Bioenergy Explained Energy Security With Biomass

Bioenergy Explained вђ Energy Security With Biomass вђ Euractiv Domestically sourced, affordable and sustainable – bioenergy holds the key to our energy security. with an import rate of less than 4%, bioenergy maintains the autonomy of the eu’s energy. As part of bioenergy europe’s video series bioenergy explained, our latest video talks about the crucial role of biomass in times of energy uncertainty, wher.

Bioenergizeme Infographic Challenge Bioenergy Creating Biofuels From Bioenergy is a source of energy from the organic material that makes up plants, known as biomass. biomass contains carbon absorbed by plants through photosynthesis. when this biomass is used to produce energy, the carbon is released during combustion and simply returns to the atmosphere, making modern bioenergy a promising near zero emission. Biomass. an energy resource derived from plant material. it includes agricultural residues (such as waste from food crops and animal manures), forest resources, purpose grown energy crops (such as algae, perennial grasses, and woody. energy crops), urban wood waste, and food waste. biomass is a unique, renewable energy resource, as it can be. Bioenergy basics. bioenergy is one of many diverse resources available to help meet our demand for energy. it is a form of renewable energy that is derived from recently living organic materials known as biomass, which can be used to produce transportation fuels, heat, electricity, and products. Jasmin kemper, iea greenhouse gas r&d programme (ieaghg), reviewer. bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, or beccs, involves capturing and permanently storing co2 from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. because plants absorb co2 as they grow, this is a way of removi.
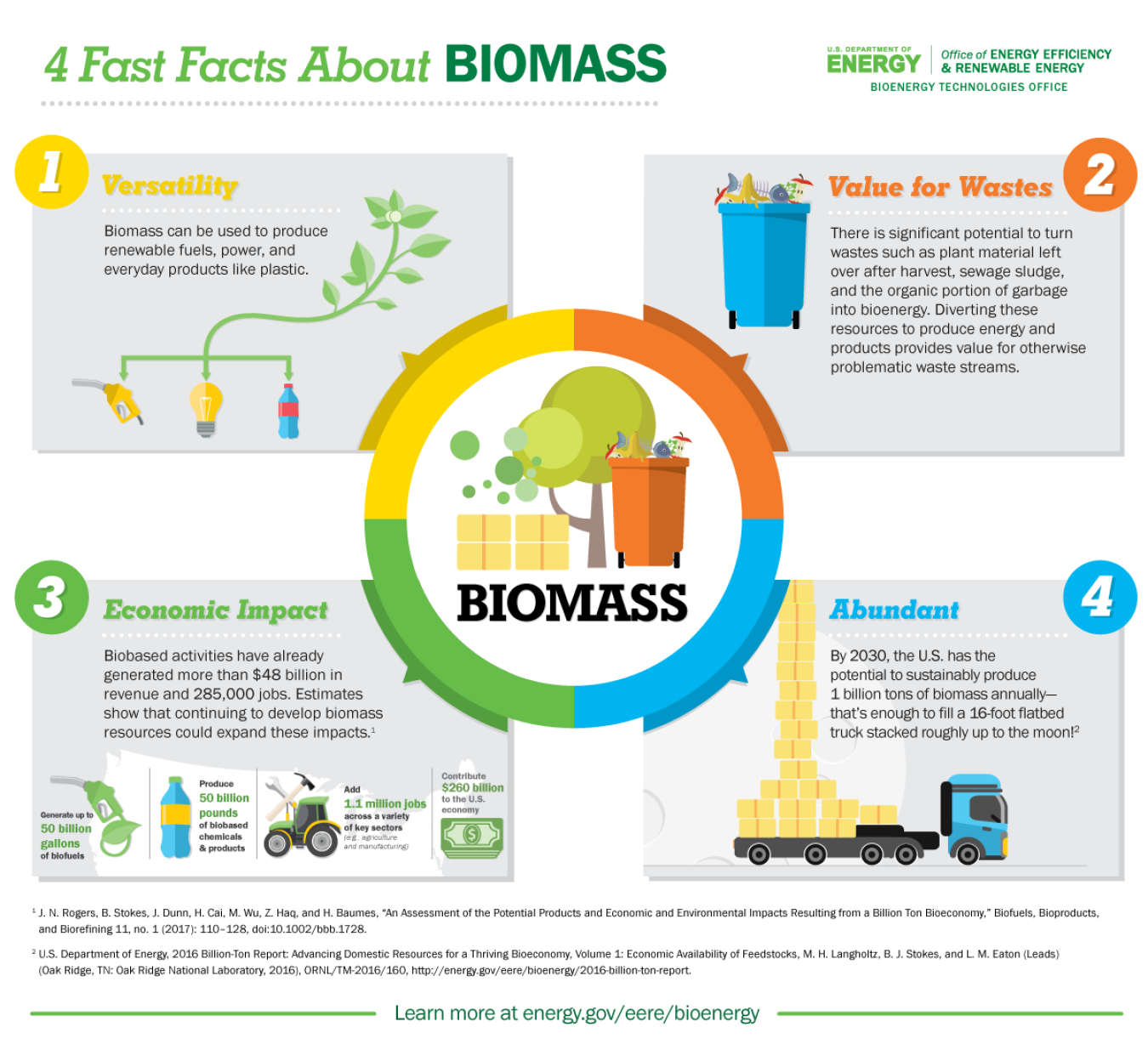
4 Fast Facts About Biomass Department Of Energy Bioenergy basics. bioenergy is one of many diverse resources available to help meet our demand for energy. it is a form of renewable energy that is derived from recently living organic materials known as biomass, which can be used to produce transportation fuels, heat, electricity, and products. Jasmin kemper, iea greenhouse gas r&d programme (ieaghg), reviewer. bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, or beccs, involves capturing and permanently storing co2 from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. because plants absorb co2 as they grow, this is a way of removi. Biomass—renewable energy from plants and animals. biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes. biomass was the largest source of total annual u.s. energy consumption until the mid 1800s. Bioenergy. while traditional use of biomass is phased out in the nze scenario, modern bioenergy use more than doubles to 2050, due to its ability to be used as a direct drop in substitute for fossil fuels. advanced feedstock supply grows considerably, supported by investments and commercialisation of advanced conversion technologies.

Biomass Carbon Cycle Bioenergy Explained Youtube Biomass—renewable energy from plants and animals. biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes. biomass was the largest source of total annual u.s. energy consumption until the mid 1800s. Bioenergy. while traditional use of biomass is phased out in the nze scenario, modern bioenergy use more than doubles to 2050, due to its ability to be used as a direct drop in substitute for fossil fuels. advanced feedstock supply grows considerably, supported by investments and commercialisation of advanced conversion technologies.

Energy Security Bioenergy Explained Youtube

Comments are closed.