Biomass Carbon Cycle Bioenergy Explained
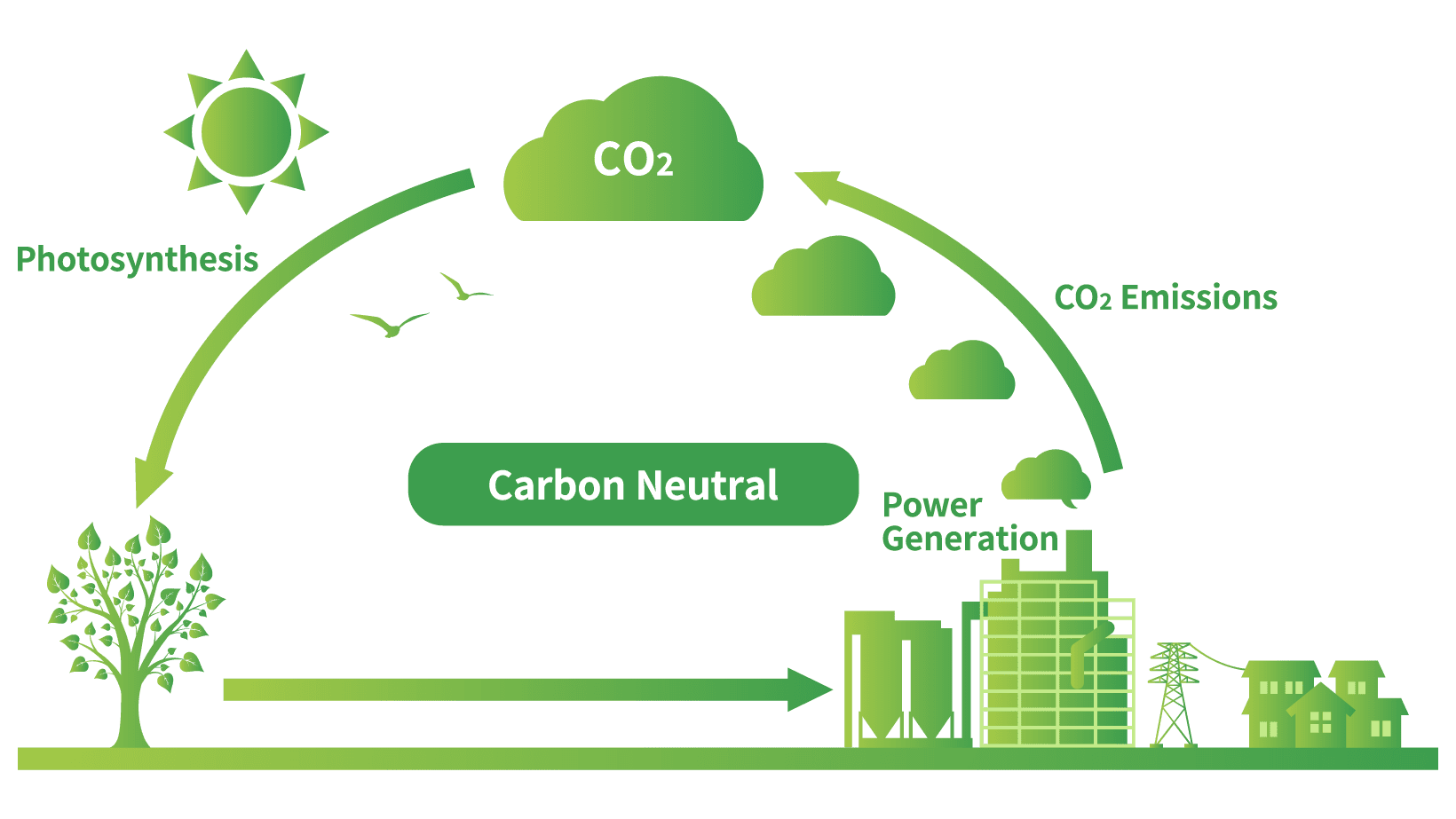
About Biomass Fuel Erex Biomass and the environment biomass is an integral part of earth’s carbon cycle. the carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is exchanged between all layers of earth: atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere. the carbon cycle takes many forms. carbon helps regulate the amount of sunlight that enters earth’s atmosphere. Biomass carbon cycle explained. bioenergy europe presents its new video which looks at the meaning of carbon neutrality. the video reviews some basic concepts that make sustainable bioenergy a key player in the eu transition to a zero emissions economy and an ally in climate change mitigation. there is scepticism over the concept of bioenergy.
