Binary Isomorphous Systems

Binary Phase Diagram Of Isomorphous System Youtube Binary isomorphous systems (iii) in one component system melting occurs at a well defined melting temperature. in multi component systems melting occurs over the range of temperatures, between the solidus and liquidus lines. solid and liquid phases are at equilibrium with each other in this temperature range. α l α l liquid solution liquid. Binary isomorphous systems • complete liquid and solid solubility of the two components • cu ni solid solution • liquidus line • solidus line • melting temperatures • phase composition • phase relative amount: tie line and lever rule.

Binary Diagrams Phase Diagrams Physical Metallurgy In a binary system. 3.2.1 isomorphous systems: preliminary concepts key concept 3.2: isomorphous binary alloys the simplest possible binary alloy phase diagram is called an isomor phous system, in which the liquid and solid phases are completely miscible over the entire composition range. in such systems, the indi. 13.2.2 solid–liquid systems. figure 13.1 temperature–composition phase diagram for a binary system exhibiting a eutectic point. figure 13.1 is a temperature–composition phase diagram at a fixed pressure. the composition variable is the mole fraction of component b in the system as a whole. These diagrams are called 'isomorphous' because only a single type of crystal structure is obtained at the all possible compositions. examples : cu ni, au ag, au cu, mo w, mo ti etc. the above figure shows the classic example of isomorphous system of cu zn alloy. pure copper (fcc) melts at 1083 o c whereas pure nickel (fcc) melts at 1455 o c. Congruently melting intermediates subdivide the binary system into smaller binary systems with all the characteristics of typical binary systems. • intermediate compounds are especially common in ceramics, as the pure components may form unique molecules at intermediate ratios. shown below is the example of the system mno al 2o 3: 2000 1900 1800.
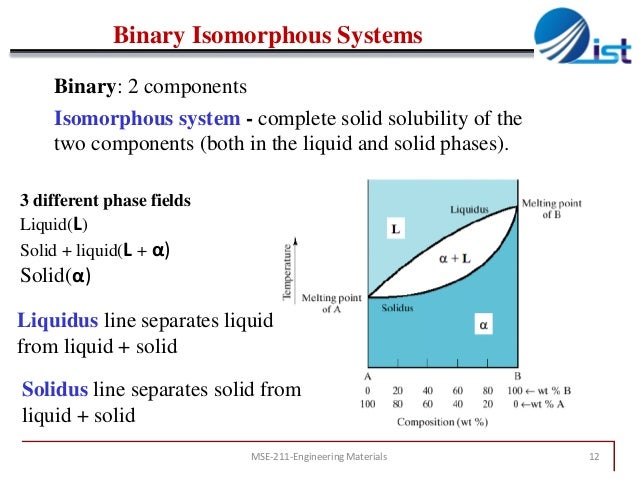
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams 1 These diagrams are called 'isomorphous' because only a single type of crystal structure is obtained at the all possible compositions. examples : cu ni, au ag, au cu, mo w, mo ti etc. the above figure shows the classic example of isomorphous system of cu zn alloy. pure copper (fcc) melts at 1083 o c whereas pure nickel (fcc) melts at 1455 o c. Congruently melting intermediates subdivide the binary system into smaller binary systems with all the characteristics of typical binary systems. • intermediate compounds are especially common in ceramics, as the pure components may form unique molecules at intermediate ratios. shown below is the example of the system mno al 2o 3: 2000 1900 1800. Binary isomorphous system phase is substitutional solid consisting of both cu and ni and having an fcc structure mutually soluble in solid state binary system with solid solution melting points mutually soluble in liquid state f=2 f=2 w. callister chapter9 mater. sci. eng. an introduction • atoms have similar radii; • both pure materials have. Binary isomorphous systems definitions and basic concepts component: pure metals and or compounds of which an alloy is composed system: a specific body of material under consideration a phase: a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics.
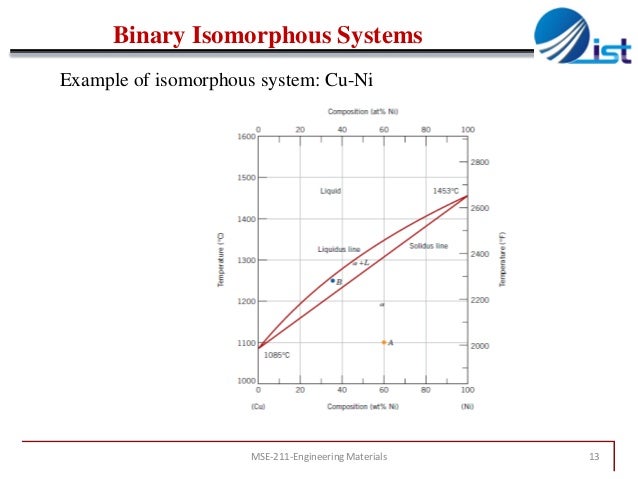
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams 1 Binary isomorphous system phase is substitutional solid consisting of both cu and ni and having an fcc structure mutually soluble in solid state binary system with solid solution melting points mutually soluble in liquid state f=2 f=2 w. callister chapter9 mater. sci. eng. an introduction • atoms have similar radii; • both pure materials have. Binary isomorphous systems definitions and basic concepts component: pure metals and or compounds of which an alloy is composed system: a specific body of material under consideration a phase: a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics.

Comments are closed.