Electromagnetic Spectrum And Corresponding Applications Of
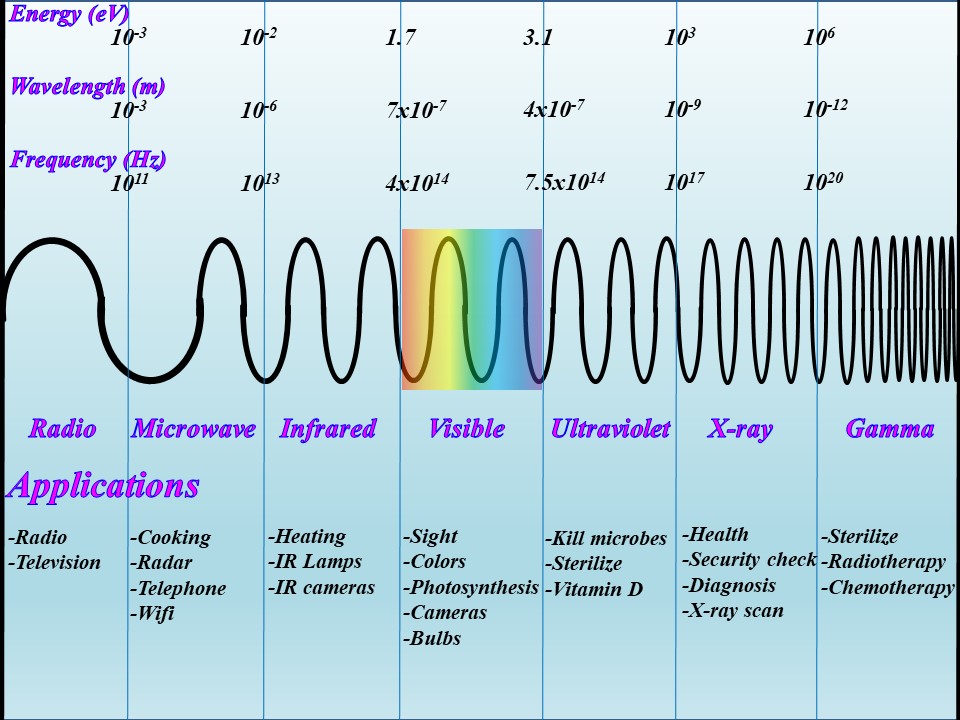
Electromagnetic Spectrum And Corresponding Applications Of The electromagnetic spectrum comprises the span of all electromagnetic radiation and consists of many subranges, commonly referred to as portions, such as visible light or ultraviolet radiation. the various portions bear different names based on differences in behaviour in the emission, transmission, and absorption of the corresponding waves. The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. it covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high end, with no gaps in the frequency range. electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space.

The Spectrum Of Electromagnetic Waves Characteristics And Medical The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. the spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. from low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x rays, and. Radio waves. radio waves are a type of electromagnetic (em) radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light. they have have frequencies from 300 ghz to as low as 3 khz, and corresponding wavelengths from 1 millimeter to 100 kilometers. The characteristics of the various types of electromagnetic waves you will read about below are related to their frequencies and wavelengths. figure 11.5.1: the electromagnetic spectrum, showing the major categories of electromagnetic waves. the range of frequencies and wavelengths is remarkable. the dividing line between some categories is. Electromagnetic spectrum: ultraviolet (uv) light. a scorpion having its picture taken within a uv light. ultraviolet (uv) light is a form of em radiation that lies just beyond the violet end of the visible light spectrum. with a wavelength of ~10 8 m, uv light has unique properties that make it both beneficial and potentially harmful.