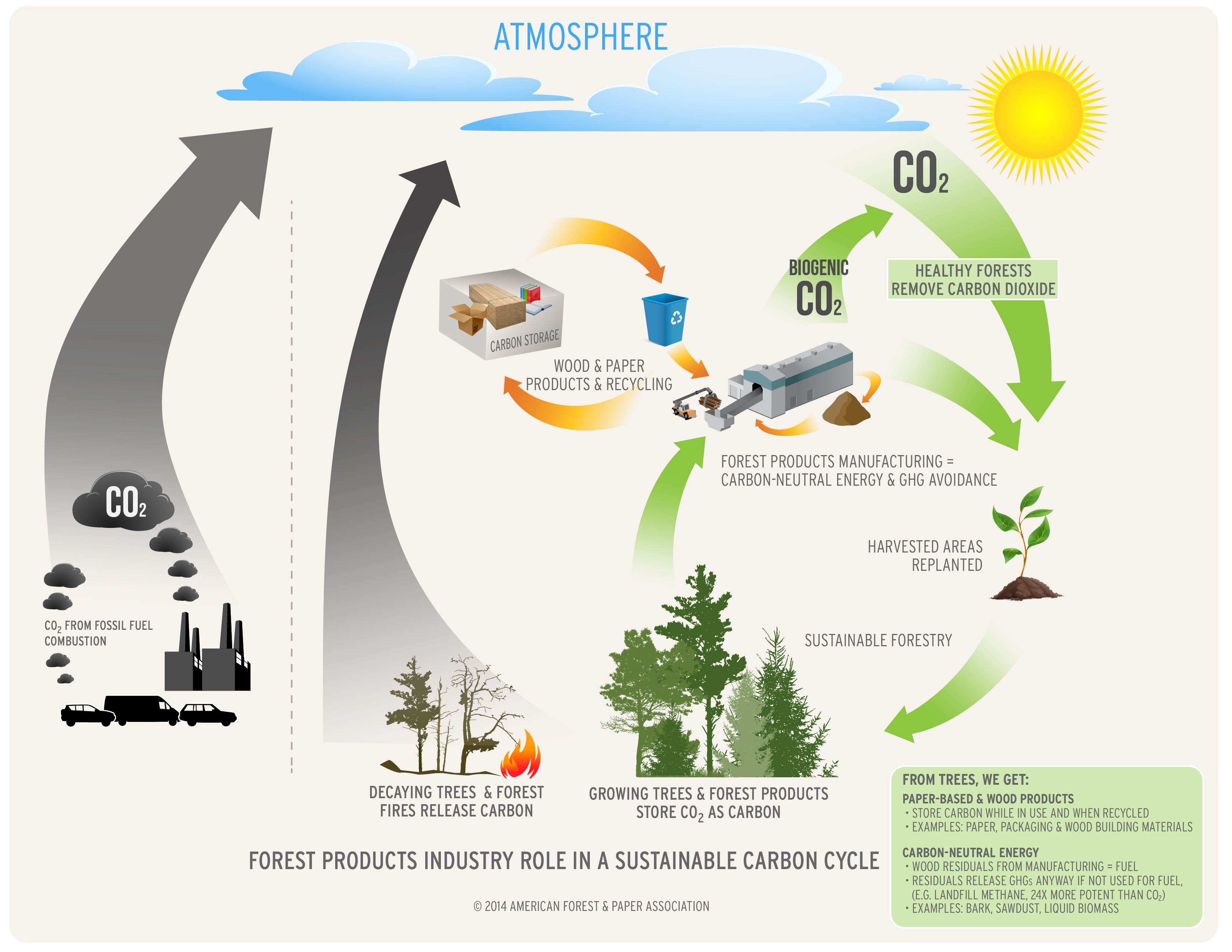
Maryland Renewable Portfolio Standard Rps Study Bioenergy is this video sheds light on the meaning of carbon neutrality and explains the role of bioenergy in decarbonisation and climate change mitigation. Biomass explained biomass and the environment. basics. menu. using biomass and biofuels made from biomass has positive and negative effects on the environment. one benefit is that biomass and biofuels are alternative energy sources to fossil fuels. burning fossil fuels and biomass releases carbon dioxide (co 2), a greenhouse gas. Biomass. an energy resource derived from plant material. it includes agricultural residues (such as waste from food crops and animal manures), forest resources, purpose grown energy crops (such as algae, perennial grasses, and woody. energy crops), urban wood waste, and food waste. biomass is a unique, renewable energy resource, as it can be. Bioenergy basics. bioenergy is one of many diverse resources available to help meet our demand for energy. it is a form of renewable energy that is derived from recently living organic materials known as biomass, which can be used to produce transportation fuels, heat, electricity, and products.
