Example Of Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Ppt Second Law Of Thermodynamics Powerpoint Presentation Free The expansion of balloons serves as a real life example of the principle of the second law of thermodynamics, showcasing how gas molecules move from a more ordered state to a more dispersed, random state. 17. fading of colours. the fading of colours over time is a phenomenon rooted in the principles of thermodynamics. And this process also occurs on its own. thus this is an example of second law of thermodynamics which shows that the entropy of the universe increases due to this spontaneous process. 3) hot coffee cools down automatically. this example is also based on the principle of increase in entropy.
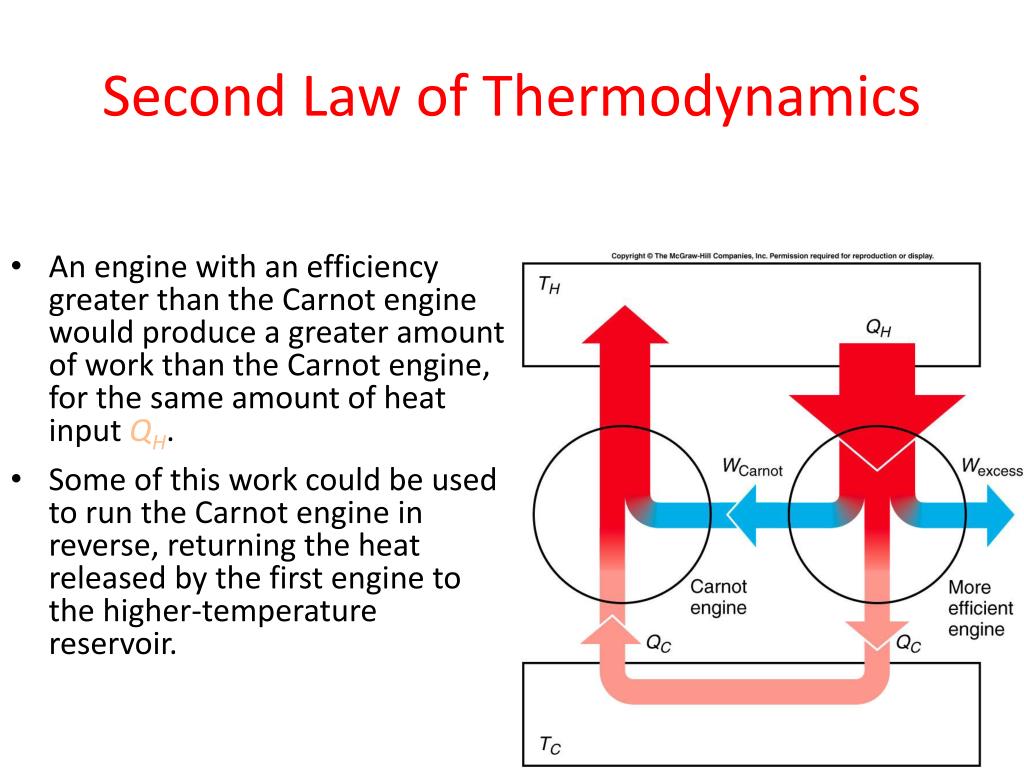
What Is The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Definition Examples The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; it never decreases. an important implication of this law is that heat transfers energy spontaneously from higher to lower temperature objects, but never spontaneously in the reverse direction. The example of a heat engine illustrates one of the many ways in which the second law of thermodynamics can be applied. one way to generalize the example is to consider the heat engine and its heat reservoir as parts of an isolated (or closed) system—i.e., one that does not exchange heat or work with its surroundings. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. it predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. for example, the. Learn the statement, equation, and example of the second law of thermodynamics, which deals with the increase of entropy in natural and spontaneous processes. find out the alternative statements of the second law and their applications to heat engines and refrigerators.

Examples Of Second Law Of Thermodynamics 8 Best Examples The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. it predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. for example, the. Learn the statement, equation, and example of the second law of thermodynamics, which deals with the increase of entropy in natural and spontaneous processes. find out the alternative statements of the second law and their applications to heat engines and refrigerators. The second law of thermodynamics: a law stating that states that the entropy of an isolated system never decreases, because isolated systems spontaneously evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium—the state of maximum entropy. equivalently, perpetual motion machines of the second kind are impossible. heat engine: any device which converts heat. Learn the definition, statements, and applications of the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy never decreases in an isolated system or a cyclic process. explore the carnot engine, the equivalence of clausius' and kelvin's statements, and the implications for the direction of time.

Comments are closed.