Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia
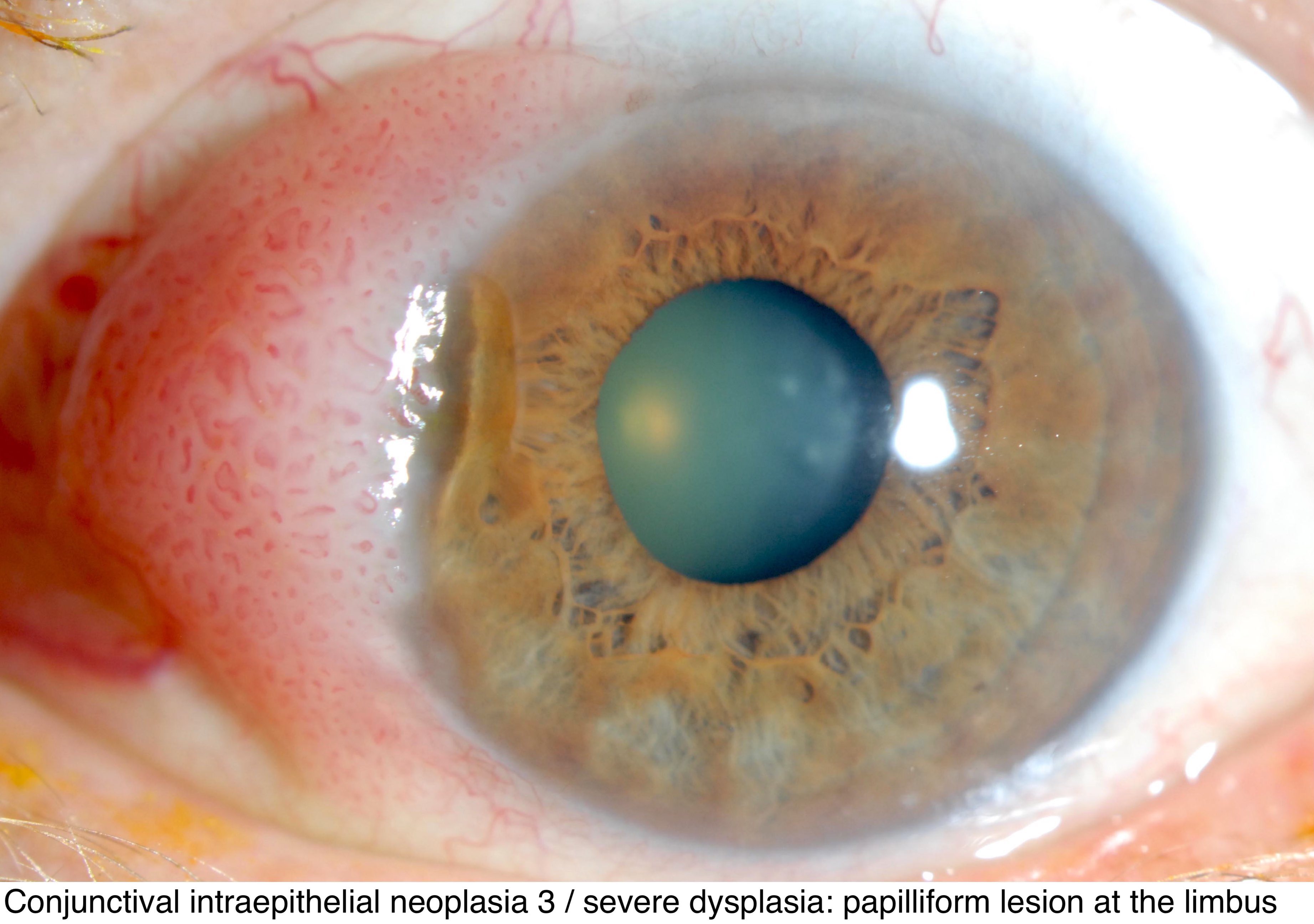
Pathology Outlines Conjunctiva Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia A comprehensive overview of the anatomy, histology, classification and treatment of conjunctival neoplasms. conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia is a premalignant lesion that can progress to squamous cell carcinoma. Learn about the disease entity, epidemiology, etiology, pathology, diagnosis, and management of ocular surface squamous neoplasia (ossn), which includes conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (cin). cin is a non invasive tumor that arises from a single mutated cell on the ocular surface and may be associated with uv light, hiv, or hpv.