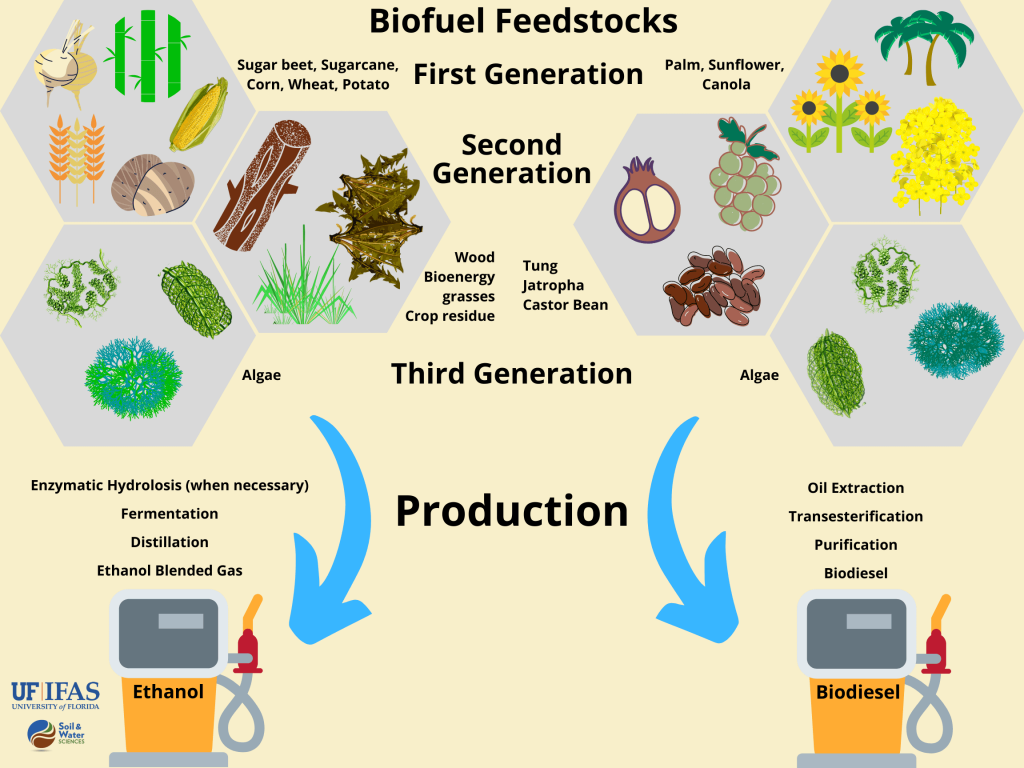
Get To Know Biofuels Soil Water And Ecosystem Sciences Biomass. an energy resource derived from plant material. it includes agricultural residues (such as waste from food crops and animal manures), forest resources, purpose grown energy crops (such as algae, perennial grasses, and woody. energy crops), urban wood waste, and food waste. biomass is a unique, renewable energy resource, as it can be. Bioenergy basics. bioenergy is one of many diverse resources available to help meet our demand for energy. it is a form of renewable energy that is derived from recently living organic materials known as biomass, which can be used to produce transportation fuels, heat, electricity, and products. Jasmin kemper, iea greenhouse gas r&d programme (ieaghg), reviewer. bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, or beccs, involves capturing and permanently storing co2 from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. because plants absorb co2 as they grow, this is a way of removi. Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes. biomass was the largest source of total annual u.s. energy consumption until the mid 1800s.
