Diagram Of Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation

Premed Hq Pulmonary Systemic Circulation Premed Hq Pulmonary circulation facilitates the process of external respiration: deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs. it absorbs oxygen from tiny air sacs (the alveoli) and releases carbon dioxide to be exhaled. systemic circulation facilitates internal respiration: oxygenated blood flows into capillaries through the rest of the body. the blood. Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation, then back to the heart again. oxygen depleted blood from the body leaves the systemic circulation when it enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. the blood is then pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
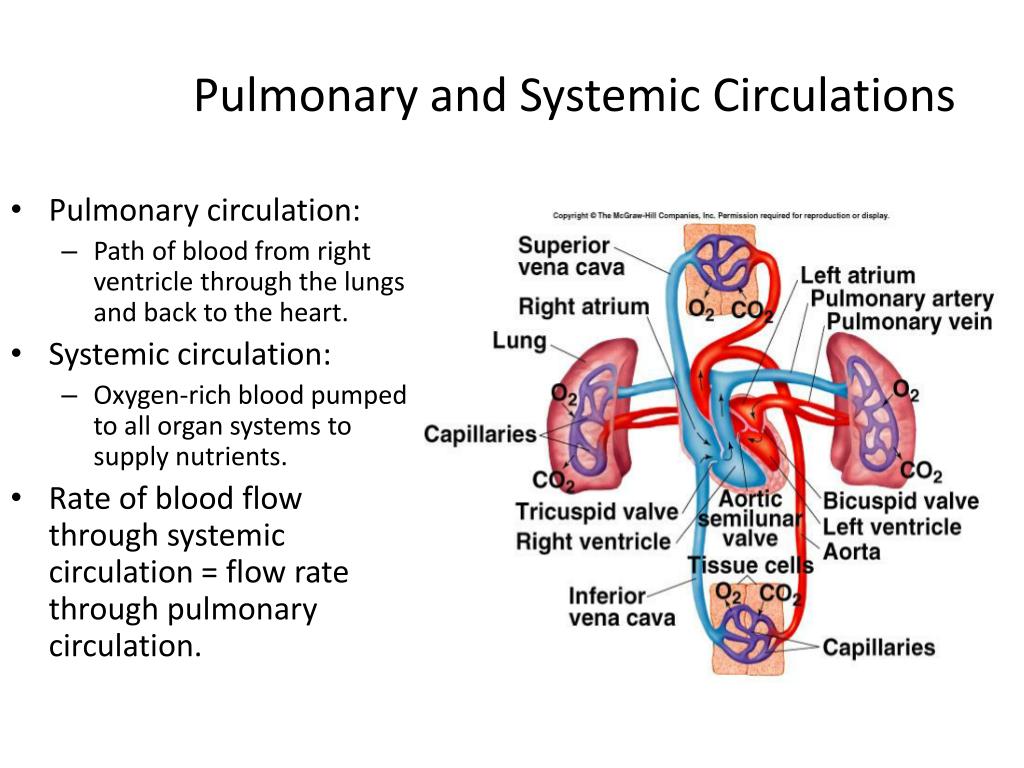
Diagram Of Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation The cardiovascular (circulatory) system is composed of two types of circulatory circuits: the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation.the shorter pulmonary circulation is responsible for pumping blood between the heart and lungs whereas the longer systemic circulation pumps blood between the heart and all the organs and tissues. Pulmonary circulation. recall that blood returning from the systemic circuit enters the right atrium (figure 20.5.2) via the superior and inferior venae cavae and the coronary sinus, which drains the blood supply of the heart muscle. these vessels will be described more fully later in this section. Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava. in contrast, deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart via the superior vena. Pulmonary vein diagram. pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. on the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, the first animals to acquire.

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation вђ Hsc Pdhpe Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava. in contrast, deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart via the superior vena. Pulmonary vein diagram. pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. on the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, the first animals to acquire. Summary. the pulmonary circulation is the portion that brings blood to the lungs and back. the systemic circulation is the portion that brings oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. the heart gets its own supply of blood through the coronary circulation. coronary arteries deliver oxygenated blood from the aorta to the heart. The circulatory system works thanks to constant pressure from the heart and valves throughout the body. this pressure ensures that veins carry blood to the heart and arteries transport it away.

Comments are closed.