Can International Travel Related Control Measures Contain The Spread Of
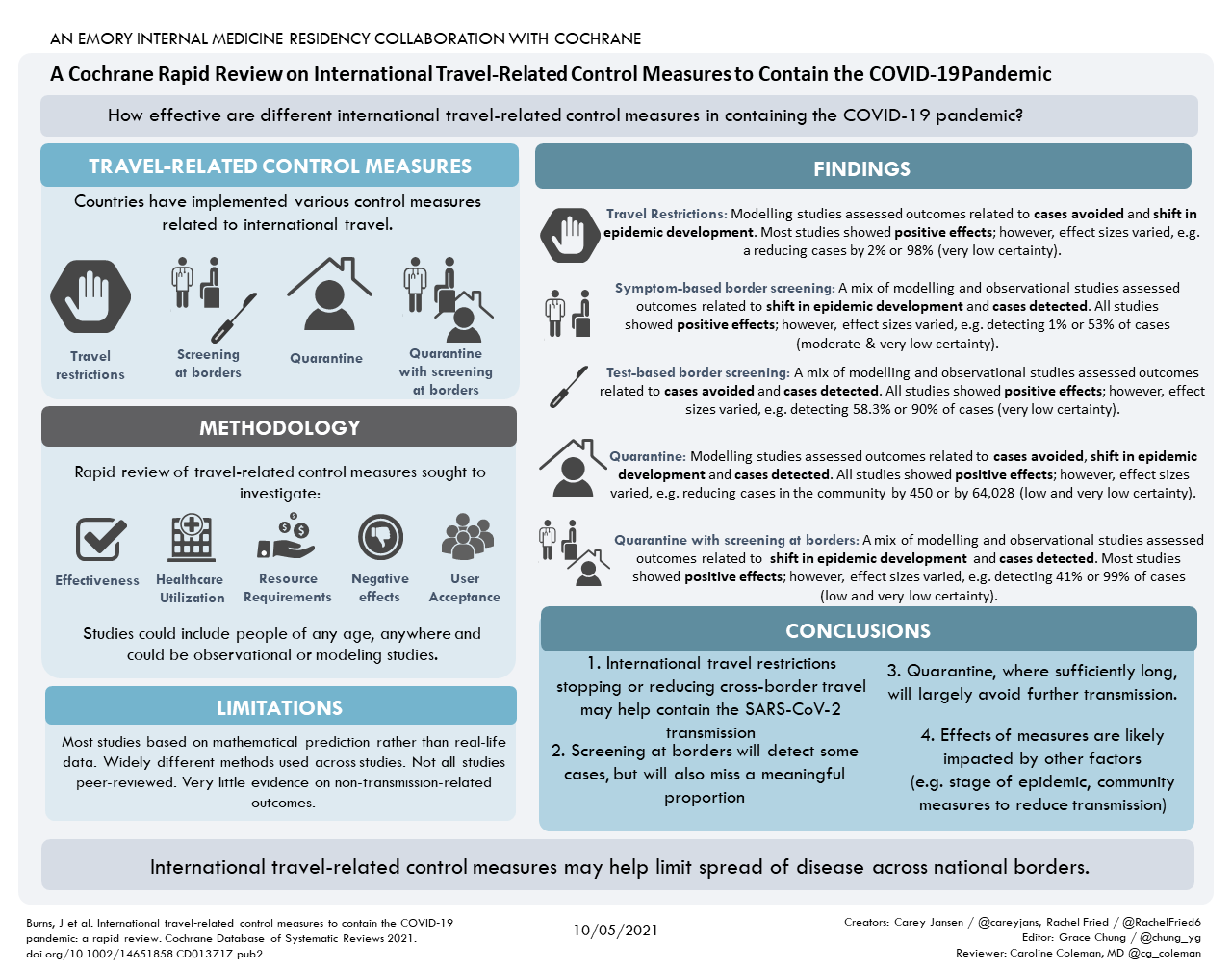
Can International Travel Related Control Measures Contain The Spread Of Abstract. background: in late 2019, the first cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) were reported in wuhan, china, followed by a worldwide spread. numerous countries have implemented control measures related to international travel, including border closures, travel restrictions, screening at borders, and quarantine of travellers. Overall, international travel related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid 19 across national borders. restricting cross border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers only for symptoms at borders is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases if only performed upon arrival.
