Can A Function Be Continuous At Only One Point
Continuity And One Sided Limits Ppt Download This function is continuous only at x = 0 x = 0. added: the same basic idea can be used to build a function that is continuous at any single specified point. with a little more ingenuity, you can use it to get, for instance, a function that is continuous just at the integers: f(x) ={sin πx, 0, if x ∈qif x ∈r ∖q. f (x) = {sin. 1) according to the definition given in spivak's book and also in , since $\lim {x\to1}f$ doesn't exist because $1$ is not an accumulation point, then the function is not continuous at $1$ (otherwise it should be $\lim {x\to 1}f=f(1)$). 2) according to this answer, as far as i can understand a function is continuous at an isolated point.

Continuous And Uniformly Continuous Functions Youtube Definition. a function f (x) f (x) is continuous at a point a a if and only if the following three conditions are satisfied: f (a) f (a) is defined. lim x→af (x) lim x → a f (x) exists. lim x→af (x) = f (a) lim x → a f (x) = f (a) a function is discontinuous at a point a a if it fails to be continuous at a a. the following procedure can. 1. according to my textbook , function should be continuous only at one point and to be defined everywhere. for example , f(x) ={x if x ∈ q −x if x ∉ q f (x) = {x if x ∈ q − x if x ∉ q. the above example is continuous at x = 0 x = 0 and defined everywhere. my question is what does this means to be defined everywhere and how a. Continuity over an interval. now that we have explored the concept of continuity at a point, we extend that idea to continuity over an interval.as we develop this idea for different types of intervals, it may be useful to keep in mind the intuitive idea that a function is continuous over an interval if we can use a pencil to trace the function between any two points in the interval without. Continuity at a point; types of discontinuities; continuity over an interval; the intermediate value theorem; key concepts; glossary. contributors; summary: for a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point must equal the value of the limit at that point.
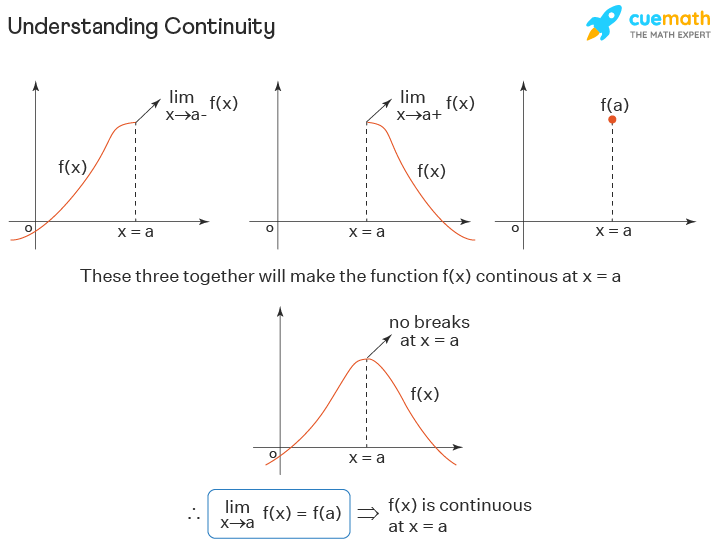
Definition For Continuous At Christian Hayes Blog Continuity over an interval. now that we have explored the concept of continuity at a point, we extend that idea to continuity over an interval.as we develop this idea for different types of intervals, it may be useful to keep in mind the intuitive idea that a function is continuous over an interval if we can use a pencil to trace the function between any two points in the interval without. Continuity at a point; types of discontinuities; continuity over an interval; the intermediate value theorem; key concepts; glossary. contributors; summary: for a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point must equal the value of the limit at that point. A function is continuous on an open interval if the interval is contained in the function's domain and the function is continuous at every interval point. a function that is continuous on the interval (, ) (the whole real line) is often called simply a continuous function; one also says that such a function is continuous everywhere. The function is continuous at this point since the function and limit have the same value. finally \(x = 3\). \[f\left( 3 \right) = 1\hspace{0.5in}\mathop {\lim }\limits {x \to 3} f\left( x \right) = 0\] the function is not continuous at this point. this kind of discontinuity is called a removable discontinuity. removable discontinuities are.

Comments are closed.