Chapter 3 Cell Structure And Function Eukaryotic Cell
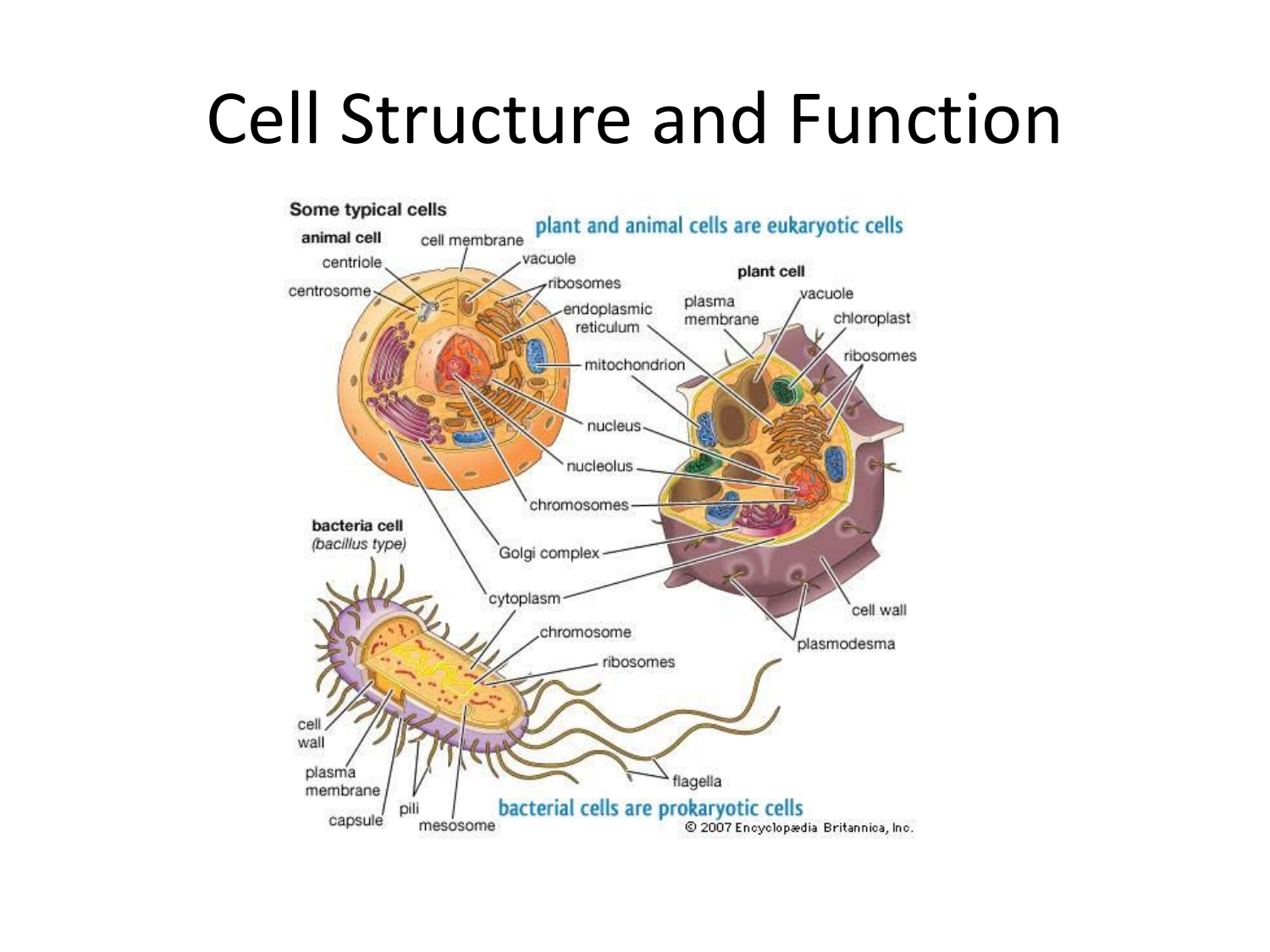
Eukaryotic Cell Structure And Function Theory that states that all organisms are made of cells, all cells are produced by other living cells, and the cell is the most basic unit of life. jellylike substance inside cells that contains molecules and in some cells organelles. membrane bound structure that is specialized to perform a distinct process within a cell. Before discussing the functions of organelles within a eukaryotic cell, let us first examine two important components of the cell: the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm. visual connection figure 3.7 this figure shows (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical plant cell.