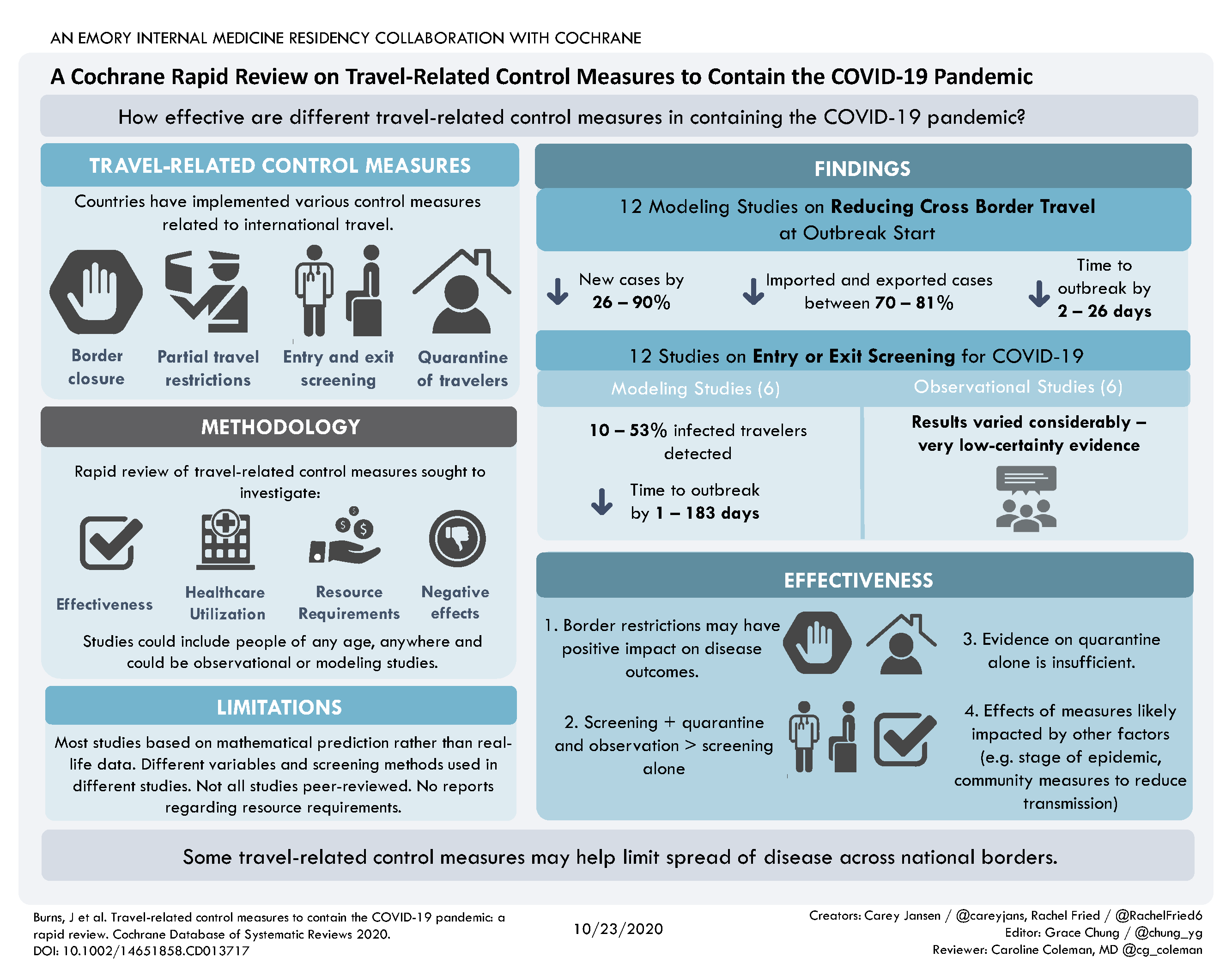
Can Travel Related Control Measures Contain The Spread Of Overall, international travel related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid 19 across national borders. restricting cross border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers for symptoms at points of entry or exit is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases. Jake: travel related control measures, even as they've been implemented during the covid 19 pandemic, can refer to many things, but in the latest version of our review we focused specifically on restrictions that reduce cross border international travel. these include measures such as border closures or restricting entry for people from high. Overall, international travel‐related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid‐19 across national borders. restricting cross‐border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers only for symptoms at borders is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases if only performed upon arrival. Overall, international travel‐related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid‐19 across national borders. restricting cross‐border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers only for symptoms at borders is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases if only performed upon arrival.

Travel Related Measures For Controlling The Spread Of Covid 19 Overall, international travel‐related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid‐19 across national borders. restricting cross‐border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers only for symptoms at borders is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases if only performed upon arrival. Overall, international travel‐related control measures may help to limit the spread of covid‐19 across national borders. restricting cross‐border travel can be a helpful measure. screening travellers only for symptoms at borders is likely to miss many cases; testing may be more effective but may also miss cases if only performed upon arrival. Background covid 19 has proven to be more difficult to manage for many reasons including its high infectivity rate. one of the potential ways to limit its spread is by controlling international travel. the objective of this systematic review is to identify, critically appraise and summarize evidence on international travel related control measures. methods this review is based on the cochrane. These included (i) observational studies evaluating entry and or exit screening measures reporting only limited data regarding the effectiveness of the measure, (ii) observational ecological studies examining the aggregated impact of various travel‐related control measures across countries, and (iii) modelling studies using overly simplistic.

Comments are closed.