Circulatory System Pulmonary Circulation

Premed Hq Pulmonary Systemic Circulation Premed Hq The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to sustain the body with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. pulmonary circulation facilitates the process of external respiration: deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs. it absorbs oxygen from tiny air sacs (the alveoli) and releases carbon dioxide to be exhaled. The cardiovascular (circulatory) system is composed of two types of circulatory circuits: the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation. the shorter pulmonary circulation is responsible for pumping blood between the heart and lungs whereas the longer systemic circulation pumps blood between the heart and all the organs and tissues.
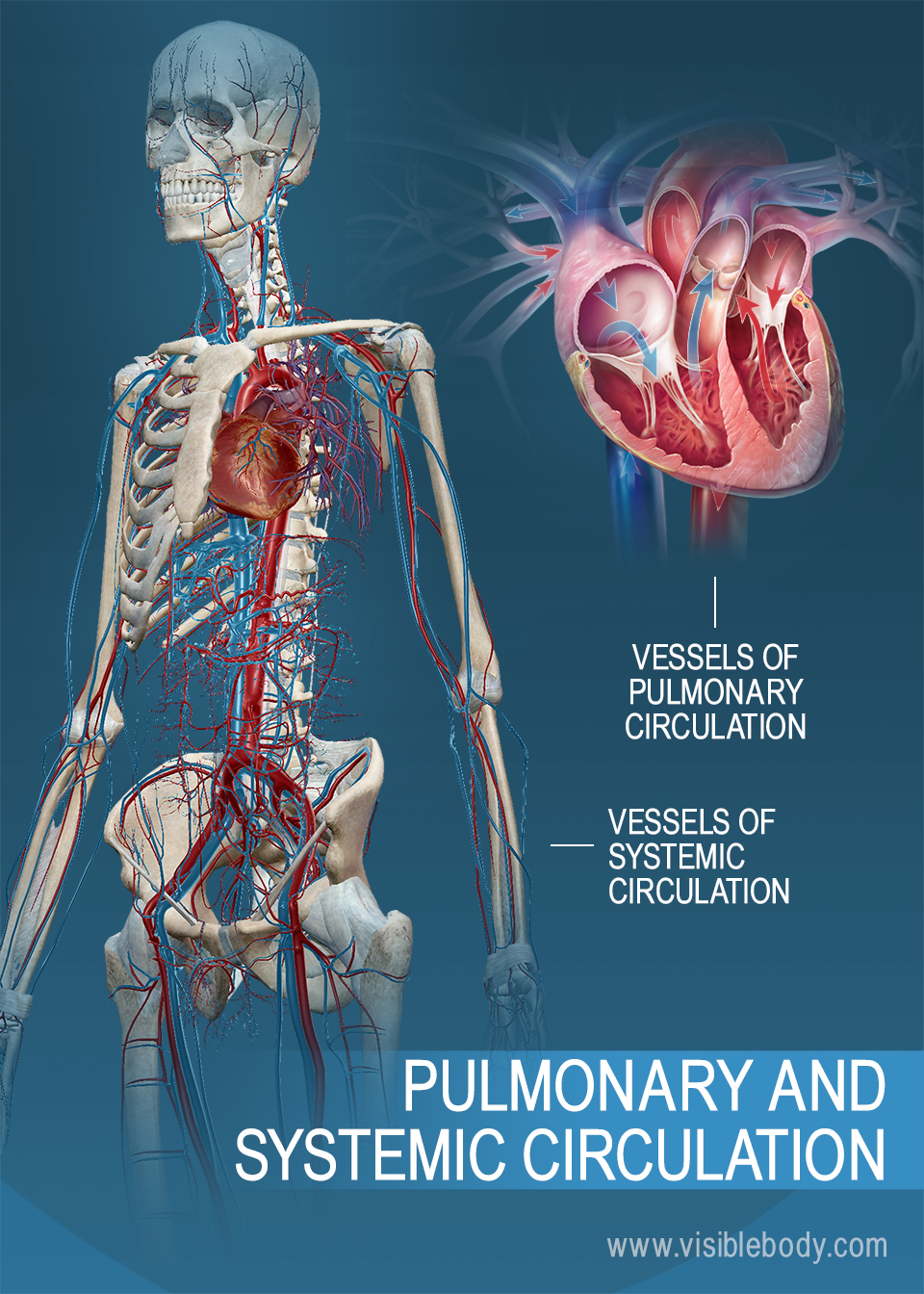
Circulatory Pulmonary Systemic Circulation The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. the circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. in the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit. Pulmonary circulation includes a vast network of arteries, veins, and lymphatics that function to exchange blood and other tissue fluids between the heart, the lungs, and back. they are designed to perform certain specific functions that are unique to the pulmonary circulation, such as ventilation and gas exchange. the pulmonary circulation receives the entirety of the cardiac output from the. The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths: pulmonary circulation, the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated, and systemic circulation, the circuit through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. in the pulmonary circulation, blood travels through capillaries on the alveoli, air sacs in the lungs. Pulmonary vein diagram. pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. on the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, the first animals to acquire.

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation вђ Hsc Pdhpe The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths: pulmonary circulation, the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated, and systemic circulation, the circuit through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. in the pulmonary circulation, blood travels through capillaries on the alveoli, air sacs in the lungs. Pulmonary vein diagram. pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. on the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, the first animals to acquire. Low pressure – the pulmonary circulation is a lower pressure system (mean arterial pressure of 5 15mmhg) compared to the systemic circulation (mean arterial pressure of 93mmhg). this is because the pulmonary arteries have thin vascular walls and high compliance, allowing them to carry more blood. low resistance – the pulmonary vessels are. Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava. in contrast, deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart via the superior vena.

Comments are closed.