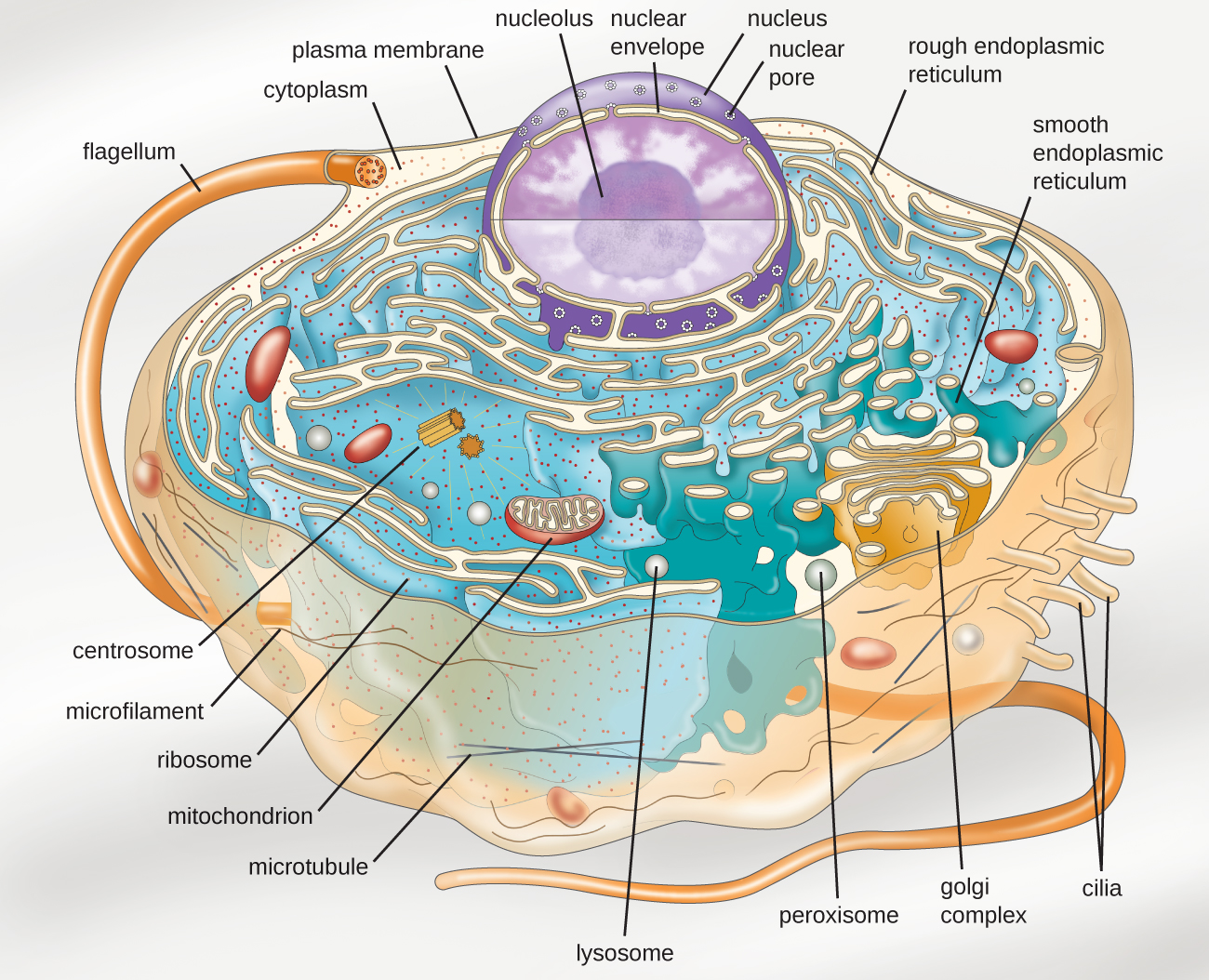
Eukaryotic Cell Structure And Function When the central vacuole holds more water, the cell gets larger without having to invest a lot of energy in synthesizing new cytoplasm. 2.3: eukaryotic cell: structure and function is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. by definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus, a. 3.5: the cell membrane. the plasma membrane is referred to as the fluid mosaic model and is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. the landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. some of these proteins serve to transport materials into. 3.3 eukaryotic cells. by the end of this section, you will be able to: watch a video about oxygen in the atmosphere. at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell. wastes (such as carbon dioxide and ammonia) also leave the cell by passing through the plasma membrane. figure 3.7 the eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it.
