Die Funktion Einer Bezierkurve Splines Legevideo Die Bezierkurve Teil 3 4

Die Funktion Einer Bг Zierkurve Splines Legevideo Die Bг Zierkur In diesem video geht es um die funnktion einer bézierkurve und wie man mehrere bézierkurven miteinander verknüpfen kann.inhalt:0:00 einführung0:17 bézier. In diesem video geht es um die bézierkurve. genauer: was eine bézierkurve ist, wie sie funktionieren und welche mathematik steckt dahinter?inhalt:0:00 was.

Bezier Curves Youtube Bézier curves in bernstein basis. • the plane where the curve lies, a 2d vector space • the space of cubic polynomials, a 4d space. • don’t be confused! • the 2d control points can be replaced by 3d points – this yields space curves. –the math stays the same, just add z(t). The mathematical basis for bézier curves—the bernstein polynomials—was established in 1912, but the polynomials were not applied to graphics until some 50 years later when mathematician paul de casteljau in 1959 developed de casteljau's algorithm, a numerically stable method for evaluating the curves, and became the first to apply them to computer aided design at french automaker citroën. Die länge der gerade bestimmt hingegen den kurvenverlauf zwischen den endpunkten. was verbirgt sich aber aus mathematischer sicht hinter einer bezierkurve? abbildung 14 abbildung 14: bezierkurve mit 4 punkten in abbildung 14 ist der punkt p 0 der start , p 3 der endpunkt. die punkte p 1 und p 2 sind die steuerpunkte. die kurve selbst wird. Man erkennt, wie die kurve bei einfügen verändern eines kontrollpunkts ihre richtung und oder krümmung variiert. bézierkurven 1. 2. 3. ordnung in geogebra – siehe auch interaktives geogebra applet. die bézierkurve [be'zje…] ist eine parametrisch modellierte kurve, die ein wichtiges werkzeug bei der beschreibung von freiformkurven und.
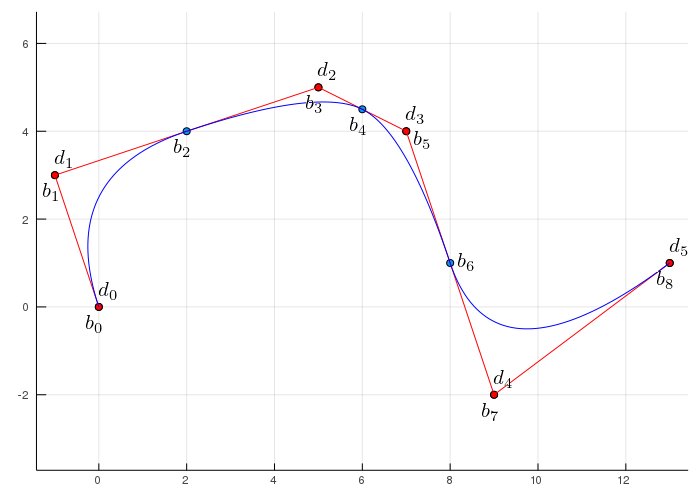
