Burn Types Treatment And Nursing Management Medical Surgical
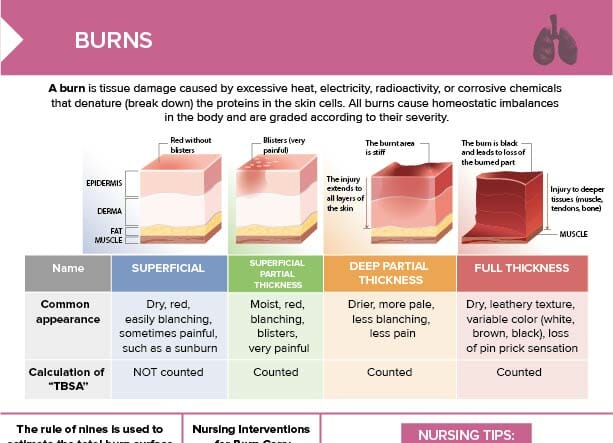
Burns Classification Free Cheat Sheet Lecturio Burn wound care and pain control are priorities at this stage. acute or intermediate phase begins 48 to 72 hours after the burn injury. focus on hemodynamic alterations, wound healing, pain and psychosocial responses, and early detection of complications. measure vital signs frequently. Advances in medical management, surgical care and physiological understanding of the thermal injury process have resulted in significant improvement in the outcome of burn victims over the past decades. yet, the short term management and long term rehabilitation of patients with major burn injuries remain challenging.
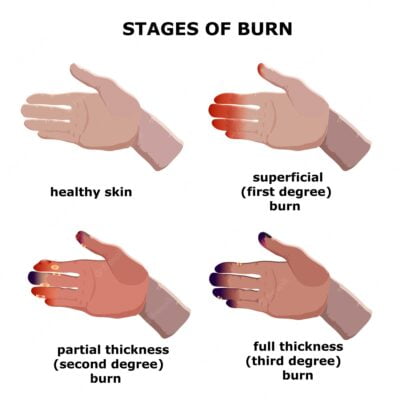
Burn Types Treatment And Nursing Management Medical Surgical A gentle cleansing of the wound with soap and water 2 or 3 times a day, followed with a topical agent such as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide, prevents infection. minor burns should heal in 7 to 10 days; however, if they take longer than 14 days, excision of the wound and a small graft may be needed. In 2015 it was recorded that burn injuries caused 500000 burns victims and 40000 hospitalizations in the united states. over $7.9 billion is estimated to be spent on emergency room visits and hospital burn care per year. survival after burns is attributed to a better understanding of when to transfer to burn centers, resuscitation protocols, and early excision and grafting. over the last 50. A variety of factors guide the evaluation and management of burns. first is the type of burn, such as thermal, chemical, electrical, or radiation. second is the extent of the burn, usually expressed as the percentage of total body surface area (%tbsa) involved. next is the depth of the burn described as superficial (first degree), partial (second degree) or full thickness (third degree. An overview of the surgical techniques used for burn reconstruction is reviewed. the general management of the burn patient and management of burn injuries according to depth of injury are discussed in separate topic reviews. (see "overview of the management of the severely burned patient" and "treatment of deep burn injury" and "treatment of.