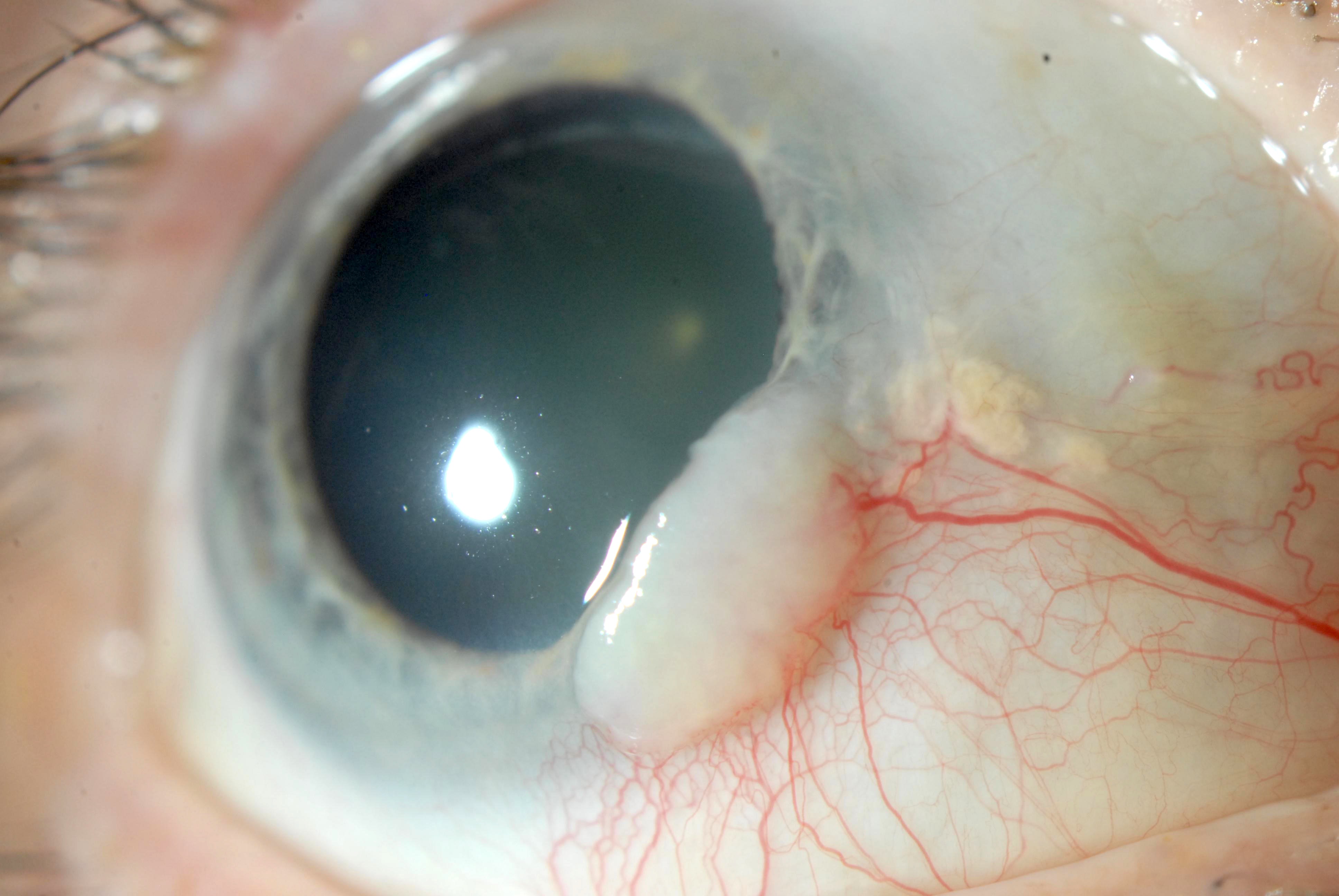
Pathology Outlines Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia is characterized by a proliferation of neoplastic squamous cells showing cellular atypia. it is considered a premalignant lesion that may progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma. hpv 6 and 11 (choice a) are associated with squamous papilloma. Learn about the common conjunctival tumors, including benign and malignant neoplasms, and how to diagnose and treat them. find out the risk factors, clinical features, classification and management options for ocular surface squamous neoplasia (ossn), lymphoid tumors, melanoma and more. Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments of squamous conjunctival neoplasia, a type of eye cancer related to sun exposure. find out how to prevent, detect and treat this tumor that can affect the conjunctiva, cornea, sclera and orbit. Conjunctival and corneal intraepithelial neoplasia (ccin) lesions are clinically diagnosed as elevated gelatinous, papilliform, or leukoplakic limbal lesions that are freely mobile over the sclera and have characteristic tufts of blood vessels. 1 involvement of the cornea is common and is in the form of a gray, opaque, thickened epithelium. 2 diagnosis typically is made clinically and can be.
