Dna Structure And Function Of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna
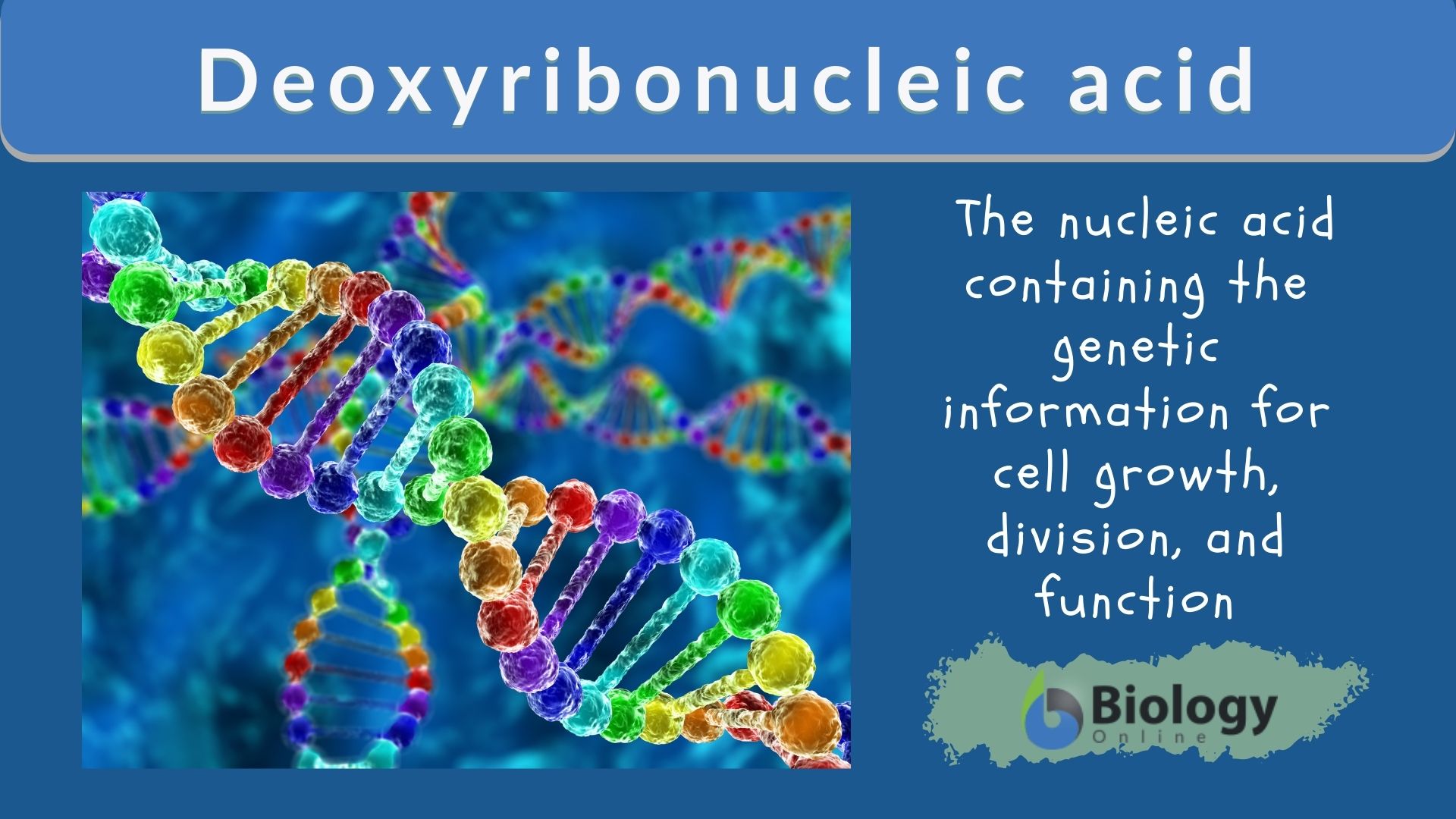
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Definition And Examples Biology Online Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the information-carrying molecule found in all living organisms In most animal, plant and fungal cells DNA is stored in the nucleus coiled up in thread-like Many people believe that American biologist James Watson and English physicist Francis Crick discovered DNA in the 1950s polynucleotide structure of the yeast nucleic acid" (1919)
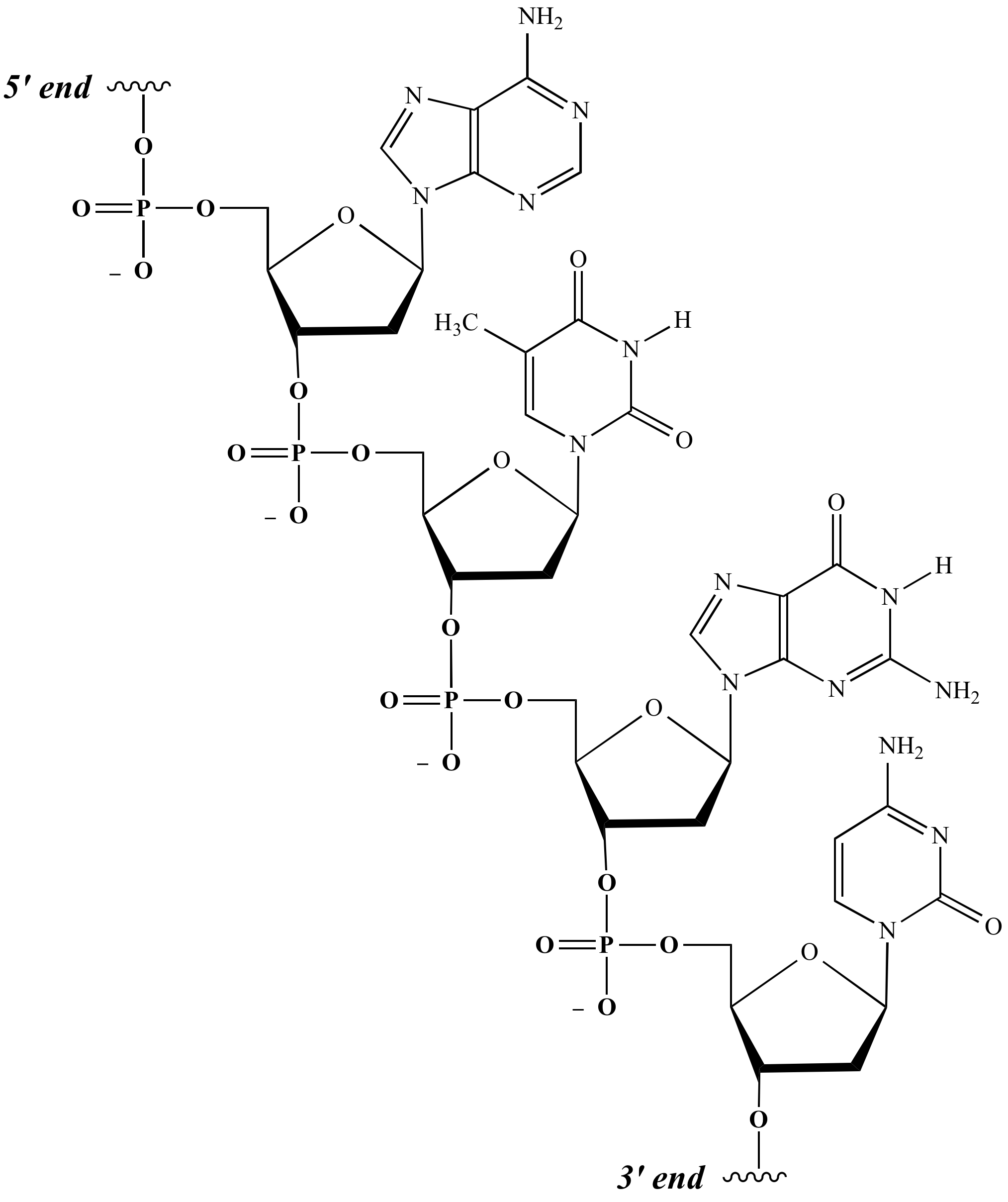
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Deoxyribonucleic Acid Earlier that morning, in the nearby Cavendish laboratory, the two scientists had discovered the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid function? How are scientists using their knowledge of DNA DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material found in nearly all DNA is a complex molecule that consists of two strands coiled around each other to form a double helix structure not nucleic acid, but by the late 1940s, DNA was largely accepted as the genetic molecule Scientists still needed to figure out this molecule's structure to be sure, and to understand how it worked The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA In DNA, two complementary strands of nucleotides pair up through hydrogen bonds between the bases (A with T and G with C) to form

Comments are closed.