Branches Of Linguistics Phonetics Phonology Morphology Syntaxsemanticspragmatics Linguistics

Branches Of Linguistics Phonetics Phonology Morphology Syntax Main theoretical areas of linguistics, i.e. phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, are covered in depth, while some areas that are arguably essential to linguistics such as sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, language contact, etc., are only touched upon, but there are no chapters dedicated to them. content accuracy rating: 4. Lexicology is the study of words including the relations between words. people who study lexicology are known as lexicologists. a lexeme is an abstract minimal unit of morphological analysis in the lexicon of a language that roughly corresponds to a set of forms of a single word.

The Branches Of Linguistics Alethes Net Lecture 22: dialects (pdf) lecture 23: historical linguistics (pdf 1 mb) lecture 24: endangered languages (pdf 1.5 mb) lecture 25: language acquisition (pdf) lecture 26: signed languages (pdf) this page contains links to the lecture note files for 24.900 introduction to linguistics. Back to: pedagogy of english unit 4 phonology. according to all about linguistics, “phonology is the study of the patterns of sounds in a language and across languages. put more formally, phonology is the study of the categorical organization of speech sounds in languages; how speech sounds are organized in the mind and used to convey meaning. This diagram outlines the various subfields of linguistics, the study of language. these include phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. figure 11.8.1 11.8. 1: major branches of linguistics. (image is in the public domain). Theoretical linguistics competence, discourse, morphology, phonetics, phonology, pragmatics, semantics, syntax, system. learn the 7 components of the linguistic system in our intro to theoretical linguistics for beginners. explore the basics of theoretical linguistics.
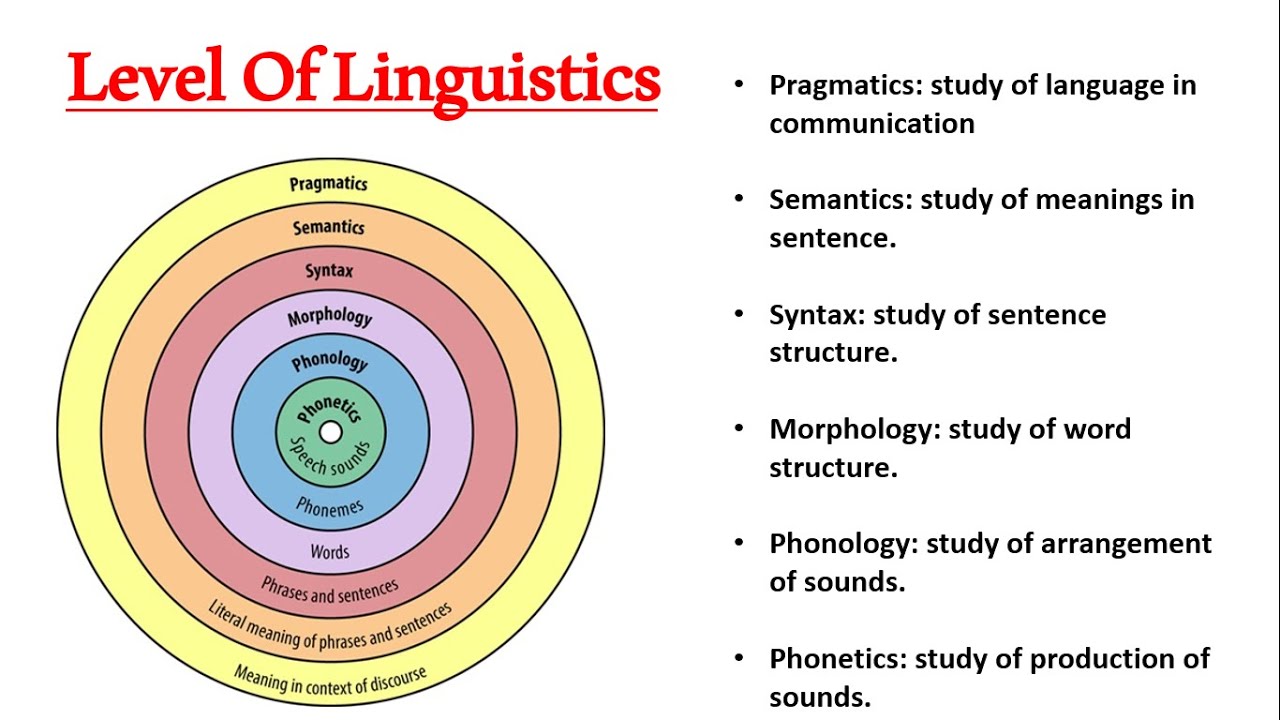
Level Of Linguistics Phonetics Phonology Morphology Syntax This diagram outlines the various subfields of linguistics, the study of language. these include phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. figure 11.8.1 11.8. 1: major branches of linguistics. (image is in the public domain). Theoretical linguistics competence, discourse, morphology, phonetics, phonology, pragmatics, semantics, syntax, system. learn the 7 components of the linguistic system in our intro to theoretical linguistics for beginners. explore the basics of theoretical linguistics. Summary. phonetics is the branch of linguistics that deals with the physical realization of meaningful distinctions in spoken language. phoneticians study the anatomy and physics of sound generation, acoustic properties of the sounds of the world’s languages, the features of the signal that listeners use to perceive the message, and the brain mechanisms involved in both production and. Linguistics morphology, syntax, semantics: the grammatical description of many, if not all, languages is conveniently divided into two complementary sections: morphology and syntax. the relationship between them, as generally stated, is as follows: morphology accounts for the internal structure of words, and syntax describes how words are combined to form phrases, clauses, and sentences.

Branches Of Linguistics Pdf Branches Of Phonetics Leverage Edu Summary. phonetics is the branch of linguistics that deals with the physical realization of meaningful distinctions in spoken language. phoneticians study the anatomy and physics of sound generation, acoustic properties of the sounds of the world’s languages, the features of the signal that listeners use to perceive the message, and the brain mechanisms involved in both production and. Linguistics morphology, syntax, semantics: the grammatical description of many, if not all, languages is conveniently divided into two complementary sections: morphology and syntax. the relationship between them, as generally stated, is as follows: morphology accounts for the internal structure of words, and syntax describes how words are combined to form phrases, clauses, and sentences.

Comments are closed.