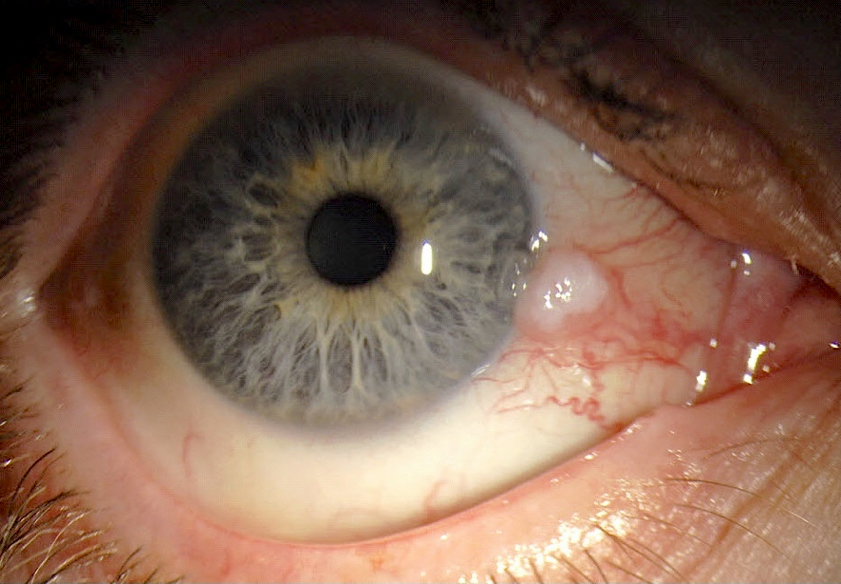
Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments of squamous conjunctival neoplasia, a type of eye cancer related to sun exposure. find out how to prevent, detect and treat this tumor that can affect the conjunctiva, cornea, sclera and orbit. Conjunctival and corneal intraepithelial neoplasia (ccin) lesions are clinically diagnosed as elevated gelatinous, papilliform, or leukoplakic limbal lesions that are freely mobile over the sclera and have characteristic tufts of blood vessels. 1 involvement of the cornea is common and is in the form of a gray, opaque, thickened epithelium. 2 diagnosis typically is made clinically and can be. Background: conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (cin) is the most common tumor of the ocular surface and is a precursor to invasive squamous cell carcinoma. cin comprises a spectrum of premalignant epithelial neoplasia that usually begins near the limbus and spreads to the cornea. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (cin) is a precancerous lesion of the ocular surface. it is reported to be the most common conjunctival malignancy in the united states and the third most common ocular tumor in the adult population. 1 typically found in white men in their mid 50s, these lesions almost always arise near the limbus in the interpalpebral area and may spread to involve the.
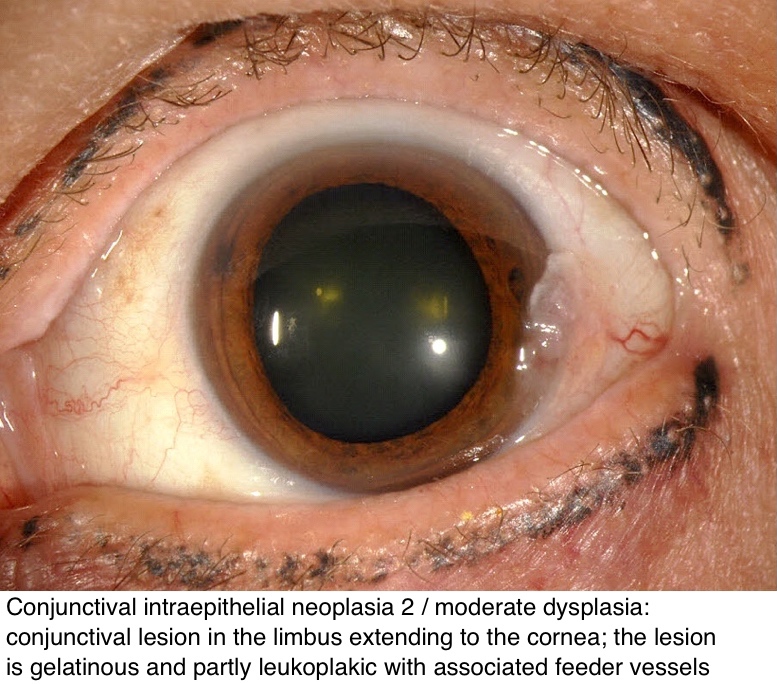
Pathology Outlines Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia Background: conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (cin) is the most common tumor of the ocular surface and is a precursor to invasive squamous cell carcinoma. cin comprises a spectrum of premalignant epithelial neoplasia that usually begins near the limbus and spreads to the cornea. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (cin) is a precancerous lesion of the ocular surface. it is reported to be the most common conjunctival malignancy in the united states and the third most common ocular tumor in the adult population. 1 typically found in white men in their mid 50s, these lesions almost always arise near the limbus in the interpalpebral area and may spread to involve the.

Comments are closed.