave propagation speed. to determine the speed, an. Fault location in the power grid is done in three ways; impedance based methods [1, 2], traveling wave based fault location (twfl) [3 5], and artificial intelligence based methods [6, 7]. the impedance based method use power frequency components of voltages and currents while the traveling wave based methods adopt high frequency transient. Basic principles of traveling waves. a fault on a line, which occurs at any time except at the zero crossing of the voltage, generates a traveling wave, which propagates from the fault location to both ends of the line with speed close to the speed of light. the principle is shown in the figure 1 for a simple transmission line when a fault. Radio frequency (rf) breakdown analysis and location are critical for successful development of high gradient traveling wave (tw) accelerators, especially those expected to generate high intensity, high power beams. compared with commonly used schemes involving dedicated devices or complicated techniques, a convenient approach for breakdown locating based on transmission line (tl) theory.
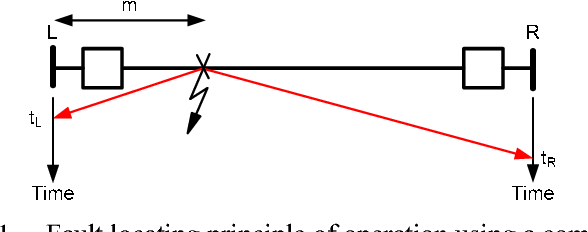
Figure 1 From A New Traveling Wave Fault Locating Algorithm For Line Basic principles of traveling waves. a fault on a line, which occurs at any time except at the zero crossing of the voltage, generates a traveling wave, which propagates from the fault location to both ends of the line with speed close to the speed of light. the principle is shown in the figure 1 for a simple transmission line when a fault. Radio frequency (rf) breakdown analysis and location are critical for successful development of high gradient traveling wave (tw) accelerators, especially those expected to generate high intensity, high power beams. compared with commonly used schemes involving dedicated devices or complicated techniques, a convenient approach for breakdown locating based on transmission line (tl) theory.

Pdf Line Length And Fault Distance Considerations In Traveling Wave

Comments are closed.