Class 99 Lipid Part 01 Introduction To Lipids Classification Of Lipids Uses Of Lipid

What Are Lipids Structure And Functions Download "solution pharmacy" mobile app to get all uploaded notes, model question papers, answer papers, online test and other gpat materials play . Abstract. the study of lipids has developed into a research field of increasing importance as their multiple biological roles in cell biology, physiology and pathology are becoming better understood. the lipid metabolites and pathways strategy (lipid maps) consortium is actively involved in an integrated approach for the detection, quantitation.

Class 99 Lipid Part 01 Introduction To Lipids Classific Lipids formed from fatty acids. fatty acids are carboxylic acids with 12 22 carbon atoms connected in a long, unbranched chain. as shown in the diagram above, most lipids are classified as esters or amides of fatty acids. waxes are esters formed from long chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols. most natural waxes are mixtures of such esters. Figure 8.1.1 8.1. 1: lipid organization based on structural relationships. lipids are not defined by the presence of specific functional groups, as carbohydrates are, but by a physical property—solubility. compounds isolated from body tissues are classified as lipids if they are more soluble in organic solvents, such as dichloromethane, than. These lipids have enormous structural variability given the large number of different fatty acids (both saturated and unsaturated) and head groups that can be attached to a phosphate attached to the carbon 3 of glycerol. the structures of the most common glycerophospholipids are shown in figure 10.1.16 10.1. 16. A lipid is generally considered to be any molecule that is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, terpenes, prenols, fat soluble vitamins (such as vitamins a, d, e.

