Deoxyribonucleic Acid Model
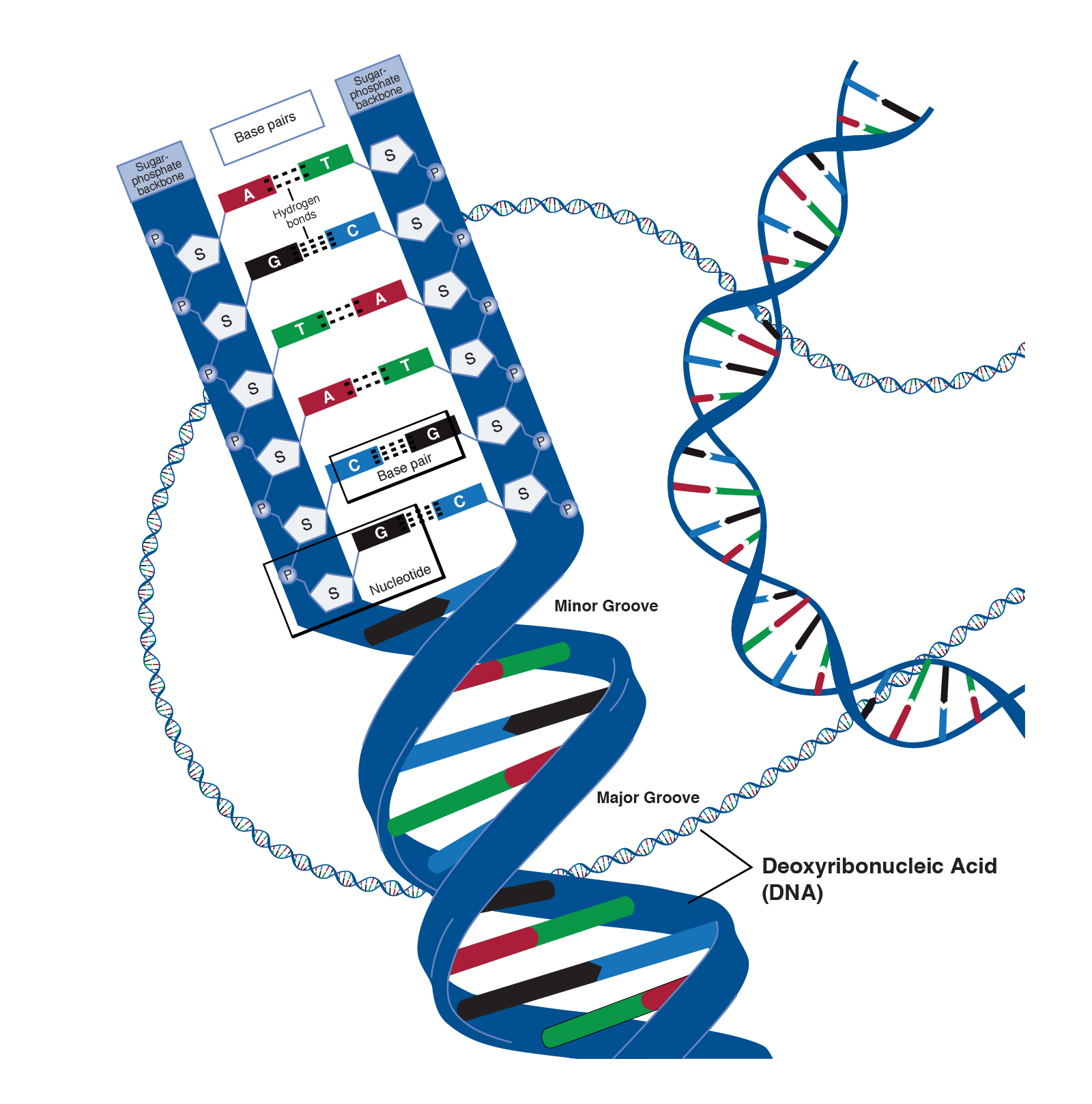
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is an organic chemical that contains genetic information and instructions for protein synthesis. it is found in most cells of every organism. dna is a key part of reproduction in which genetic heredity occurs through the passing down of dna from parent or parents to offspring. Deoxyribonucleic acid ( d iː ˈ ɒ k s ɪ ˌ r aɪ b oʊ nj uː ˌ k l iː ɪ k, ˌ k l eɪ ⓘ; [1] dna) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. the polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many.

Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Definition And Examples Biology Online Deoxyribose, also known as d deoxyribose and 2 deoxyribose, is a pentose sugar (monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms) that is a key component of the nucleic acid deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). it is derived from the pentose sugar ribose. deoxyribose has the chemical formula c 5 h 10 o 4. (the term "nuclein" was later changed to "nucleic acid" and eventually to "deoxyribonucleic acid," or "dna.") watson and crick's discovery was also made possible by recent advances in model. Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) fact sheet. deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. dna, along with the instructions it contains, is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction.