The Electromagnetic Spectrum And Corresponding Applications Download The characteristics of the various types of electromagnetic waves you will read about below are related to their frequencies and wavelengths. figure 11.5.1: the electromagnetic spectrum, showing the major categories of electromagnetic waves. the range of frequencies and wavelengths is remarkable. the dividing line between some categories is. Electromagnetic spectrum: ultraviolet (uv) light. a scorpion having its picture taken within a uv light. ultraviolet (uv) light is a form of em radiation that lies just beyond the violet end of the visible light spectrum. with a wavelength of ~10 8 m, uv light has unique properties that make it both beneficial and potentially harmful. Electromagnetic radiation is reflected or absorbed mainly by several gases in the earth's atmosphere, among the most important being water vapor, carbon dioxide, and ozone. some radiation, such as visible light, largely passes (is transmitted) through the atmosphere. these regions of the spectrum with wavelengths that can pass through the. Figure 15.5 shows the section of the em spectrum that includes visible light. the frequencies corresponding to these wavelengths are 4.0 × 10 14 s −1 at the red end to 7.9 × 10 14 s −1 at the violet end. this is a very narrow range, considering that the em spectrum spans about 20 orders of magnitude.
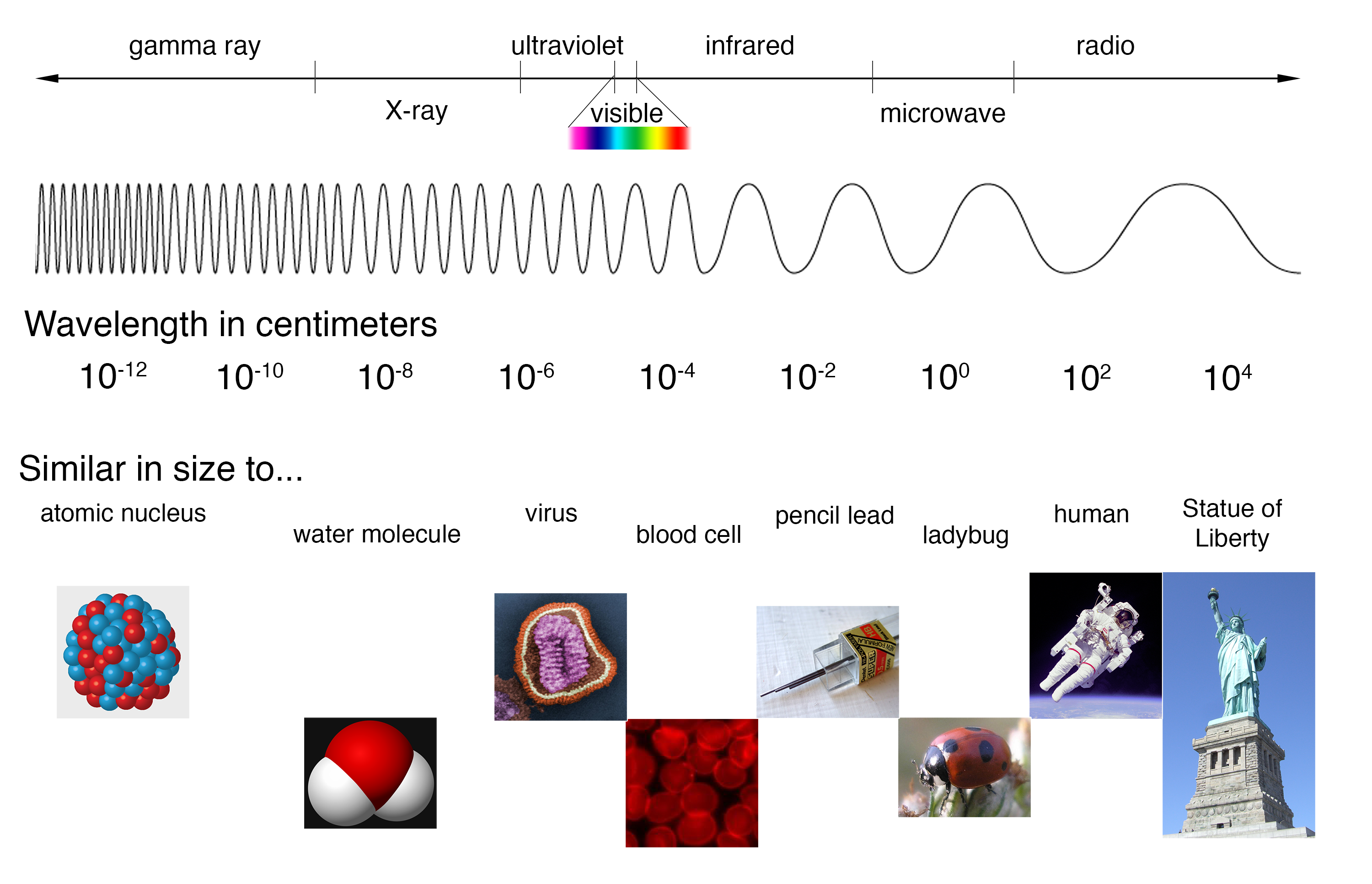
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Images And Photos Finder Electromagnetic radiation is reflected or absorbed mainly by several gases in the earth's atmosphere, among the most important being water vapor, carbon dioxide, and ozone. some radiation, such as visible light, largely passes (is transmitted) through the atmosphere. these regions of the spectrum with wavelengths that can pass through the. Figure 15.5 shows the section of the em spectrum that includes visible light. the frequencies corresponding to these wavelengths are 4.0 × 10 14 s −1 at the red end to 7.9 × 10 14 s −1 at the violet end. this is a very narrow range, considering that the em spectrum spans about 20 orders of magnitude.

Comments are closed.