Select All Of The Characteristics Of Lipids These lipids have enormous structural variability given the large number of different fatty acids (both saturated and unsaturated) and head groups that can be attached to a phosphate attached to the carbon 3 of glycerol. the structures of the most common glycerophospholipids are shown in figure 10.1.16 10.1. 16. A lipid is generally considered to be any molecule that is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, terpenes, prenols, fat soluble vitamins (such as vitamins a, d, e. The authors of this work are grateful to the uk’s wellcome trust for its support (grant 203014 z 16 z) of the lipid maps expansion to the uk (2017–present), making it possible to continue the development of lipidomics and the international lipid classification and nomenclature committee (ilcnc) building on the earlier lipid maps (lipid. Lipids are produced, transported, and recognized by the concerted actions of numerous enzymes, binding proteins, and receptors. a comprehensive analysis of lipid molecules, “lipidomics,” in the context of genomics and proteomics is crucial to understanding cellular physiology and pathology; consequently, lipid biology has become a major research target of the postgenomic revolution and.
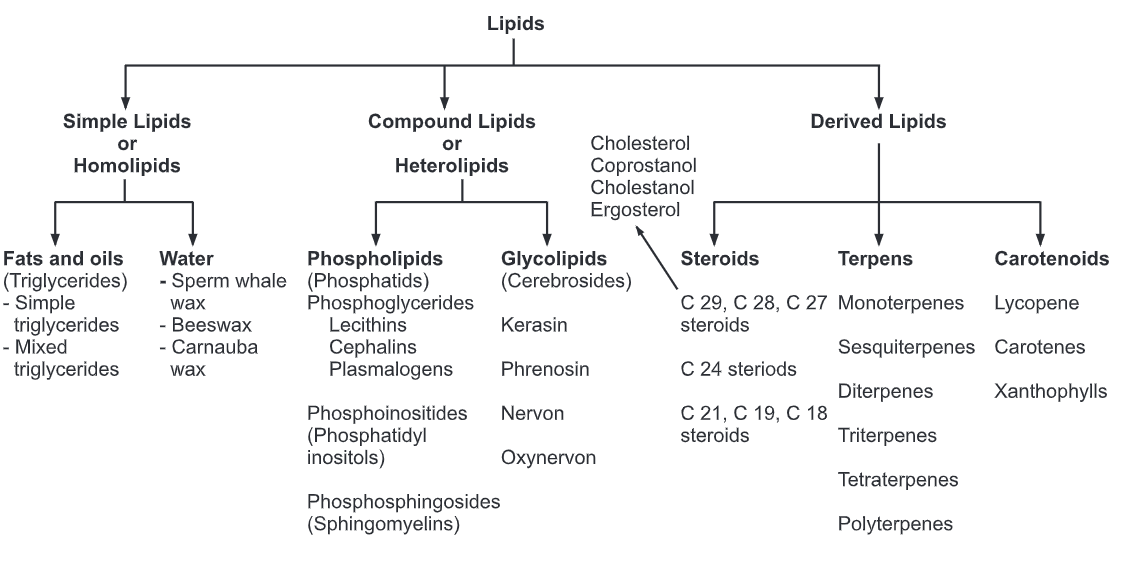
Classification Of Lipids Biology Ease The authors of this work are grateful to the uk’s wellcome trust for its support (grant 203014 z 16 z) of the lipid maps expansion to the uk (2017–present), making it possible to continue the development of lipidomics and the international lipid classification and nomenclature committee (ilcnc) building on the earlier lipid maps (lipid. Lipids are produced, transported, and recognized by the concerted actions of numerous enzymes, binding proteins, and receptors. a comprehensive analysis of lipid molecules, “lipidomics,” in the context of genomics and proteomics is crucial to understanding cellular physiology and pathology; consequently, lipid biology has become a major research target of the postgenomic revolution and.
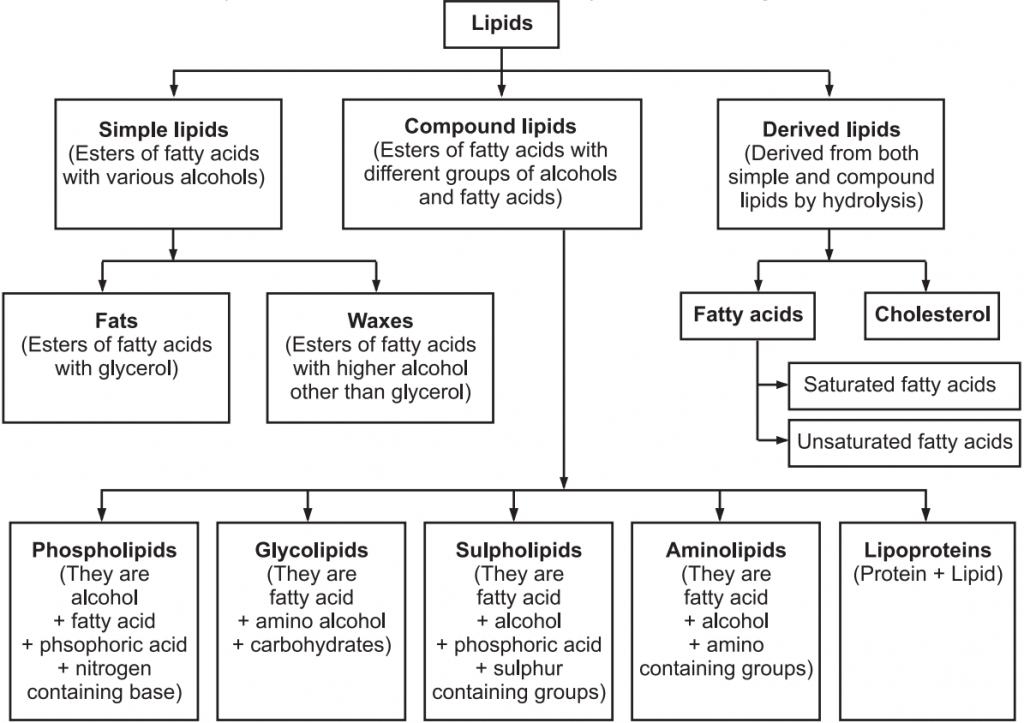
Lipids Classification

Comments are closed.