Biology Evolutionary Processes The Evolution Of Populations Adaptive
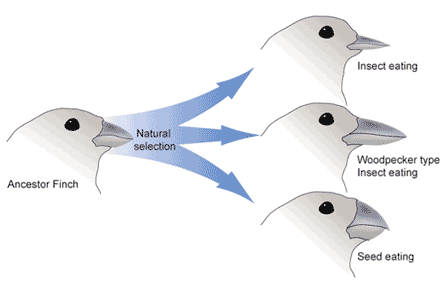
19 3a Natural Selection And Adaptive Evolution Biology Libretexts Section summary. because natural selection acts to increase the frequency of beneficial alleles and traits while decreasing the frequency of deleterious qualities, it is adaptive evolution. natural selection acts at the level of the individual, selecting for those that have a higher overall fitness compared to the rest of the population. if the. Figure 19.3.1 19.3. 1: different types of natural selection can impact the distribution of phenotypes within a population. in (a) stabilizing selection, an average phenotype is favored. in (b) directional selection, a change in the environment shifts the spectrum of phenotypes observed.

Biology Evolutionary Processes The Evolution Of Populations Adaptive Natural selection acts at the level of the individual; it selects for individuals with greater contributions to the gene pool of the next generation, known as an organism’s evolutionary fitness (or darwinian fitness). figure 19.3a. 1 19.3 a. 1: adaptive evolution in finches: through natural selection, a population of finches evolved into. Scientists consider evolution a key concept to understanding life. natural selection is one of the most dominant evolutionary forces. 19.1: population evolution. initially, the newly discovered particulate nature of genes made it difficult for biologists to understand how gradual evolution could occur. but over the next few decades genetics and. Natural selection acts on the population’s heritable traits: selecting for beneficial alleles that allow for environmental adaptation, and thus increasing their frequency in the population, while selecting against deleterious alleles and thereby decreasing their frequency. scientists call this process adaptive evolution. The theoretical principles of adaptive evolution are being put to the test in a growing range of species and populations, particularly with new sequencing technologies and high throughput.
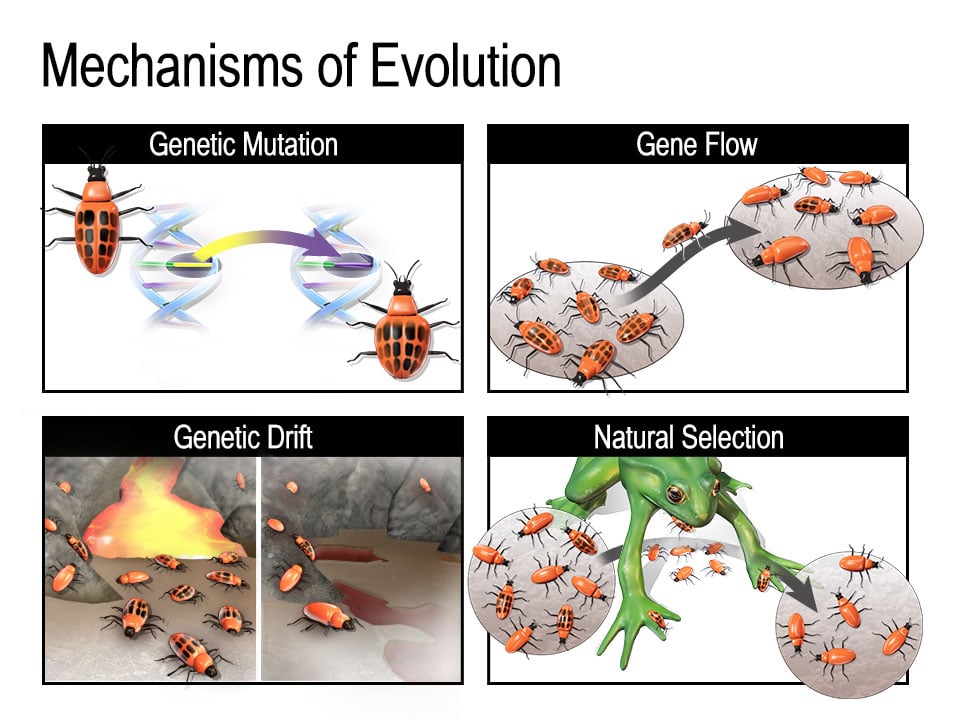
Mechanisms Of Evolution Natural selection acts on the population’s heritable traits: selecting for beneficial alleles that allow for environmental adaptation, and thus increasing their frequency in the population, while selecting against deleterious alleles and thereby decreasing their frequency. scientists call this process adaptive evolution. The theoretical principles of adaptive evolution are being put to the test in a growing range of species and populations, particularly with new sequencing technologies and high throughput. Abstract. adaptive evolution is shaped by the interaction of population genetics, natural selection and underlying network and biochemical constraints. variation created by mutation, the raw material for evolutionary change, is translated into phenotypes by flux through metabolic pathways and by the topography and dynamics of molecular networks. This will lead to change in populations over generations in a process that darwin called descent with modification. ultimately, natural selection leads to greater adaptation of the population to its local environment. it is the only mechanism known for adaptive evolution.
