Cellular Respiration Yeast Lab

Yeast Cellular Respiration Lab Youtube Part 2: aerobic respiration in yeast. optional activity or demonstration. this part of the lab investigates aerobic cellular respiration by saccharomyces cerevisiae, also referred to as “baker’s yeast” and “brewer’s yeast.” yeast is a unicellular fungus that can convert glucose into carbon dioxide and atp when oxygen is present. Obtain 15 ml of the yeast suspension. gently swirl the yeast suspension to mix the yeast that settles to the bottom. put 2 ml of the yeast suspension into the test tube labeled g (glucose). gently swirl the test tube to mix the yeast into the solution. set the test tube into the water bath and incubate for 10 minutes.
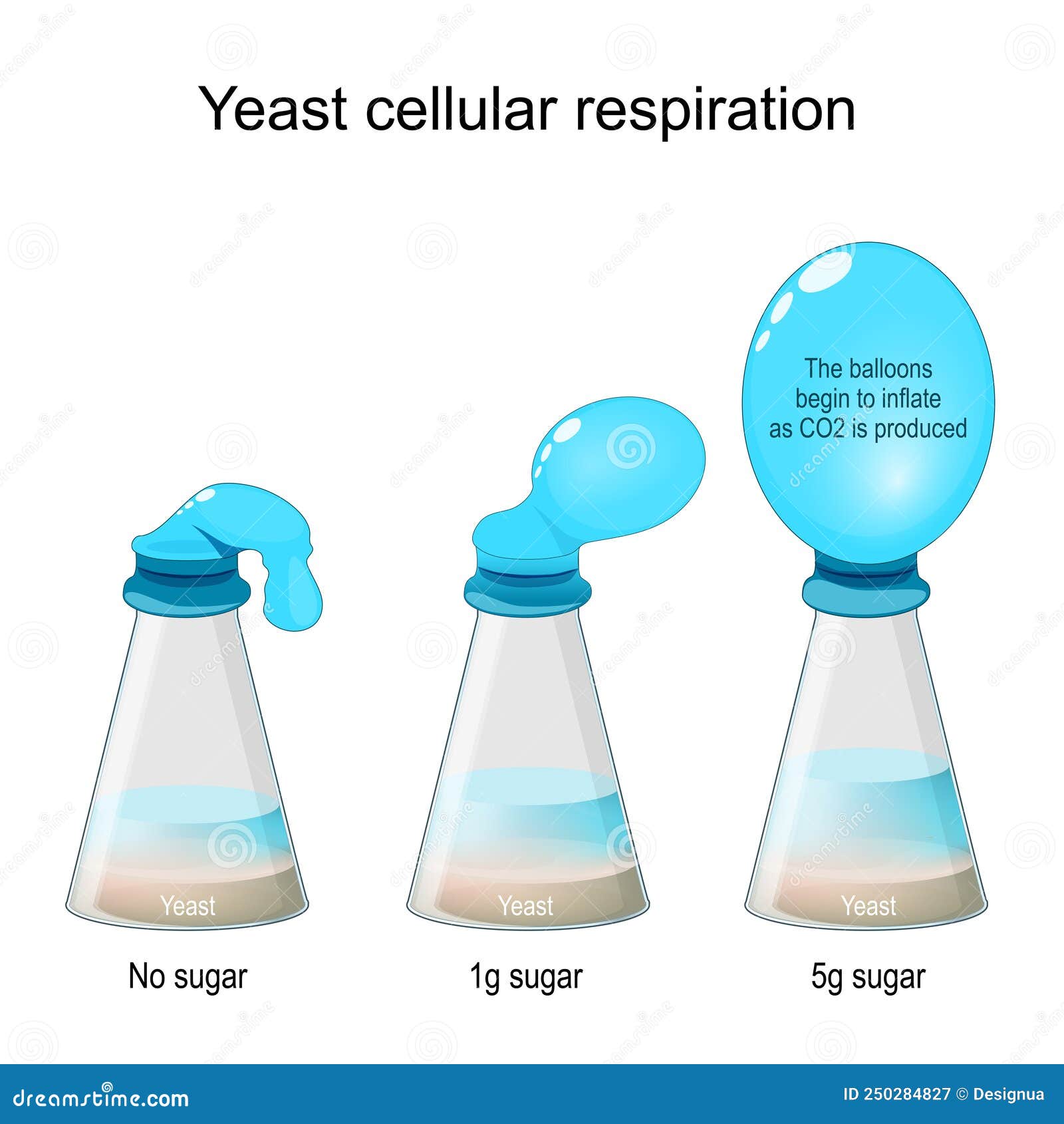
Yeast Cellular Respiration Lab Bottle Balloon Experiment Stock Vector To atp that the organism can use for its cellular. espiration is below: c6h12o6 6 o2 6 h2o 6 co2 atpin this lab. we will observe yeast cells perf. ming cellular respiration. yeast are facultative anaerobes. this means. at if oxygen is present, they will use cellular respiration. however, if there is no oxygen present i. Yeast and respiration. yeast is a living organism. in order for it to survive, it needs to make energy. in its dried form, the yeast is dormant, but as soon as you provide it with warmth, water and sugar (its food), it ‘wakens’ and becomes active. the yeast uses the sugar (glucose) and oxygen from the bottle to make water, energy and carbon. Produce cellular energy. here is the chemical reaction of fermentation, which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products. objective: in this lab, students will use the respiration powers of yeast to blow balloons. this activity will reinforce the basic principles of respiration as a fundamental metabolic process for. This lab explores the concepts of cellular respiration and fermentation in yeast. yeast do alcoholic fermentation and one of the byproducts is carbon dioxide. when you bake bread with yeast, carbon dioxide is produced, which forms bubbles in the dough, causing the dough to rise. the heat kills the yeast and the bubble pockets lighten the bread.

Cellular Respiration In Yeast Lab By Rachel Taylor Tpt Produce cellular energy. here is the chemical reaction of fermentation, which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products. objective: in this lab, students will use the respiration powers of yeast to blow balloons. this activity will reinforce the basic principles of respiration as a fundamental metabolic process for. This lab explores the concepts of cellular respiration and fermentation in yeast. yeast do alcoholic fermentation and one of the byproducts is carbon dioxide. when you bake bread with yeast, carbon dioxide is produced, which forms bubbles in the dough, causing the dough to rise. the heat kills the yeast and the bubble pockets lighten the bread. We will investigate fermentation by measuring the amount of carbon dioxide produced by yeast. the rate of cellular respiration is proportional to the amount of co 2 produced (see the equation for fermentation above). in this experiment, we will measure the rate of cellular respiration using either distilled water or one of four different food. Yeast and sugar balloon experiment. amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years. she has a master's degree in cellular and molecular physiology from tufts medical school and a master's.

Comments are closed.