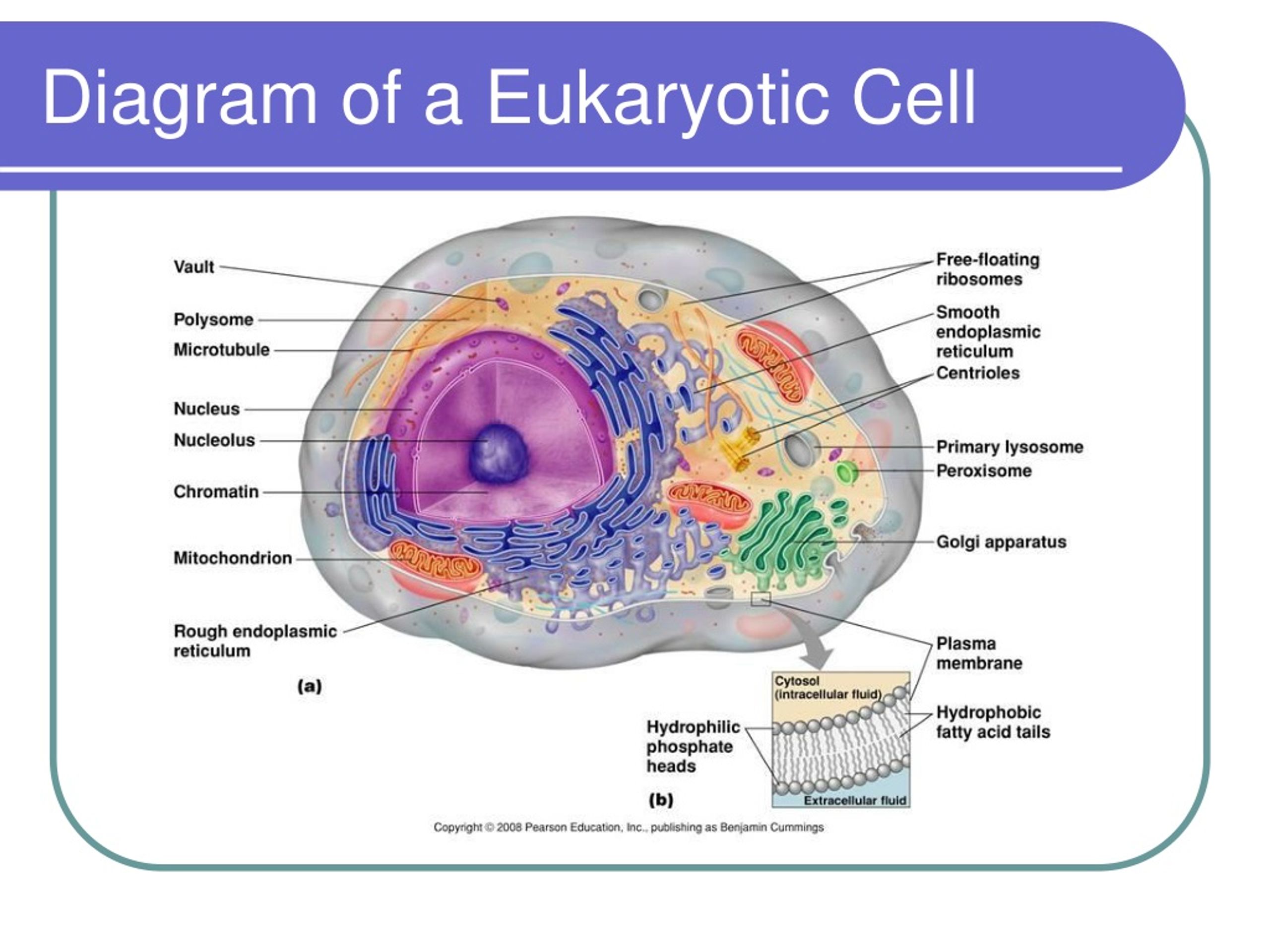
Eukaryotic Cell Structure And Function 3.3 eukaryotic cells. by the end of this section, you will be able to: watch a video about oxygen in the atmosphere. at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell. wastes (such as carbon dioxide and ammonia) also leave the cell by passing through the plasma membrane. figure 3.7 the eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell. wastes (such as carbon dioxide and ammonia) also leave the cell by passing through the plasma membrane. figure 4.9 the eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. Cytoskeleton (chapter 3.5) connections between cells (chapter 3.6) mitochondria and chloroplasts (chapter 3.7) at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time.