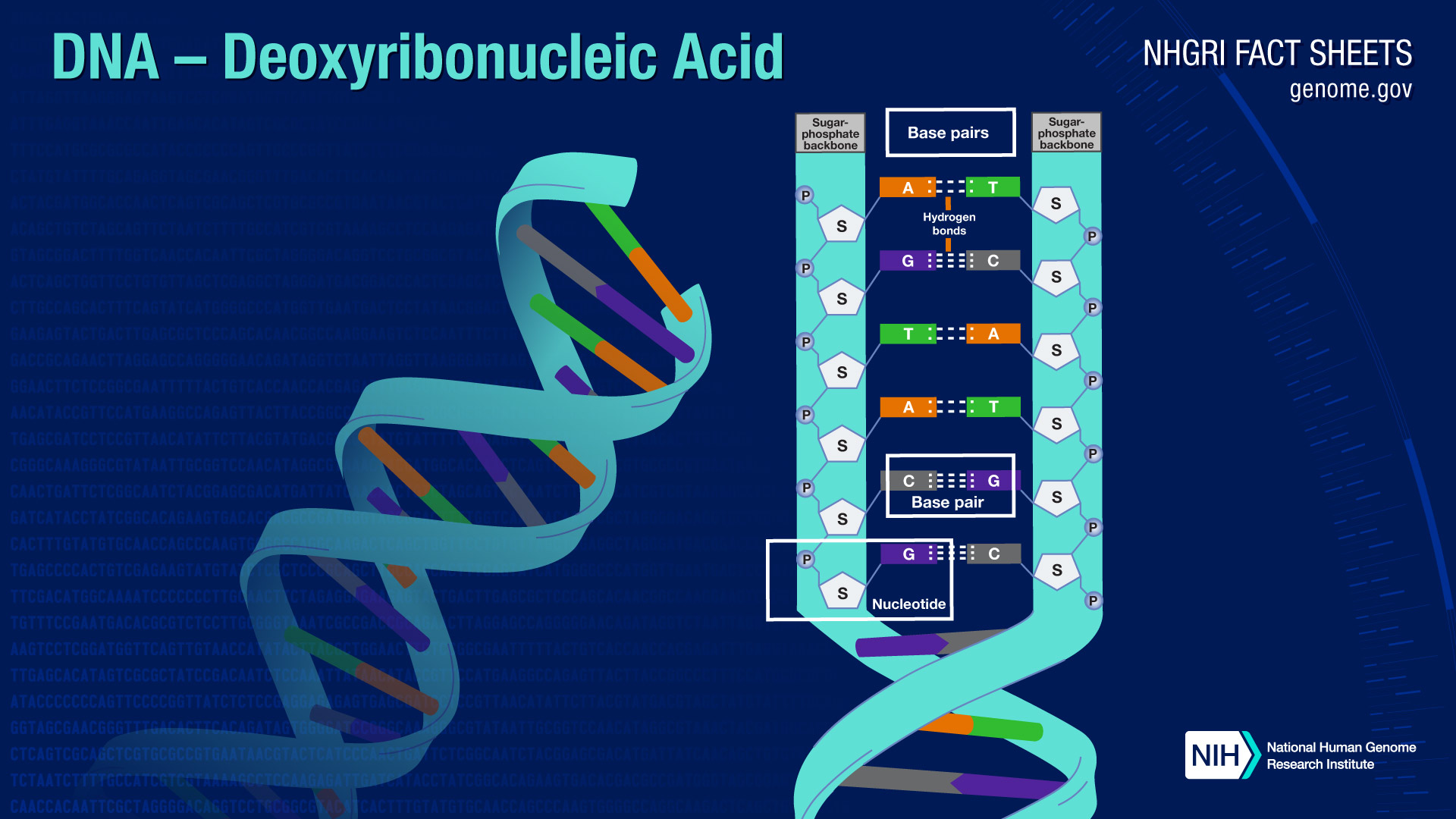
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Model Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) fact sheet. deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. dna, along with the instructions it contains, is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction. The remarkable structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), from the nucleotide up to the chromosome, plays a crucial role in its biological function. the ability of dna to function as the material through which genetic information is stored and transmitted is a direct result of its elegant structure. in their seminal 1953 paper, watson and crick unveiled two aspects of dna structure: pairing the. Each of these things — along with every other organism on earth — contains the molecular instructions for life, called deoxyribonucleic acid or dna. encoded within this dna are the directions.

Comments are closed.