Design Thinking Prototype System Concepts

Design Thinking 101 Try to resist the temptation of creating polished designs, and instead start with low fidelity prototypes that can be iterated quickly, with continuous input from your users. download our guidance on how you can succeed at this stage, and discover top tips on accessibility, the rite method and prototyping tools. design thinking; prototype. Use prototyping as a way to progress ideas (at any point in the design thinking process) by creating something tangible, which forces you to think and make decisions about how the solution will work. be open to the fact that some ideas will fail and aim to detect problems early, by starting with low fidelity prototypes and graduating to higher.
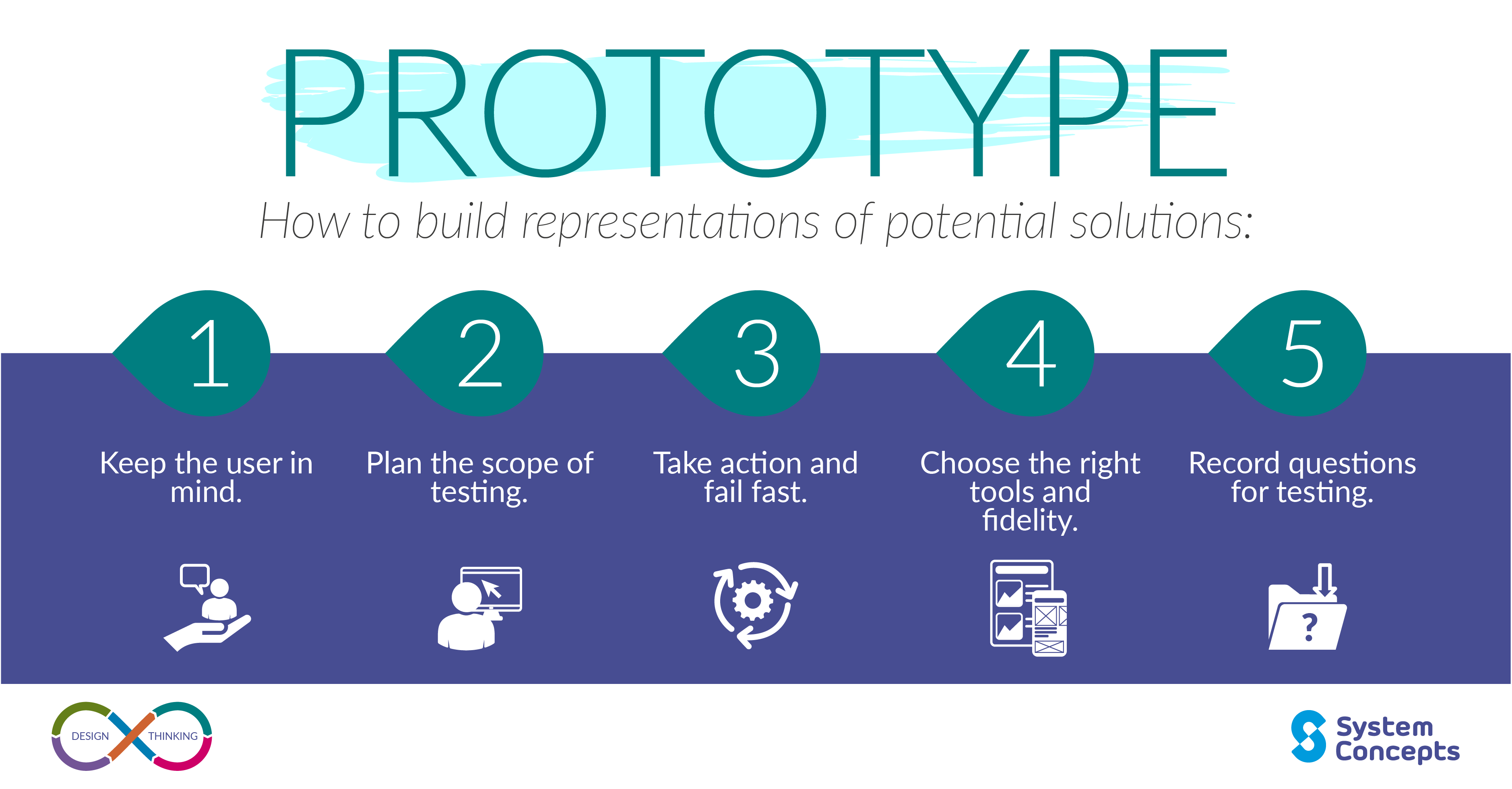
Design Thinking Prototype System Concepts 5) planning: through prototyping, the design team gets important information that helps them plan the undertaking. a prototype assists in building user stories and emphasising user needs. this fetches significant benefits to the scrum teams. 6) quick and easy: prototyping is a very quick and smooth procedure. Prototypes are often used in the final, testing phase in a design thinking process in order to determine how users behave with the prototype, to reveal new solutions to problems, or to find out whether or not the implemented solutions have been successful. the results generated from these tests are then used to redefine one or more of the. At this stage, you’ve gone through three other stages of the design thinking process: empathize: where you understand your users and their needs. define: where you agree on the core problem you need to solve. ideate: where you come up with lots of different ideas on how to solve the problem. now, you want to explore those ideas in more detail. Creating a physical version of a concept or experiment is a process known as prototyping. a prototype is basically a mockup of the solution that we want to create. examples of prototypes are a storyboard, a wall of stick on notes, a role playing game, a space, an object, or an interface.
Design Thinking An Introduction System Concepts At this stage, you’ve gone through three other stages of the design thinking process: empathize: where you understand your users and their needs. define: where you agree on the core problem you need to solve. ideate: where you come up with lots of different ideas on how to solve the problem. now, you want to explore those ideas in more detail. Creating a physical version of a concept or experiment is a process known as prototyping. a prototype is basically a mockup of the solution that we want to create. examples of prototypes are a storyboard, a wall of stick on notes, a role playing game, a space, an object, or an interface. Table of contents. what are the 5 stages of the design thinking process. stage 1: empathize—research your users' needs. stage 2: define—state your users' needs and problems. stage 3: ideate—challenge assumptions and create ideas. stage 4: prototype—start to create solutions. stage 5: test—try your solutions out. Design thinking is a non linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. it is most useful to tackle ill defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype and test.

Design Thinking Explained Mit Sloan Table of contents. what are the 5 stages of the design thinking process. stage 1: empathize—research your users' needs. stage 2: define—state your users' needs and problems. stage 3: ideate—challenge assumptions and create ideas. stage 4: prototype—start to create solutions. stage 5: test—try your solutions out. Design thinking is a non linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. it is most useful to tackle ill defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype and test.

Comments are closed.