Catalysts Free Full Text Electrochemical Reduction Of Carbon
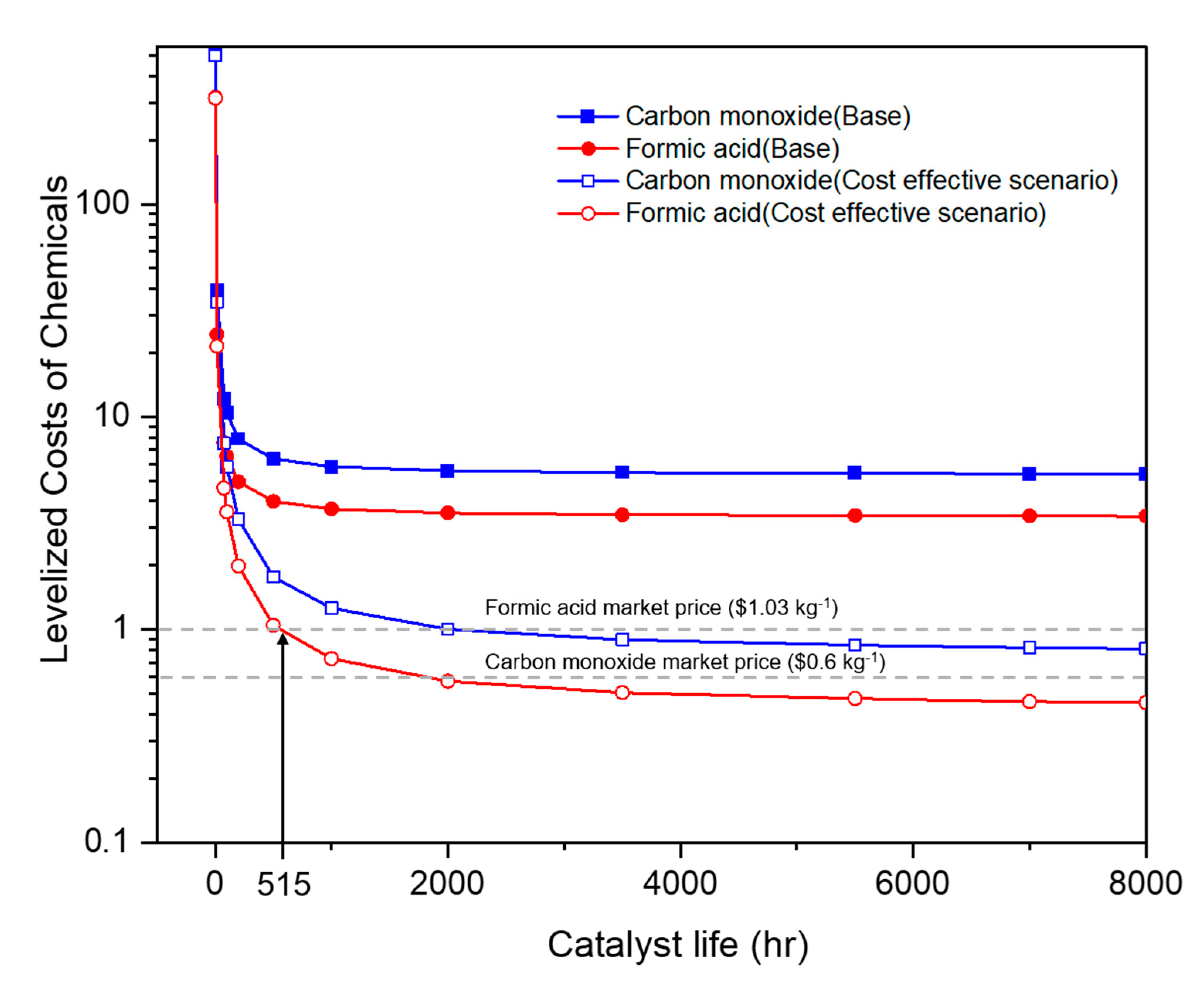
Catalysts Free Full Text Towards The Large Scale Electrochemical The electrocatalytic reduction of co2 to other high value added chemicals under ambient conditions is a promising and ecofriendly strategy to achieve sustainable carbon recycling. however, the co2 reduction reaction (co2rr) is still confronted with a large number of challenges, such as high reaction overpotential and low product selectivity. therefore, the rapid development of appropriate. The severe increase in the co2 concentration is a causative factor of global warming, which accelerates the destruction of ecosystems. the massive utilization of co2 for value added chemical production is a key to commercialization to guarantee both economic feasibility and negative carbon emission. although the electrochemical reduction of co2 is one of the most promising technologies, there.