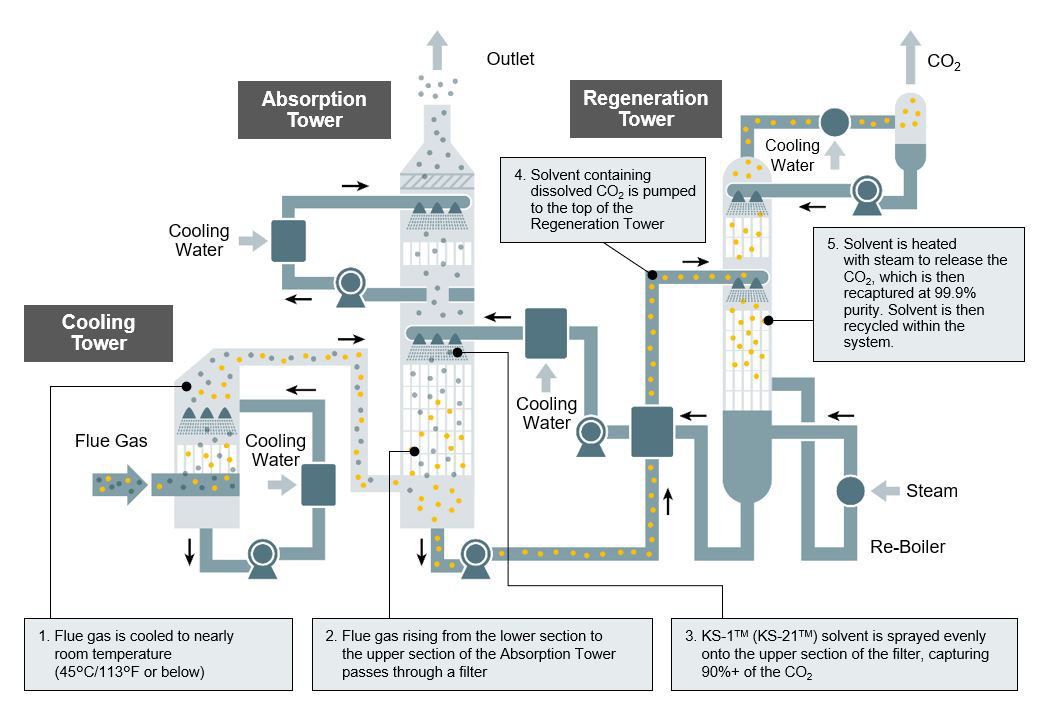
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd Global Website Co2 Capture Jasmin kemper, iea greenhouse gas r&d programme (ieaghg), reviewer. bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, or beccs, involves capturing and permanently storing co2 from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. because plants absorb co2 as they grow, this is a way of removi. Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes. biomass was the largest source of total annual u.s. energy consumption until the mid 1800s.

Comments are closed.