Composite Class Ii Restoration

Composite Restoration Class Ii Clinical Case Of Dr Dennis Hartlieb For 70% of clinicians, contact creation is the most challenging part of a class ii restoration. 1. you'll love our palodent family of matrix systems! when using resin based composite materials, both isolation and accurate contact creation are essential for successful class ii restorations. Class i, ii, and vi direct composite restorations. posterior composite restorations were introduced in the late 1960s and early 1970s. 1–7 because of the improved physical properties of composites and bonding systems, studies typically report successful results for their use in posterior teeth. 8–15 the american dental association (ada) indicates the appropriateness of composites for use.

Class Ii Composite Restorations Youtube The placement of a successful class ii composite resin restoration can be compared to the construction of a three legged stool. to function, all three legs have to be made correctly, that is, be. The step by step process of a class ii procedure. 1. local anesthesia. to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure, local anesthesia is applied to the area around the decayed or damaged tooth. this typically involves using a topical gel to numb the surface, followed by an injection to numb the deeper tissues. In selected cases, large composite restorations may be used where an interim restoration is indicated . contraindications main contraindication for use of composite for class i, ii, and vi restorations is an operating area that cannot be adequately isolated. when heavy occlusal stresses are present bluepenonline. Recently, this became even more obvious when i heard a trainer encouraging new in office cad cam users to do indirect class ii inlays as a substitute for direct class ii composite restorations. the argument was that, because direct class ii composites are so unpredictable and complicated, it would be easier and better to do indirect class ii in.
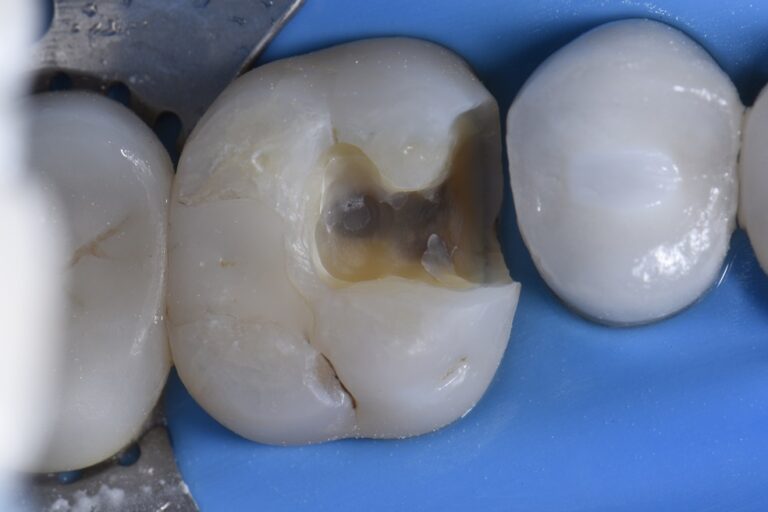
Skulpting Class Ii Restorations Using A Prototype Composite In selected cases, large composite restorations may be used where an interim restoration is indicated . contraindications main contraindication for use of composite for class i, ii, and vi restorations is an operating area that cannot be adequately isolated. when heavy occlusal stresses are present bluepenonline. Recently, this became even more obvious when i heard a trainer encouraging new in office cad cam users to do indirect class ii inlays as a substitute for direct class ii composite restorations. the argument was that, because direct class ii composites are so unpredictable and complicated, it would be easier and better to do indirect class ii in. By megan shelton, dmd while it may be one of the most common procedures in most restorative dental offices, the efficient placement of multiple class ii composites in a single quadrant can be technically demanding. creating strong and natural proximal contours and contacts with the restoration of even a single class ii composite restoration can pose a challenge using traditional matrix systems. The typical class ii posterior composite restoration is “placed on blind faith” using techniques and armamentarium designed specifically for amalgam placement. it is extremely difficult to evaluate the quality of composite layering in an interproximal preparation that is between the buccal and lingual line angles and thus, not clinically.

Comments are closed.