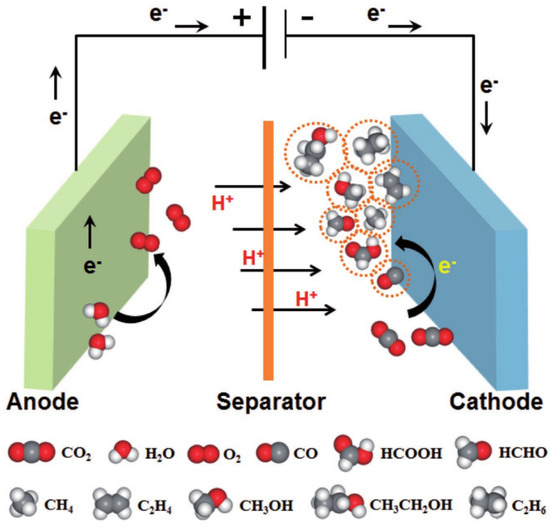
Catalysts Free Full Text Electrochemical Reduction Of Carbon Electrochemical co2 reduction reaction (co2rr) provides a promising approach to curbing harmful emissions contributing to global warming. however, several challenges hinder the commercialization of this technology, including high overpotentials, electrode instability, and low faradic efficiencies of desirable products. several materials have been developed to overcome these challenges. this. The electrochemical reduction of co2 has gained significant interest recently as it has the potential to trigger a sustainable solar fuel based economy. in this perspective, we highlight several heterogeneous and molecular electrocatalysts for the reduction of co2 and discuss the reaction pathways through which they form various products. among those, copper is a unique catalyst as it yields. Electrochemical reduction of co2 to multicarbon (c2 ) products is desirable because of the higher energy density and economic value of c2 products and the significant scientific issue for coupling of multicarbons. however, efficient conversion of co2 into c2 products remains challenging because of the difficulty in c–c coupling. recently, numerous papers have reported carbon based. Recent reports 39,42 have also shown that acid tolerant catalysts, such as molecular or metal nitrogen carbon catalysts, are more selective than silver catalysts for co 2 reduction due to their.

Catalysts Free Full Text Towards The Large Scale Electrochemical Electrochemical reduction of co2 to multicarbon (c2 ) products is desirable because of the higher energy density and economic value of c2 products and the significant scientific issue for coupling of multicarbons. however, efficient conversion of co2 into c2 products remains challenging because of the difficulty in c–c coupling. recently, numerous papers have reported carbon based. Recent reports 39,42 have also shown that acid tolerant catalysts, such as molecular or metal nitrogen carbon catalysts, are more selective than silver catalysts for co 2 reduction due to their. Developing metal free catalysts for reduction of co2 into energy rich products is a popular yet very challenging topic. using density functional theory calculations, we investigated the electrocatalytic performance of c doped and line defect (ld) embedded boron nitride nanoribbons (bnnrs) for co2 reduction reaction (crr). because of the presence of bare edge b atoms neighboring to c dopant and. Then the emerging metal free doped carbon and aromatic n heterocycle catalysts for electrochemical reduction of co 2 with an emphasis on the formation of multicarbon hydrocarbons and oxygenates are discussed. following that, the recent progress in metal–nitrogen–carbon structures as an extension of carbon based catalysts is scrutinized.

Catalysts Free Full Text Towards The Large Scale Electrochemical Developing metal free catalysts for reduction of co2 into energy rich products is a popular yet very challenging topic. using density functional theory calculations, we investigated the electrocatalytic performance of c doped and line defect (ld) embedded boron nitride nanoribbons (bnnrs) for co2 reduction reaction (crr). because of the presence of bare edge b atoms neighboring to c dopant and. Then the emerging metal free doped carbon and aromatic n heterocycle catalysts for electrochemical reduction of co 2 with an emphasis on the formation of multicarbon hydrocarbons and oxygenates are discussed. following that, the recent progress in metal–nitrogen–carbon structures as an extension of carbon based catalysts is scrutinized.
