Explaining An Electrical Circuit

Different Types Of Circuit Diagram A circuit is an unbroken loop of conductive material that allows charge carriers to flow through continuously without beginning or end. if a circuit is “broken,” that means its conductive elements no longer form a complete path, and continuous charge flow cannot occur in it. the location of a break in a circuit is irrelevant to its. Electric circuit, path for transmitting electric current. an electric circuit includes a device that gives energy to the charged particles constituting the current, such as a battery or a generator; devices that use current, such as lamps, electric motors, or computers; and the connecting wires or transmission lines. two of the basic laws that.

Explaining Electrical Circuits A circuit is a path that starts and stops at the same place, which is exactly what we're doing. click this link to see a simulation of current flowing through a simple circuit. this simulation requires java to run. *benjamin franklin originally wrote that electricity flows from the positive side of a voltage source to the negative side. A basic electrical circuit (diagram) consists of three main components: the source, the load, and the conductors. the battery has two terminals. these terminals are connection points for the two conductors. one terminal is marked with a plus sign ( ) and the other a negative sign (–). these two markings are referred to as polarity markings. Journey of a typical electron. an electric circuit involves the flow of charge in a complete conducting loop. when here is an electric circuit light bulbs light, motors run, and a compass needle placed near a wire in the circuit will undergo a deflection. when there is an electric circuit, a current is said to exist. An electric circuit is a closed loop of conductive material that allows the flow of electrical current. the circuit consists of three main components: a power source, a conductor, and a load. the power source, which can be a battery or a power outlet, provides the energy to the circuit. the conductor, usually made of copper wire, allows the.

Explaining An Electrical Circuit Youtube Journey of a typical electron. an electric circuit involves the flow of charge in a complete conducting loop. when here is an electric circuit light bulbs light, motors run, and a compass needle placed near a wire in the circuit will undergo a deflection. when there is an electric circuit, a current is said to exist. An electric circuit is a closed loop of conductive material that allows the flow of electrical current. the circuit consists of three main components: a power source, a conductor, and a load. the power source, which can be a battery or a power outlet, provides the energy to the circuit. the conductor, usually made of copper wire, allows the. In electrical circuits, resistance works similarly—it's like the narrow part of the pipe, hindering the flow of electric current in a circuit and causing it to slow down. figure 3: explaining resistance with water pipes. resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), hinders the flow of electric current in a circuit, causing it to slow down. The amount of water in the tank is defined as 1 volt and the "narrowness" (resistance to flow) of the hose is defined as 1 ohm. using ohms law, this gives us a flow (current) of 1 amp. using this analogy, let's now look at the tank with the narrow hose. because the hose is narrower, its resistance to flow is higher.

Labeled Diagram Of An Electrical Circuit In electrical circuits, resistance works similarly—it's like the narrow part of the pipe, hindering the flow of electric current in a circuit and causing it to slow down. figure 3: explaining resistance with water pipes. resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), hinders the flow of electric current in a circuit, causing it to slow down. The amount of water in the tank is defined as 1 volt and the "narrowness" (resistance to flow) of the hose is defined as 1 ohm. using ohms law, this gives us a flow (current) of 1 amp. using this analogy, let's now look at the tank with the narrow hose. because the hose is narrower, its resistance to flow is higher.
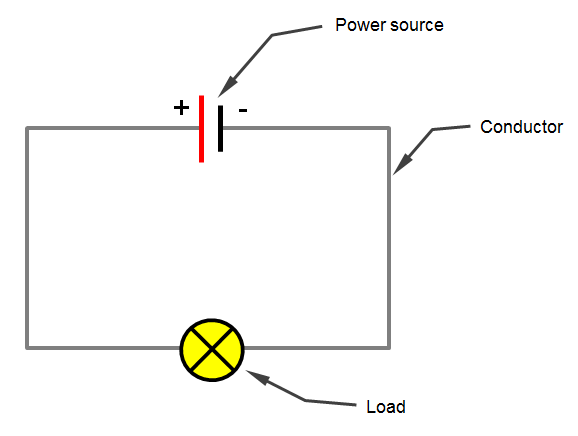
Labeled Diagram Of An Electrical Circuit

Comments are closed.