Clinical Update On The Management Of Fatty Liver Disease In T2dm Patients

Clinical Update On The Management Of Fatty Liver Disease In T The 2023 aasld practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nafld recommends screening for advanced fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm), obesity with metabolic complications, individuals with nafld in the context of moderate alcohol use (up to 21–39 g d in women and up to 31–59 g d in men), and in. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is the most common chronic liver condition of adults in developed countries (1,2).according to current guidelines, the diagnosis is based on the following criteria (3,4): 1) the presence of hepatic steatosis (>5% of hepatocytes determined by histology or >5.6% determined by nuclear magnetic resonance techniques); 2) no significant alcohol consumption.

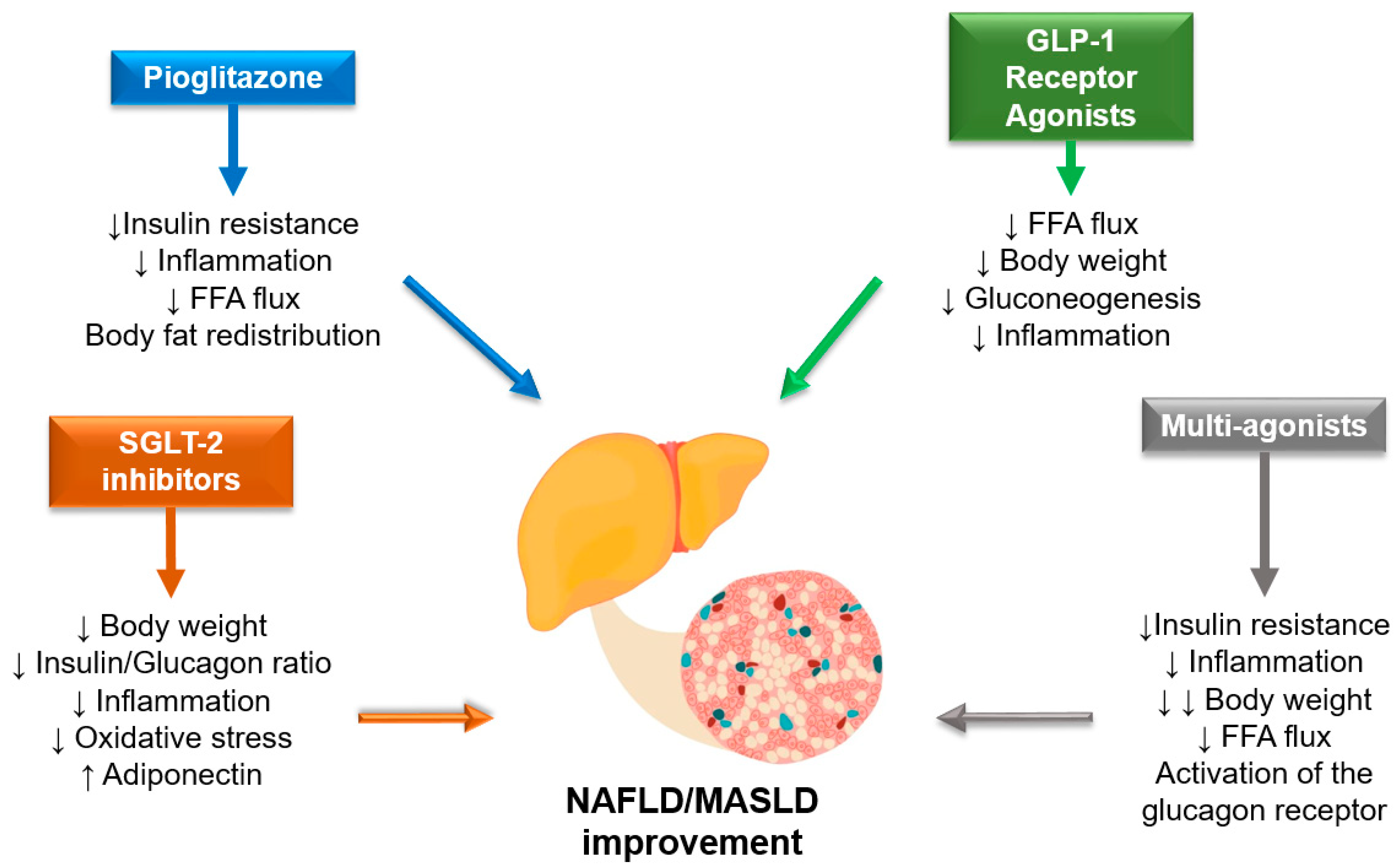
Aga Clinical Practice Update Diagnosis And Management Of Nonalcoholic Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (masld), previously termed non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld), is defined as steatotic liver disease (sld) in the presence of one or more cardiometabolic risk factor(s) and the absence of harmful alcohol intake. the spectrum of masld includes steatosis, metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (mash, previously nash. Abstract. type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) commonly exist together. it has been regarded as a manifestation of the metabolic syndrome. the presentations of nafld range from simple steatosis (nafl), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (nash), and cirrhosis. nafld has a prevalence of 70% among t2dm patients. Flow chart for diagnosis and management of suspected nafld patients. ① the european associations for the study of the liver, diabetes and obesity (easl easd easo) and asia pacific guidelines. ② the national institute for health and care excellence (nice) guidelines. ③ the american association for the study of liver diseases (aasld) and easl easd easo guidelines. ④ the aasld guidelines. The european association for the study of liver (easl) and the european diabetes and obesity societies recommend screening for nafld in all patients with obesity or metabolic syndrome. 21 the american diabetes association recommends evaluation for nash and hepatic fibrosis in persons with t2dm and elevated liver biochemical tests or fatty liver.
Jcm Free Full Text Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease In Patients Flow chart for diagnosis and management of suspected nafld patients. ① the european associations for the study of the liver, diabetes and obesity (easl easd easo) and asia pacific guidelines. ② the national institute for health and care excellence (nice) guidelines. ③ the american association for the study of liver diseases (aasld) and easl easd easo guidelines. ④ the aasld guidelines. The european association for the study of liver (easl) and the european diabetes and obesity societies recommend screening for nafld in all patients with obesity or metabolic syndrome. 21 the american diabetes association recommends evaluation for nash and hepatic fibrosis in persons with t2dm and elevated liver biochemical tests or fatty liver. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is the most common chronic liver disease in the united states and in other industrialized nations. its increase in prevalence and severity correlates with the rise in obesity and the metabolic syndrome, and nafld now represents a leading indication for liver transplantation in the united states. 1 the. Non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is defined by the presence of fat in the liver without evidence of other causes of fat accumulation in the liver such as alcohol use, hepatitis c, or certain medications. it is commonly associated with obesity, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol. currently, about 25% of the global population has a.

Diagnostic Approach In Nafld Patients With T2dm Nafld Nonalcoholic Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is the most common chronic liver disease in the united states and in other industrialized nations. its increase in prevalence and severity correlates with the rise in obesity and the metabolic syndrome, and nafld now represents a leading indication for liver transplantation in the united states. 1 the. Non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is defined by the presence of fat in the liver without evidence of other causes of fat accumulation in the liver such as alcohol use, hepatitis c, or certain medications. it is commonly associated with obesity, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol. currently, about 25% of the global population has a.

Diagnosis Of Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Nafld In Patients With

Comments are closed.