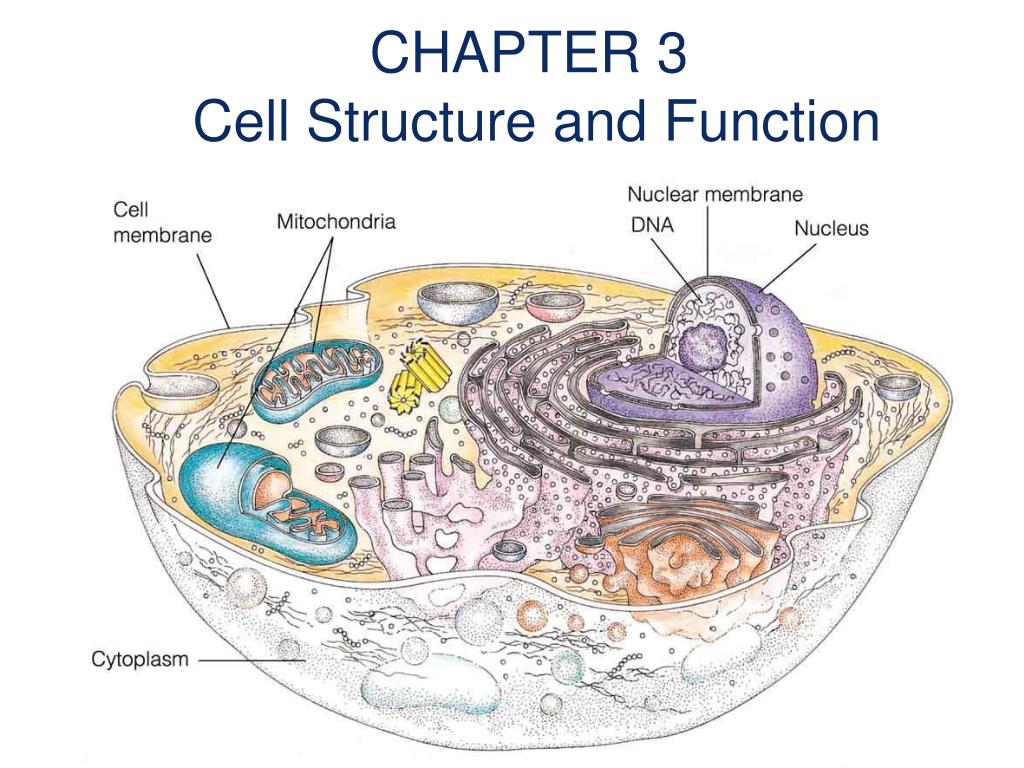
Ppt Chapter 3 Cell Structure And Function Powerpoint Presentation The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell. wastes (such as carbon dioxide and ammonia) also leave the cell by passing through the plasma membrane. figure 4.9 the eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. Cytoskeleton (chapter 3.5) connections between cells (chapter 3.6) mitochondria and chloroplasts (chapter 3.7) at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time.
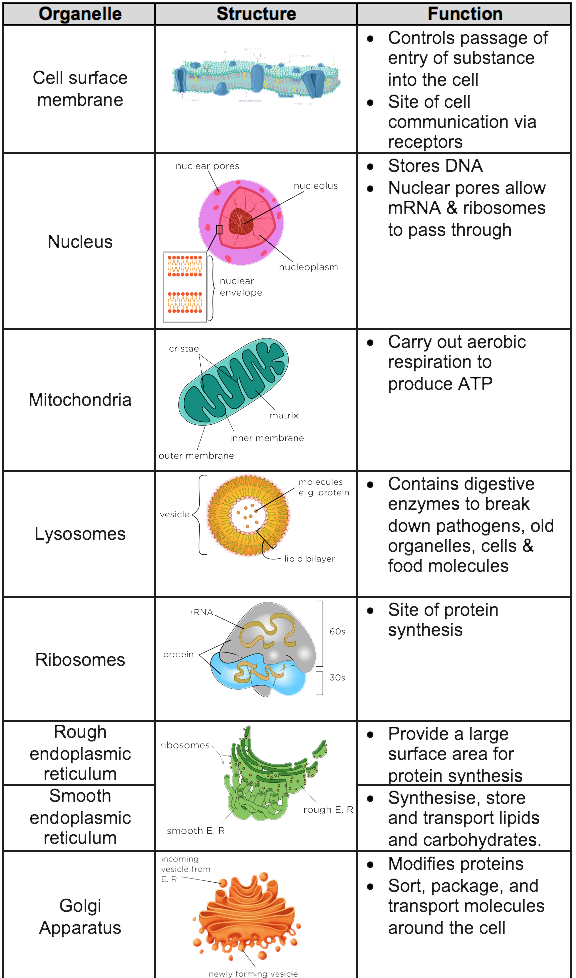
A Level Biology Aqa Notes Structure Of Eukaryotic Cells A Level Notes

Comments are closed.