Brdf Carbon Cycle
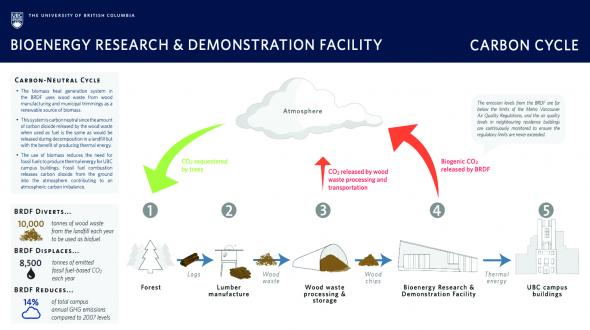
Brdf Carbon Cycle The biomass heat generation system in the bioenergy research and demonstration facility (brdf) uses wood waste from wood manufacturing and municipal trimmings as a renewable source of biomass. file download brdf carbon cycle final.pdf. Carbon neutral cycle the biomass heat generation system in the brdf uses wood waste from wood manufacturing and municipal trimmings as a renewable source of biomass. ths si ystem is carbon neutral sni ce thea mount of carbon dioxide released by the wood waste when used as fuel is the same as would be.

Bioenergy Research And Demonstration Facility 77 brdf effects are most pronounced (chen et al. 2005). consequently, the exact nature of these 78 angular to structural relationships has been difficult to quantify at the relevant view angle geo 79 metries of satellite sensors that routinely sample the brdf over a single overpass (leroy et al. Carbon 3d will be an essential contribution to carbon cycle investigations by providing crucial and unique data on vegetation biomass, vegetation productivity, and vegetation types and structure. model based extensions of these data will also allow estimations of soil carbon stocks and dynamics with unprecedented spatial detail, and hence the. Predicted warming and drying in western temperate north america (seager et al., 2007) could have profound effects on the carbon cycle (schwalm et al., 2012), with increasing temperatures and aridity driving reductions in growing season productivity and carbon uptake, although tbms suggest that carbon loss due to climate change will be partially. The bioenergy research demonstration facility (brdf) responds to this challenge while demonstrating small scale power production that is relevant and replicable in other communities. in addition to generating energy for the ubc campus, the brdf is also a campus as a living lab project integrating our core academic mandate of research and.
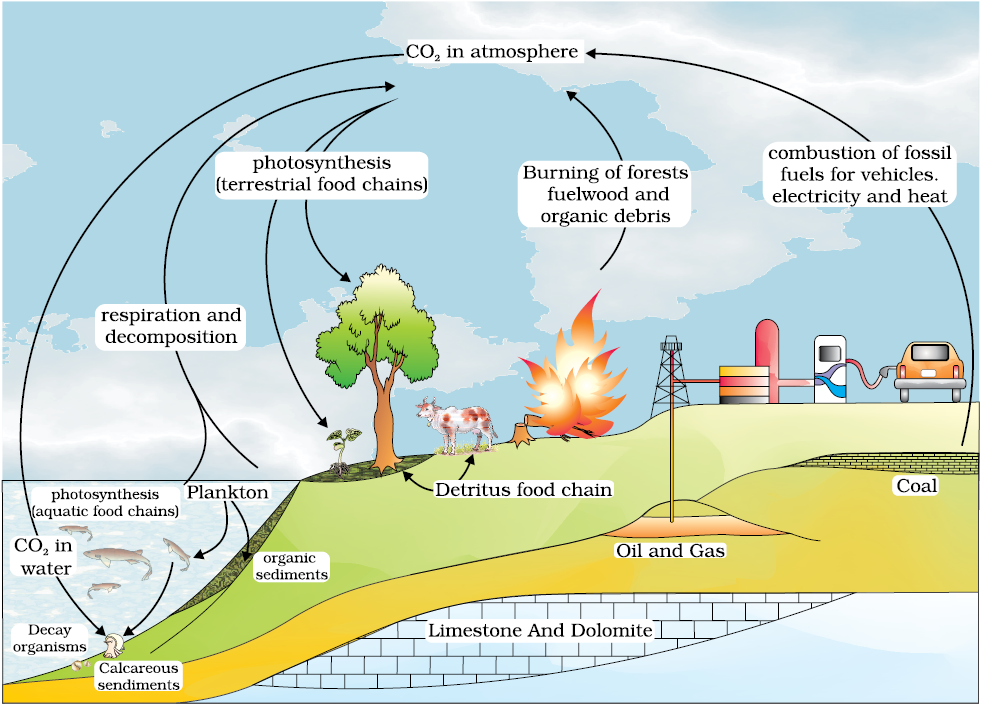
14 Ecosystem Biology Predicted warming and drying in western temperate north america (seager et al., 2007) could have profound effects on the carbon cycle (schwalm et al., 2012), with increasing temperatures and aridity driving reductions in growing season productivity and carbon uptake, although tbms suggest that carbon loss due to climate change will be partially. The bioenergy research demonstration facility (brdf) responds to this challenge while demonstrating small scale power production that is relevant and replicable in other communities. in addition to generating energy for the ubc campus, the brdf is also a campus as a living lab project integrating our core academic mandate of research and. The bioenergy research and demonstration facility (brdf), located at the ubc vancouver campus, is an energy generation facility that processes renewable biomass sourced from urban wood waste to generate thermal energy for heating campus buildings. a first of its kind project in north america, the system reduces ubc’s reliance on fossil fuels. Dynamic global vegetation models (dgvms), driven by observed environmental changes, are used for global carbon budget assessments and long term (climate) prediction. benchmarking these and other models globally with data driven gpp estimates is critical for understanding the land sink and ensuring accurate forecasts of the carbon cycle.