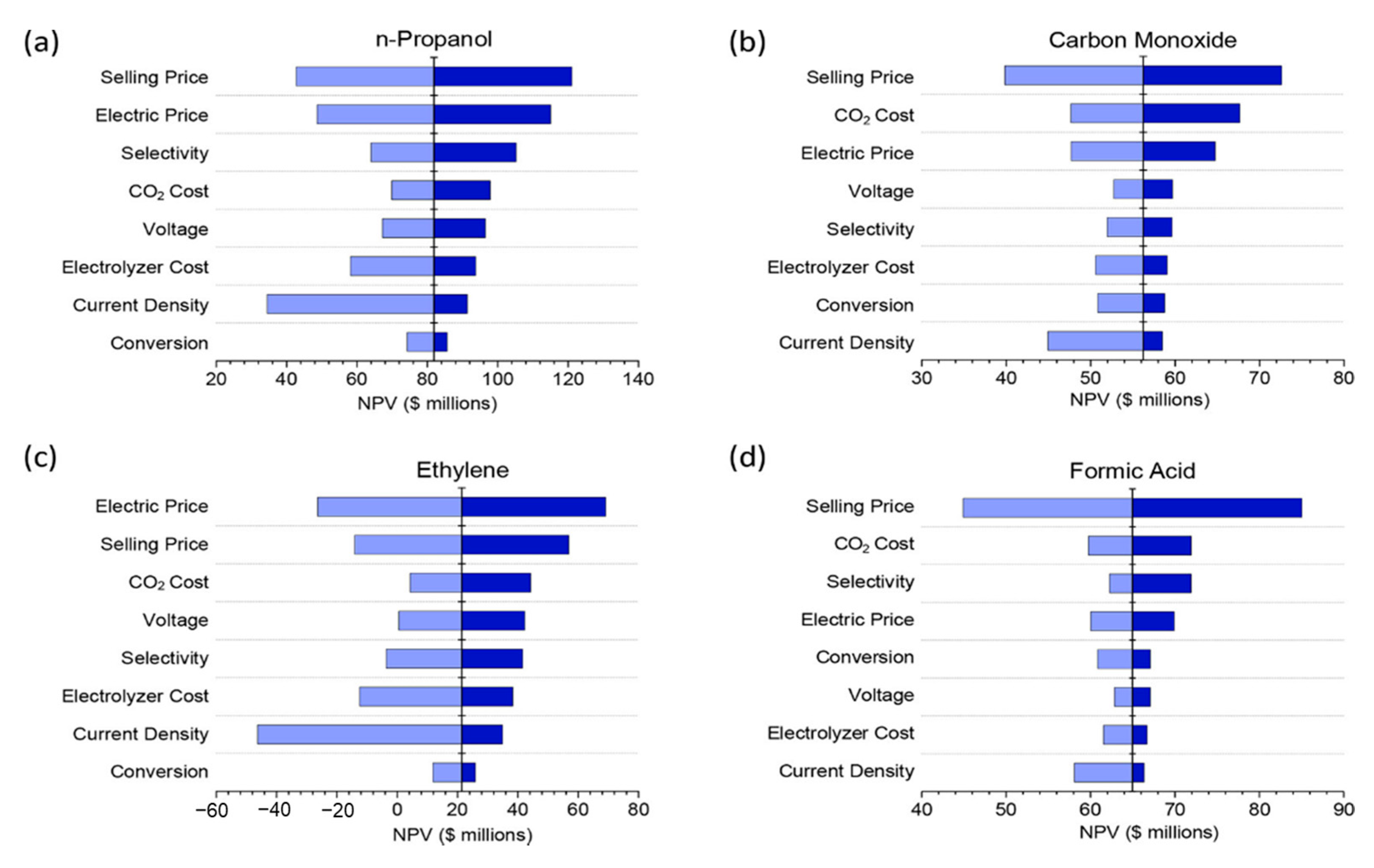
Catalysts Free Full Text Towards The Large Scale Electrochemical

Comments are closed.