Cycle Of Poverty Theory The Diagram Below Illustrates A Poverty Trap

Cycle Of Poverty Theory The Diagram Below Illustrates A Poverty Trap Cycle of poverty. in economics, a cycle of poverty or poverty trap is when poverty seems to be inherited, preventing subsequent generations from escaping it. [1] it is caused by self reinforcing mechanisms that cause poverty, once it exists, to persist unless there is outside intervention. [2] it can persist across generations, and when applied. A poverty trap refers to an economic system in which it is difficult to escape poverty. a poverty trap is not merely the absence of economic means. it is created due to a mix of factors, such as.
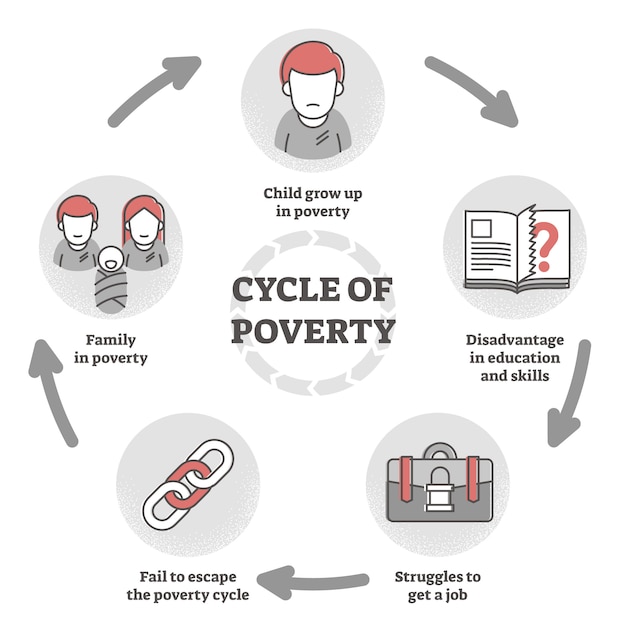
Premium Vector Cycle Of Poverty Trap Diagram In Flat Outline Lecture 2: poverty traps: theory. description: part 1 of 2 of poverty traps. the first half discusses the dasgupta and ray (1986) model of nutrition based poverty traps. the second half discusses how to use evidence to test for a poverty trap, focusing on evidence for a nutrition based poverty trap. session 2 lecture slides (pdf 1.0mb). Poverty cycle (poverty trap) arises when low income result in low (or zero) savings, permitting only low (or zero) investments in physical, human and natural capital, and therefore low productivity of labour and of land. this gives rise to low, if any, growth in income (sometimes growth may be negative), and hence low income once again. Figure 15.4 loosening the poverty trap: reducing government assistance by 50 cents for every $1 earned on the original labor leisure opportunity set, the lower, downward sloping budget set, the preferred choice p is 500 hours of leisure and $16,000 of income. then, the government created an antipoverty program that guarantees $18,000 in income. Poverty trap. poverty trap is a self perpetuating condition where an economy, caught in a vicious cycle, suffers from persistent underdevelopment. although it is often modeled as a low level equilibrium in a static model of coordination failures, we discuss the concept in a dynamic setting. this is because, in a static setting, we will not be.

Poverty Cycle Figure 15.4 loosening the poverty trap: reducing government assistance by 50 cents for every $1 earned on the original labor leisure opportunity set, the lower, downward sloping budget set, the preferred choice p is 500 hours of leisure and $16,000 of income. then, the government created an antipoverty program that guarantees $18,000 in income. Poverty trap. poverty trap is a self perpetuating condition where an economy, caught in a vicious cycle, suffers from persistent underdevelopment. although it is often modeled as a low level equilibrium in a static model of coordination failures, we discuss the concept in a dynamic setting. this is because, in a static setting, we will not be. Figure 7 8c.1 (based on barbier 2010) illustrates the elements of the poverty trap that can occur in marginal areas, and the threat posed by environmental risks. the vicious cycle depicted in the figure is inherently a dynamic process that can lead to a downward poverty spiral for many households in such areas. That poverty begets poverty, so that current poverty is itself a direct cause of poverty in the future. this notion is called a poverty trap, understood as self reinforcing mechanisms whereby poor individuals or countries remain poor. 1, whereas other countries or individuals with the same fundamental buts also the.

Sociological Perspectives On Poverty Figure 7 8c.1 (based on barbier 2010) illustrates the elements of the poverty trap that can occur in marginal areas, and the threat posed by environmental risks. the vicious cycle depicted in the figure is inherently a dynamic process that can lead to a downward poverty spiral for many households in such areas. That poverty begets poverty, so that current poverty is itself a direct cause of poverty in the future. this notion is called a poverty trap, understood as self reinforcing mechanisms whereby poor individuals or countries remain poor. 1, whereas other countries or individuals with the same fundamental buts also the.

Comments are closed.