Unit 10 2 Modelling Curves Bezier Splines Part 2 Yout Vrogue Co Die länge der gerade bestimmt hingegen den kurvenverlauf zwischen den endpunkten. was verbirgt sich aber aus mathematischer sicht hinter einer bezierkurve? abbildung 14 abbildung 14: bezierkurve mit 4 punkten in abbildung 14 ist der punkt p 0 der start , p 3 der endpunkt. die punkte p 1 und p 2 sind die steuerpunkte. die kurve selbst wird. Man erkennt, wie die kurve bei einfügen verändern eines kontrollpunkts ihre richtung und oder krümmung variiert. bézierkurven 1. 2. 3. ordnung in geogebra – siehe auch interaktives geogebra applet. die bézierkurve [be'zje…] ist eine parametrisch modellierte kurve, die ein wichtiges werkzeug bei der beschreibung von freiformkurven und. Bézier splines are implemented in the wolfram language as beziercurve [pts]. a "rational" bézier curve is defined by. where is the order, are the bernstein polynomials, are control points, and the weight of is the last ordinate of the homogeneous point . these curves are closed under perspective transformations, and can represent conic. 1.3.4 definition of bézier curve and its properties. a bézier curve is a parametric curve that uses the bernstein polynomials as a basis. a bézier curve of degree (order ) is represented by. (1.40) the coefficients, , are the control points or bézier points and together with the basis function determine the shape of the curve. lines drawn.
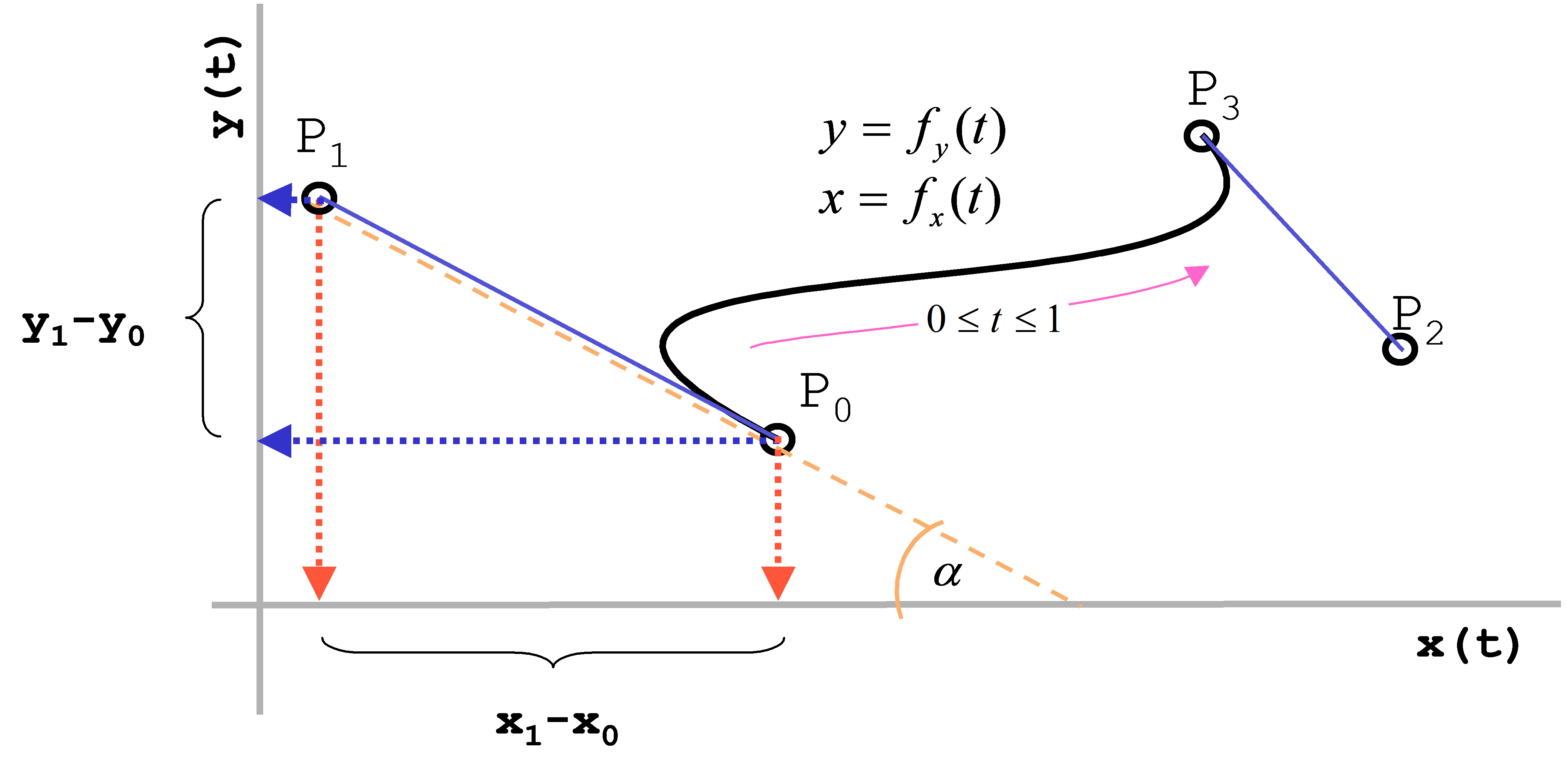
Bezierkurven Matheretter Bézier splines are implemented in the wolfram language as beziercurve [pts]. a "rational" bézier curve is defined by. where is the order, are the bernstein polynomials, are control points, and the weight of is the last ordinate of the homogeneous point . these curves are closed under perspective transformations, and can represent conic. 1.3.4 definition of bézier curve and its properties. a bézier curve is a parametric curve that uses the bernstein polynomials as a basis. a bézier curve of degree (order ) is represented by. (1.40) the coefficients, , are the control points or bézier points and together with the basis function determine the shape of the curve. lines drawn.

Comments are closed.