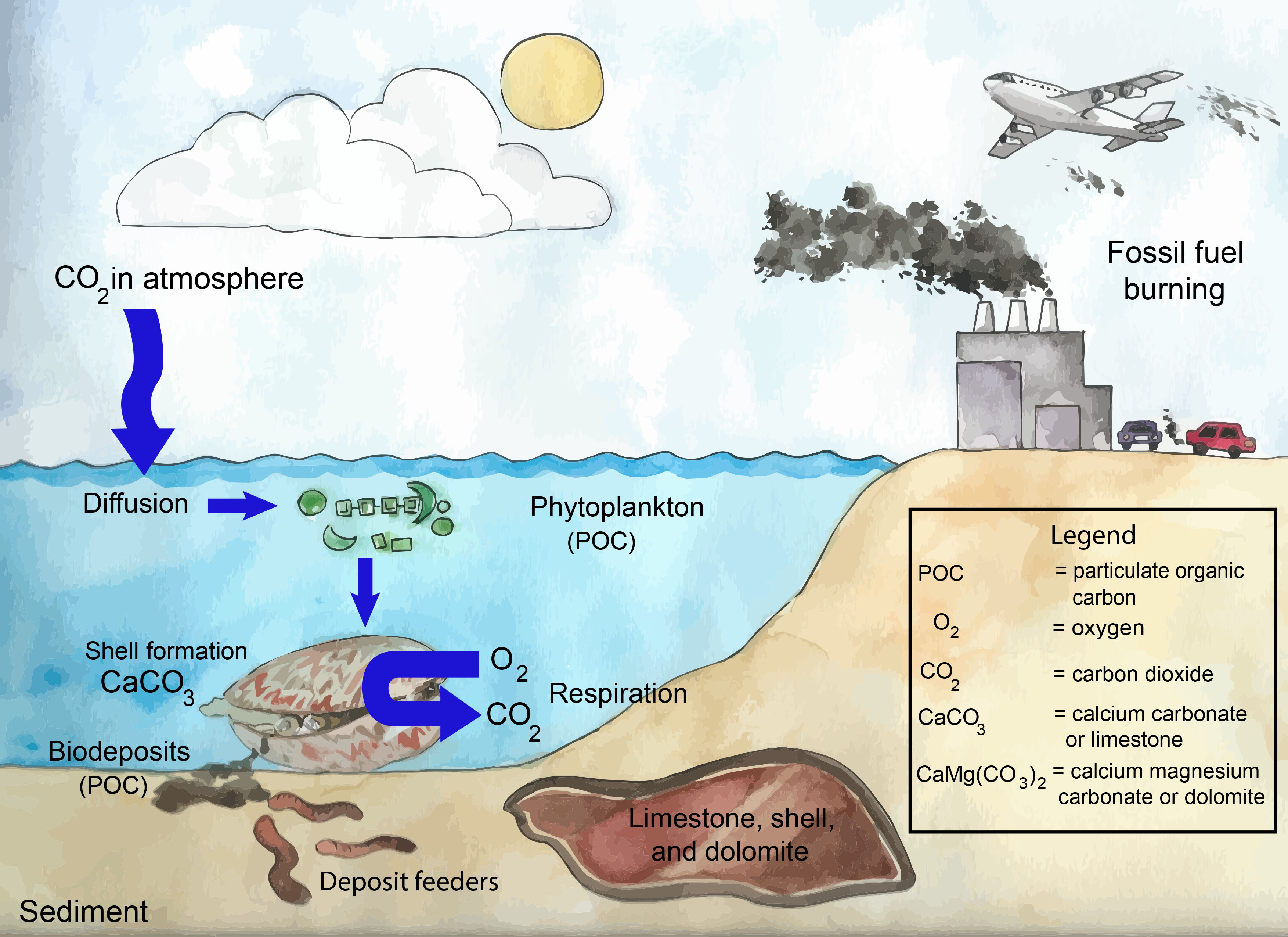
Environmental Benefits Florida Shellfish Aquaculture Online Resource The bioenergy research and demonstration facility (brdf), located at the ubc vancouver campus, is an energy generation facility that processes renewable biomass sourced from urban wood waste to generate thermal energy for heating campus buildings. a first of its kind project in north america, the system reduces ubc’s reliance on fossil fuels. Dynamic global vegetation models (dgvms), driven by observed environmental changes, are used for global carbon budget assessments and long term (climate) prediction. benchmarking these and other models globally with data driven gpp estimates is critical for understanding the land sink and ensuring accurate forecasts of the carbon cycle.

Comments are closed.