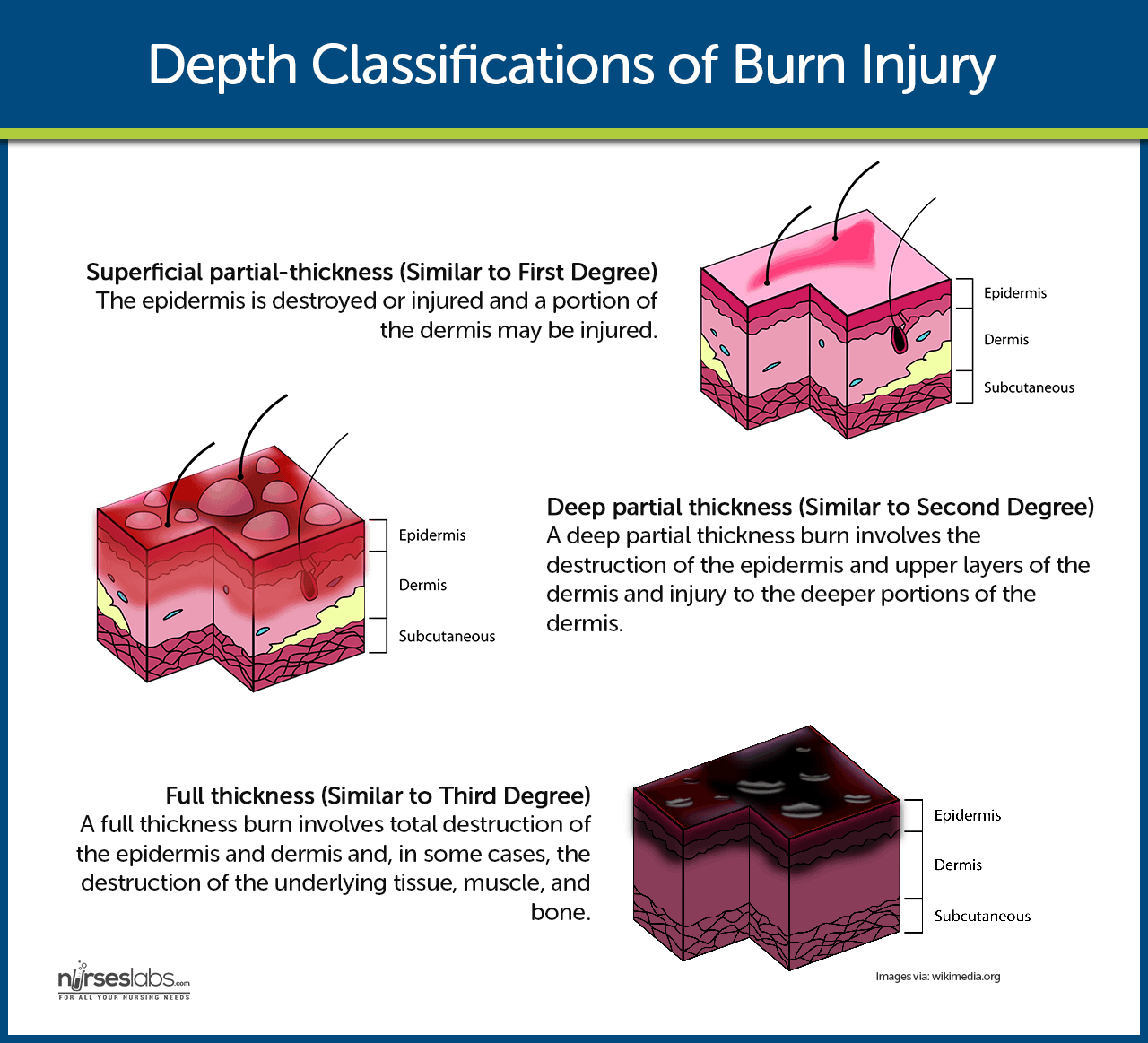
Burn Injury Nursing Care Management And Study Guide A variety of factors guide the evaluation and management of burns. first is the type of burn, such as thermal, chemical, electrical, or radiation. second is the extent of the burn, usually expressed as the percentage of total body surface area (%tbsa) involved. next is the depth of the burn described as superficial (first degree), partial (second degree) or full thickness (third degree. An overview of the surgical techniques used for burn reconstruction is reviewed. the general management of the burn patient and management of burn injuries according to depth of injury are discussed in separate topic reviews. (see "overview of the management of the severely burned patient" and "treatment of deep burn injury" and "treatment of. Management of a patient with a severe burn injury is a long term process that addresses the local burn wound as well as the systemic, psychologic, and social consequences of the injury. in situations where resources are limited (mass casualty, natural disaster), triage, stabilization, and transfer provide optimal outcomes. Approximately 500,000 patients seek medical care for burns every year in , 42 sunburns are the most common and preventable type of burns in surgical management of the burn wound and use of.

Comments are closed.