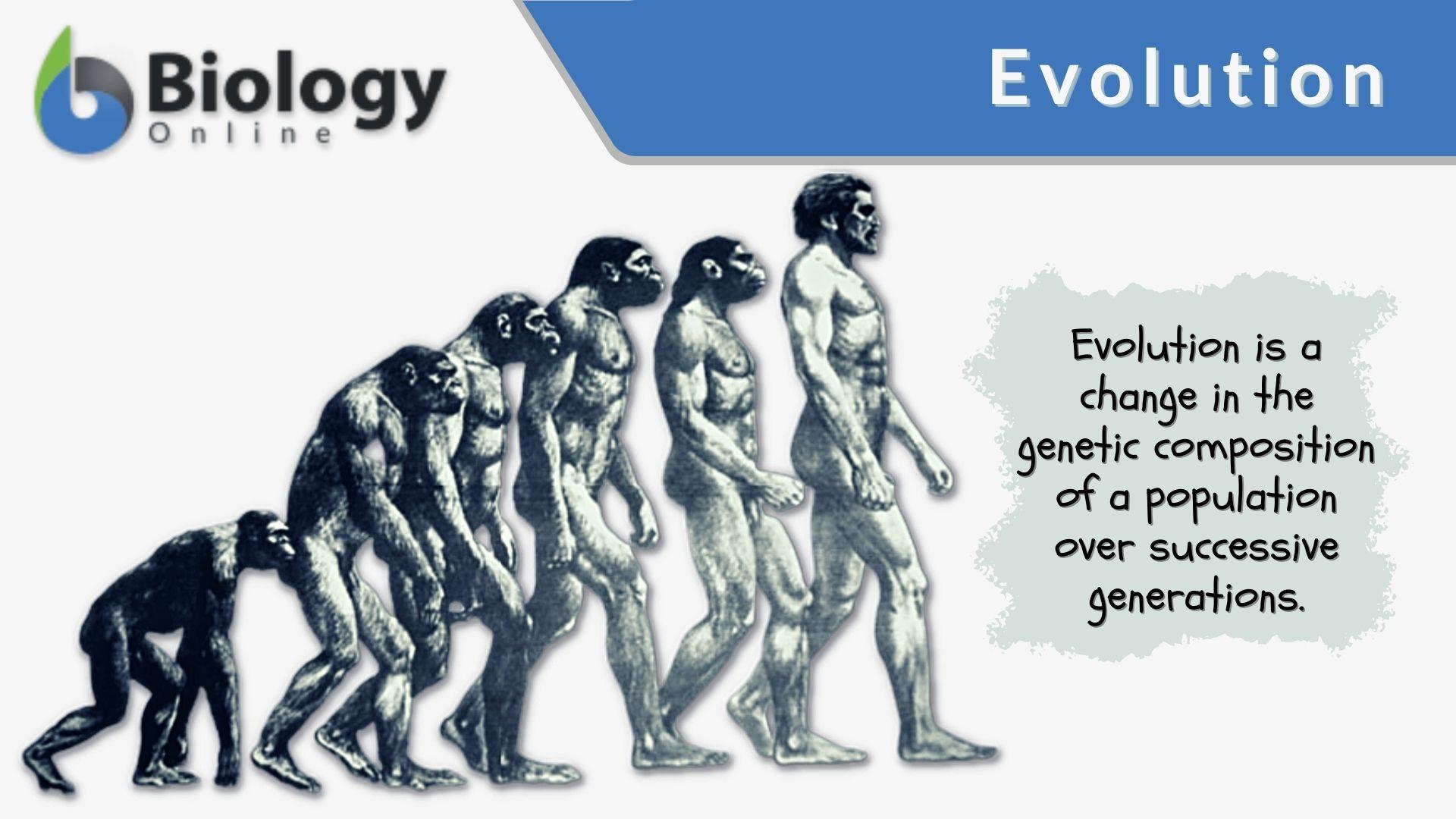
Evolution Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Abstract. adaptive evolution is shaped by the interaction of population genetics, natural selection and underlying network and biochemical constraints. variation created by mutation, the raw material for evolutionary change, is translated into phenotypes by flux through metabolic pathways and by the topography and dynamics of molecular networks. This will lead to change in populations over generations in a process that darwin called descent with modification. ultimately, natural selection leads to greater adaptation of the population to its local environment. it is the only mechanism known for adaptive evolution.

Comments are closed.